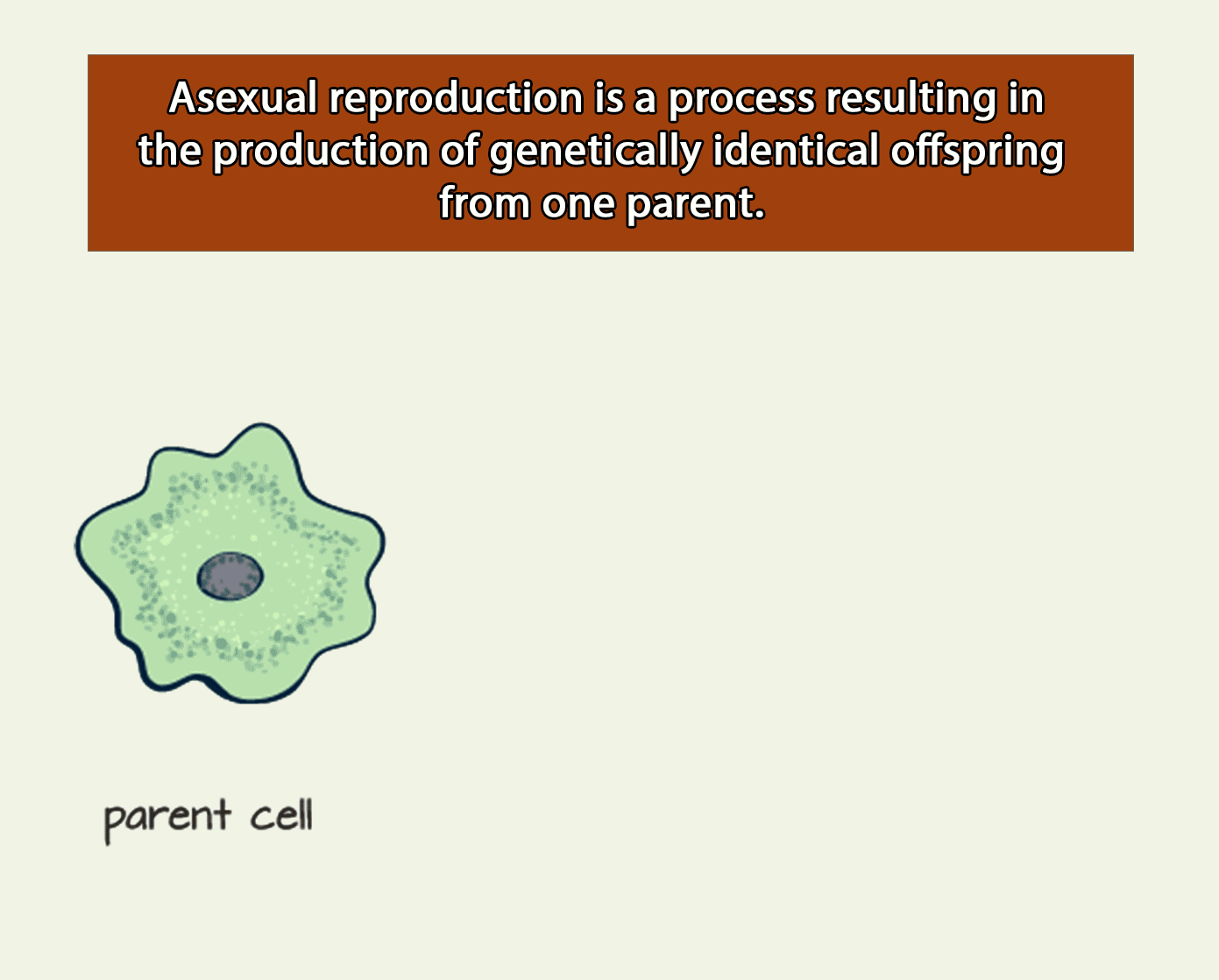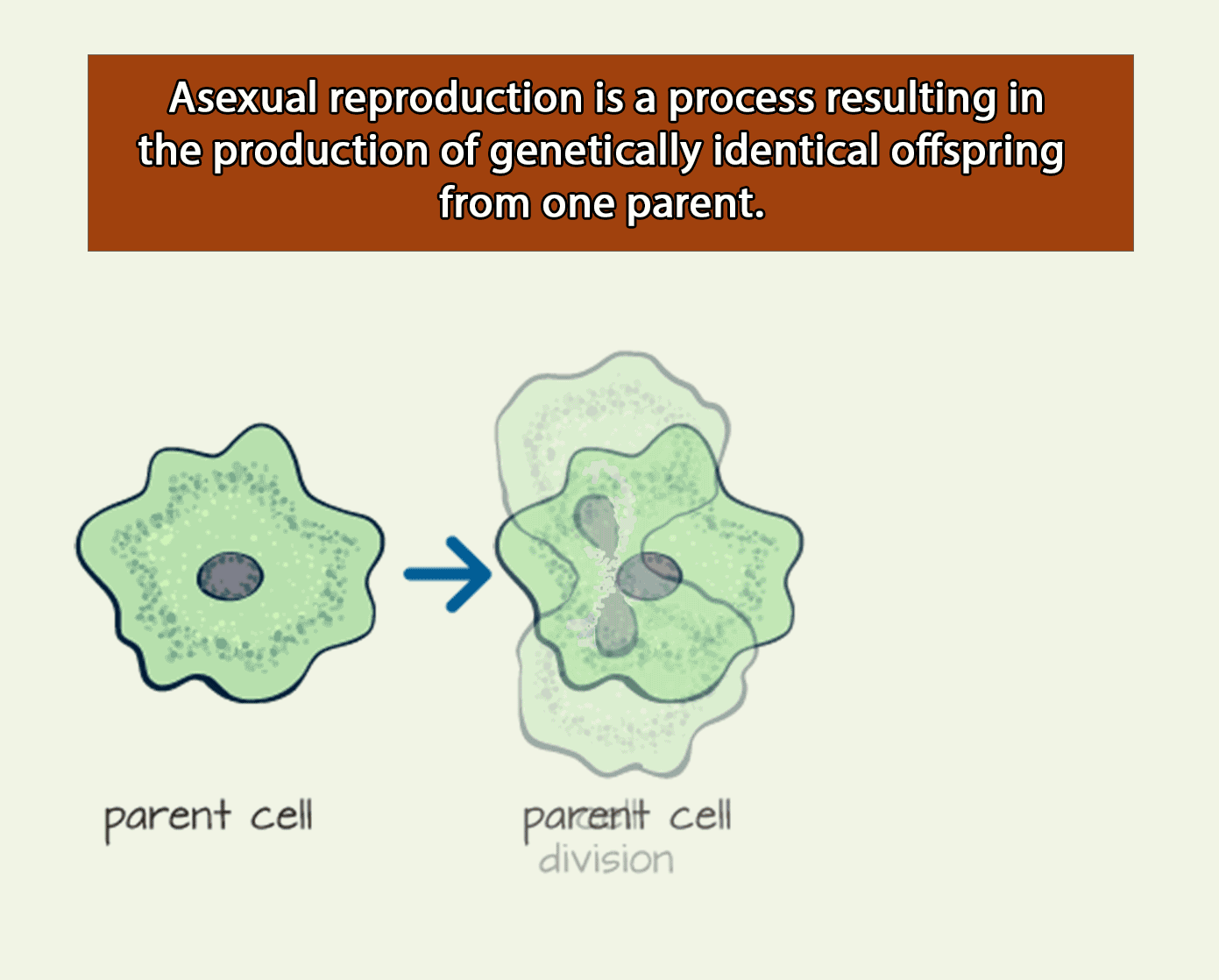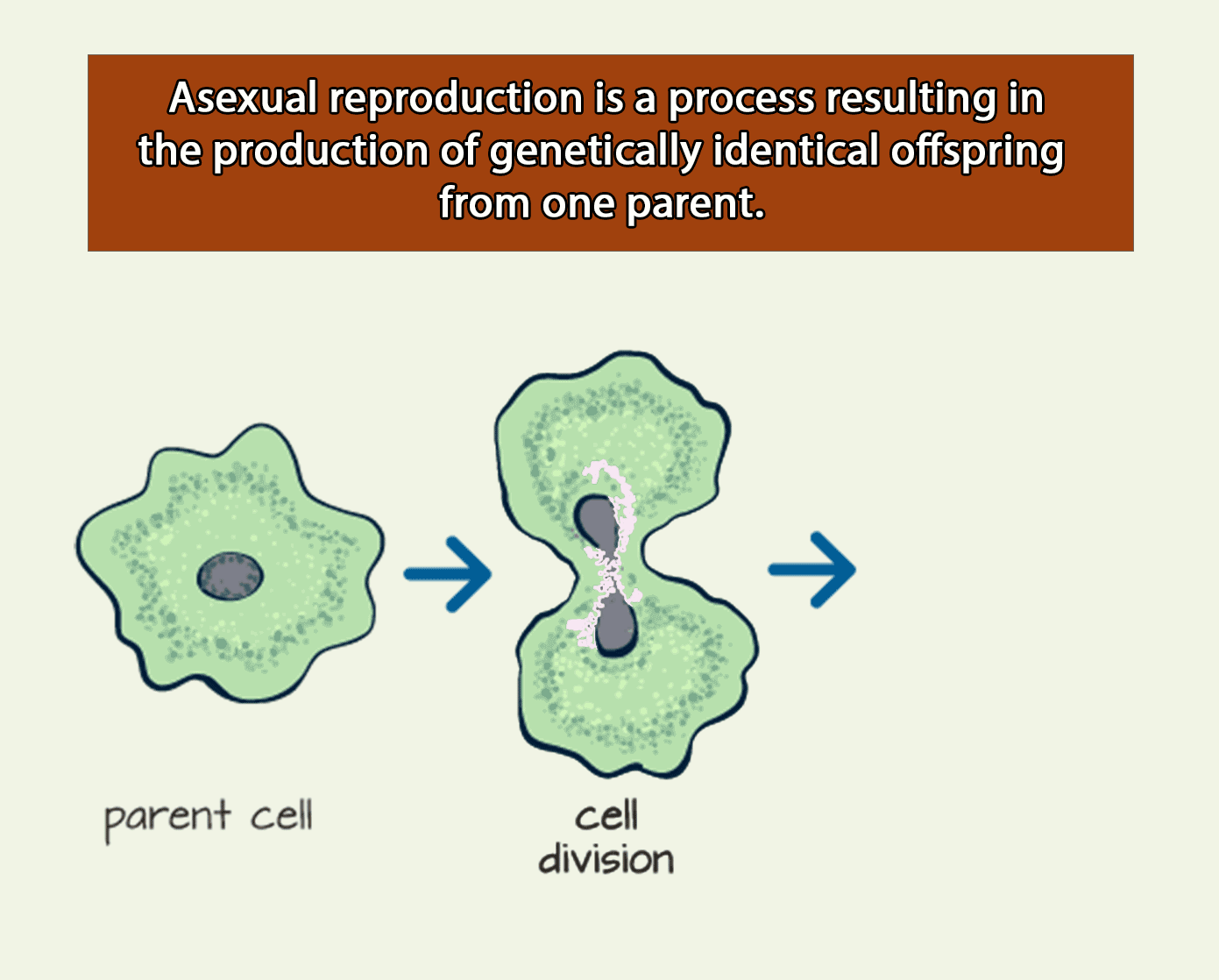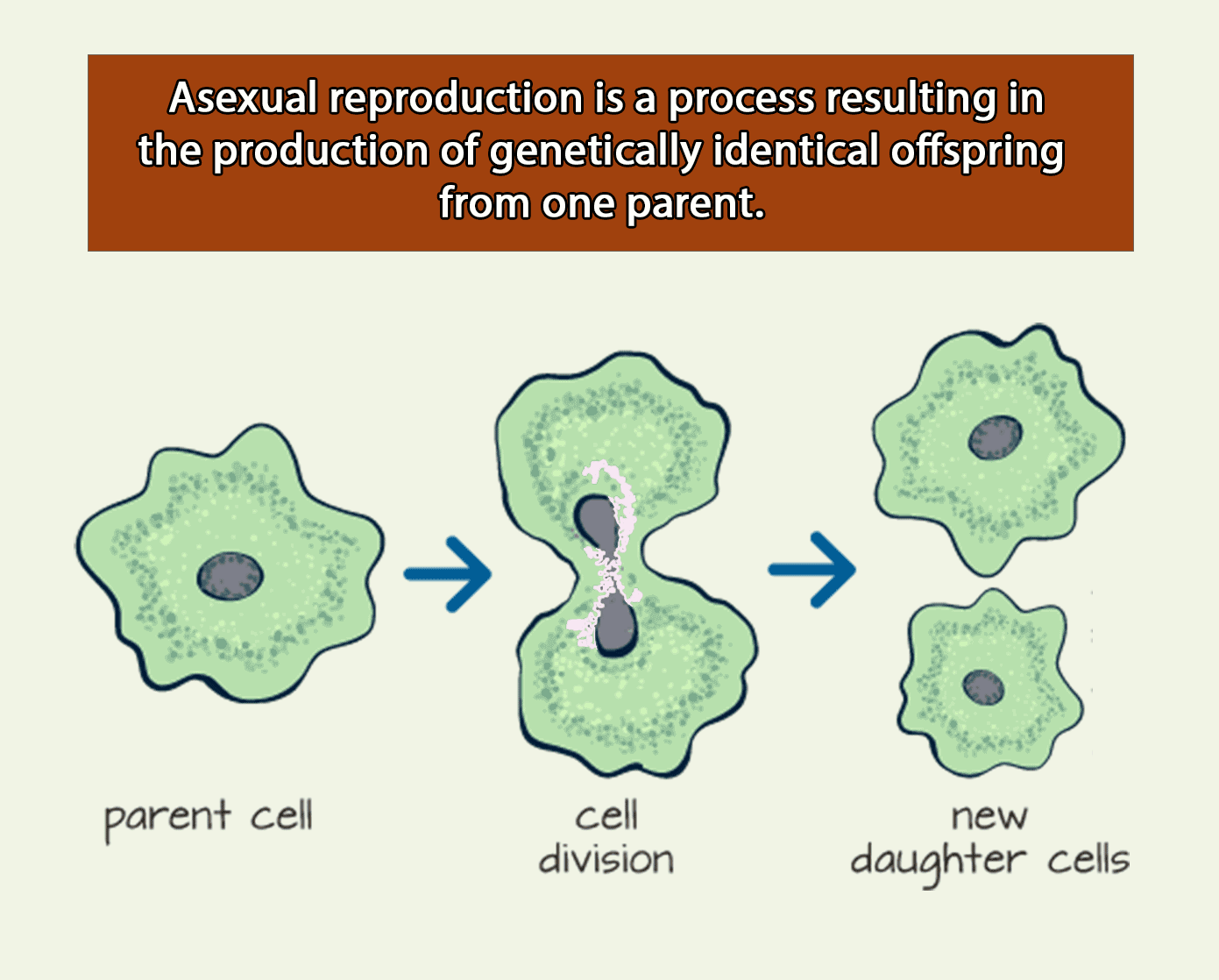
Definition: Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction results in daughter nuclei that have an identical replica of the genes of their parent nuclei.
Asexual Reproduction Examples
Examples of asexual reproduction include the binary fission of a bacteria, production of tubers by a potato plant, spore formation by fungi etc.
Definition: Sexual Reproduction
Insect-Pollinated Flower Structure
Here
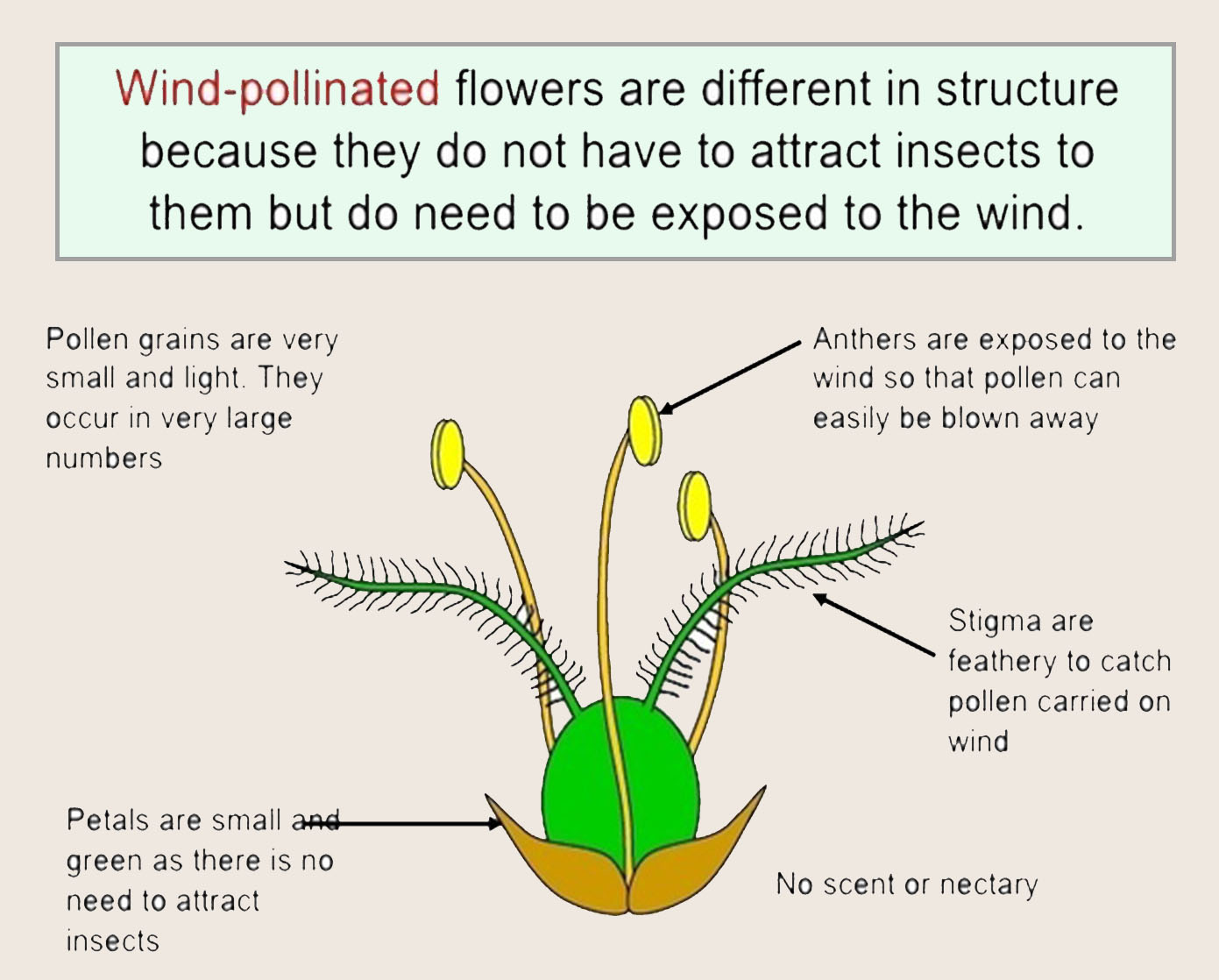
[Supplementary] Wind-pollinated flower
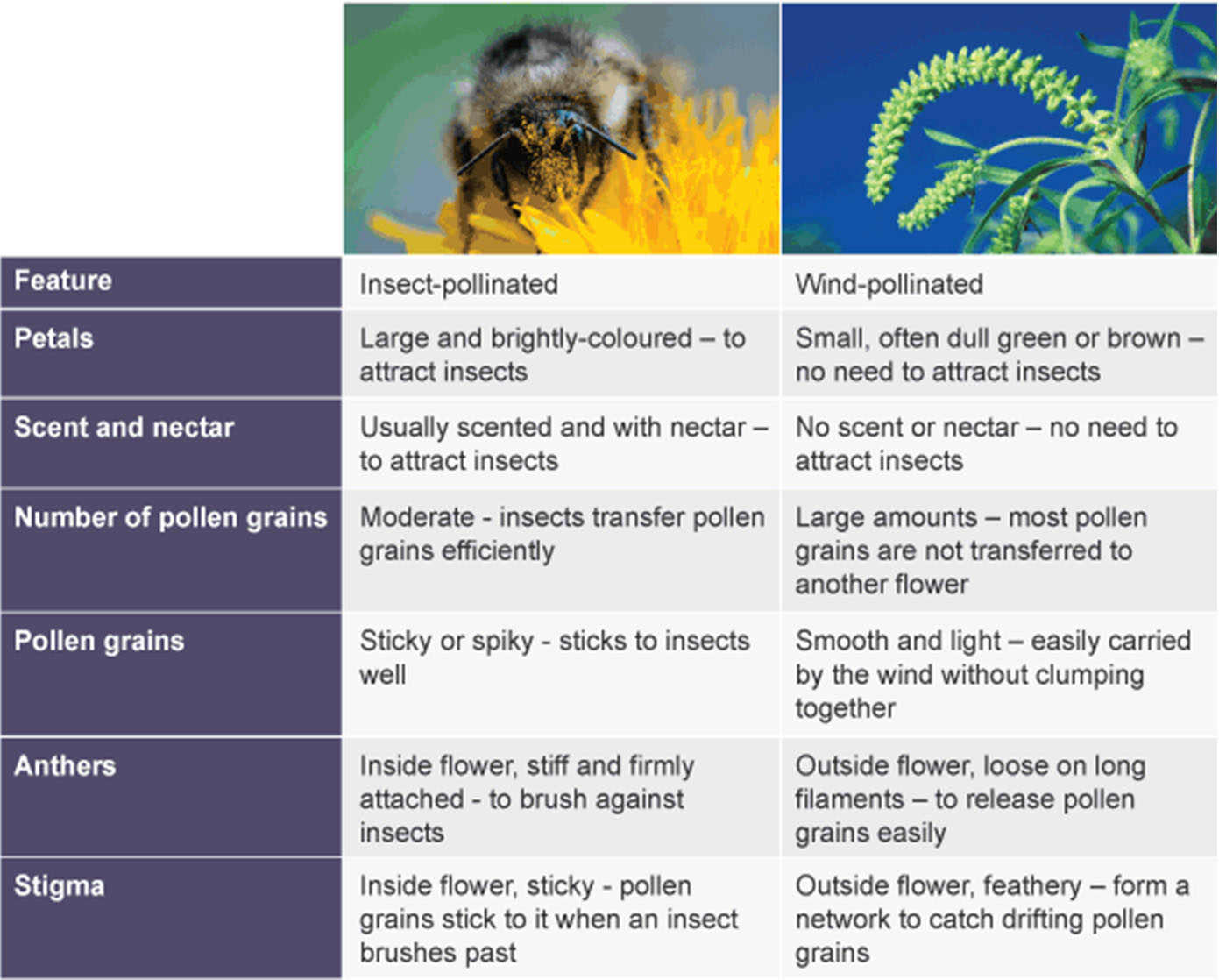
[Supplementary] Structural adaptations of Wind vs Inseact Pollinated plant
[Supplementary] Adaptation of Animal pollinated flowers:
The petal acts as a landing platform which allows the bees to collect nectar from the flower. In return, the bee would collect pollen from the anther and help to pollinate the other flowers Insect pollinated flowers usually have a scent to attract the smell of animals and insects. Also the flowers of animal pollinated flowers are large and colourful to attract animals
Adaptation of Animal pollinated flowers:
Have scents to attract the smell of animals
Have large colourful flowers to attract the attention of animals
Have nectar to attract animals to come to flower for food
[Supplementary] Adaptations of wind pollinated plants
Lots of pollen is generated in wind pollinated flowers. Many plants which are wind pollinated are adapted to have pollen grains which have air sacs.
Small petals to allow pollen to be blown away
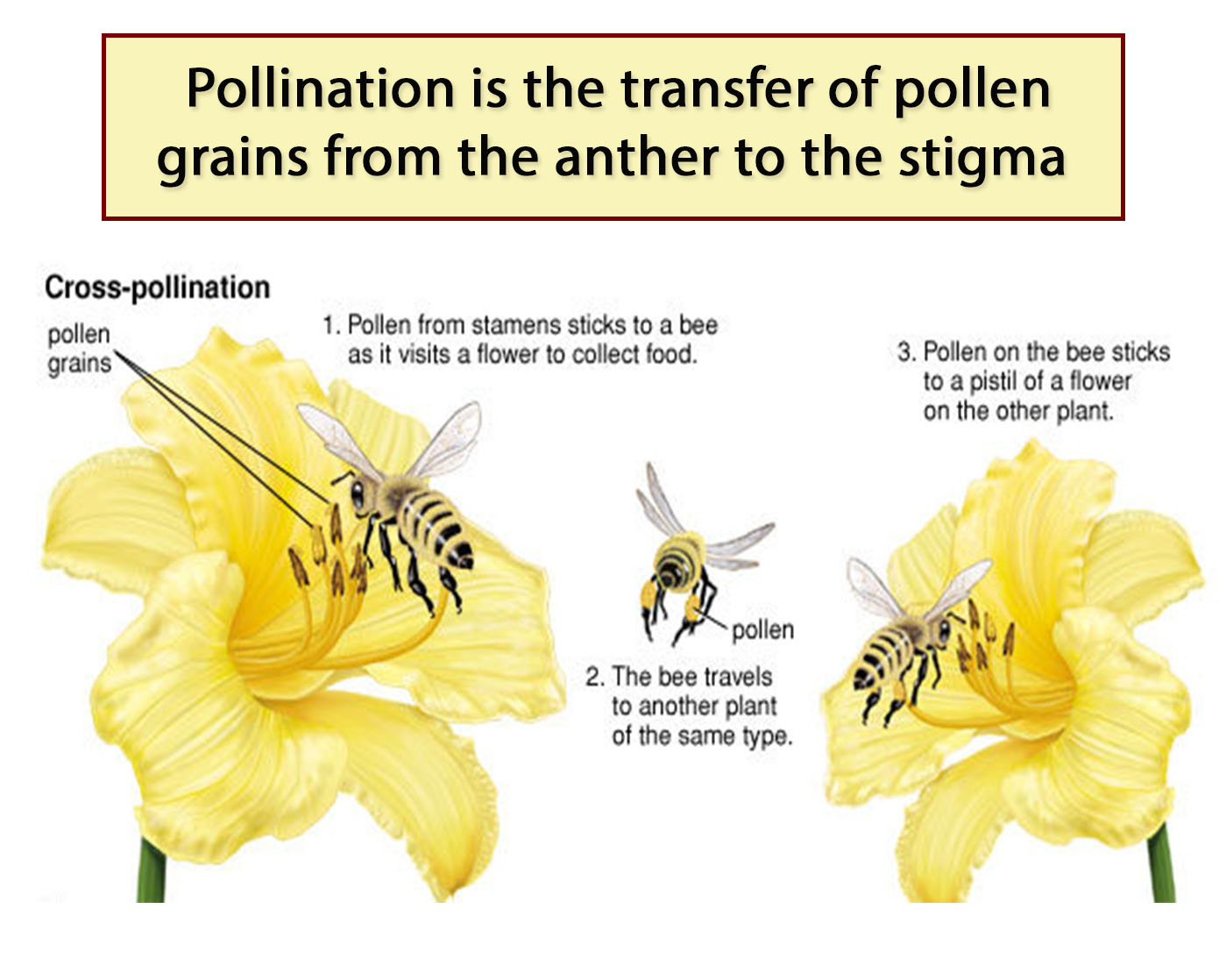
Definition: Pollination
Agents of Pollination
Animals etc insects

Wind

Water

Definition: Plant Fertilisation
Fertilisation occurs when a pollen nucleus fuses with a nucleus in an ovule.
Environmental conditions that affect germination of seeds
Seeds mostly require three environmental conditions for germination: oxygen, water and growth.
1. Oxygen is required for respiration, which provides the seed with the energy required for germination.
2. Water is required to make the food in the food stores of the seed soluble so that they can be transported to the seed embryo and used in respiration. It is also required for the seed to swell and burst so that the root and shoot can emerge.
3. Most seeds require warmth to germinate, which is why most plants only grow in spring and summer.
Male Reproductive System
Click on the structures to learn about their functions.
Female Reproductive System
Click on the structures to learn about their functions.
Fertilisation
Fertilisation is the fusion of the nuclei from a male gamete (sperm) and a female gamete (egg cell/ovum)
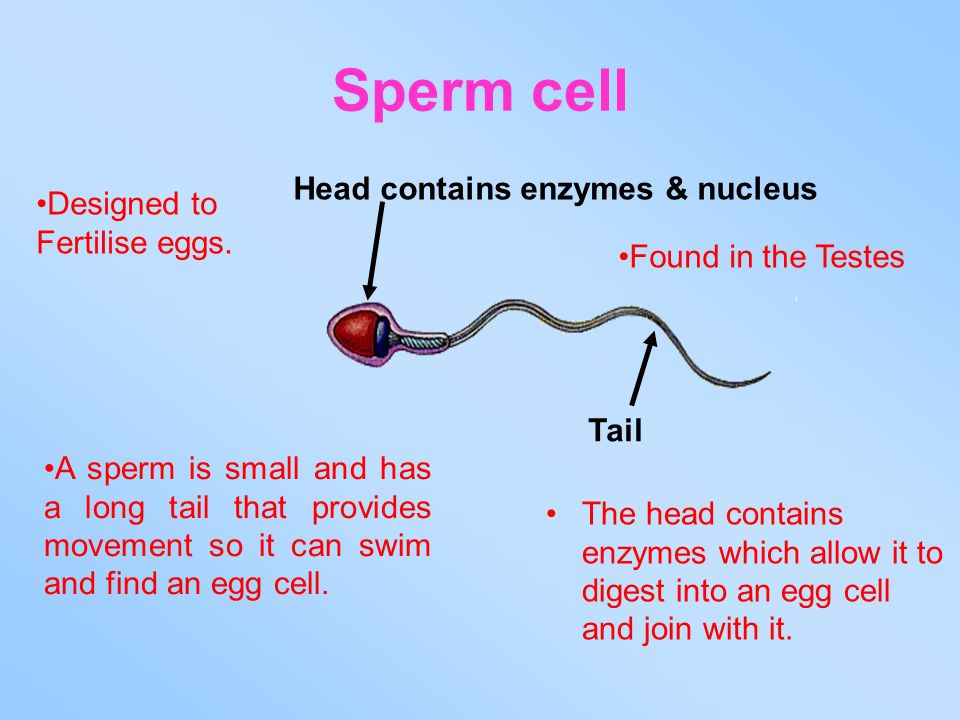
[Supplementary] Sperms vs Egg
Sperm: Millions, Very fast, small
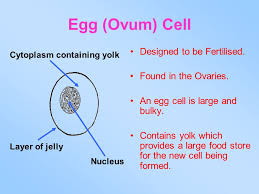
Egg Cell: Usually one, big, stationary
Sperm
Egg
[Supplementary] Sperm Adaptations
[Supplementary] Egg Adaptations
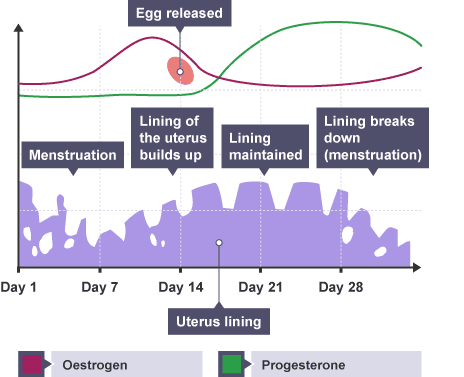
[Supplementary] Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a monthly cycle in which a woman
Zygote
In early development, the zygote forms an embryo which is a ball of cells that implants into the wall of the uterus.
[Supplementary] Functions of the umbilical cord, placenta, amniotic sac and amniotic fluid
Click on the structures to learn about their functions.
AIDS and HIV
People commonly use the terms AIDS and HIV interchangeably, but both terms are referring to very different things.
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a sexually-transmitted
How does HIV spread?
1) Sexual intercourse with infected individual
2) Blood transfusion with infected blood
3) During pregnancy, from mother to child
4) Use of contaminated needles
Controlling the Spread
There are many ways to control the spread of HIV. Listed here are just some of the ways.