How do we find the rate of a reaction?
To find the rate of a reaction,
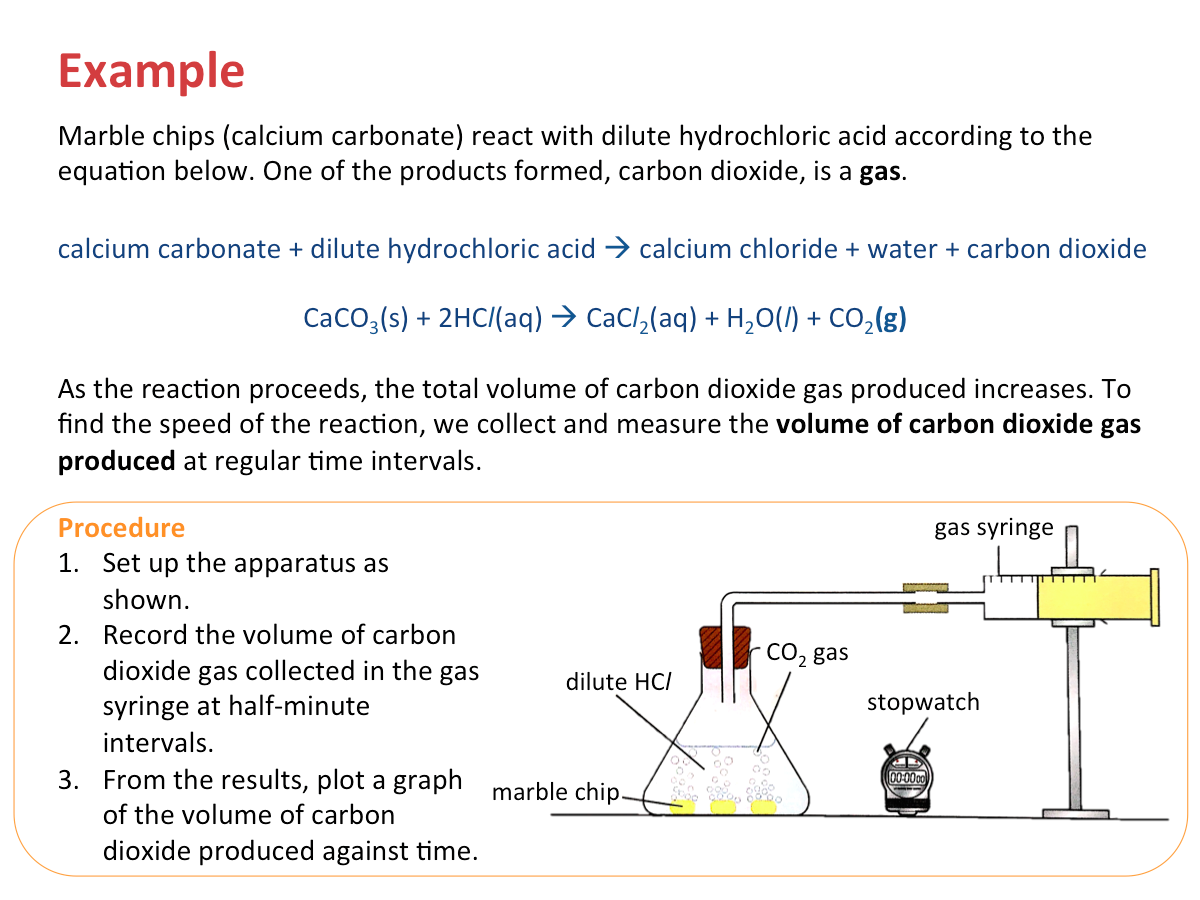
We can measure the quantities of products or reactants at regular time intervals:
- volume of the gas produced in the reaction
- mass of the reactant that remains
Measuring the Volume of Gas Produced
If one of the products in a chemical reaction is a gas, we can find the speed of reaction by measuring the volume of gas produced in a certain time.
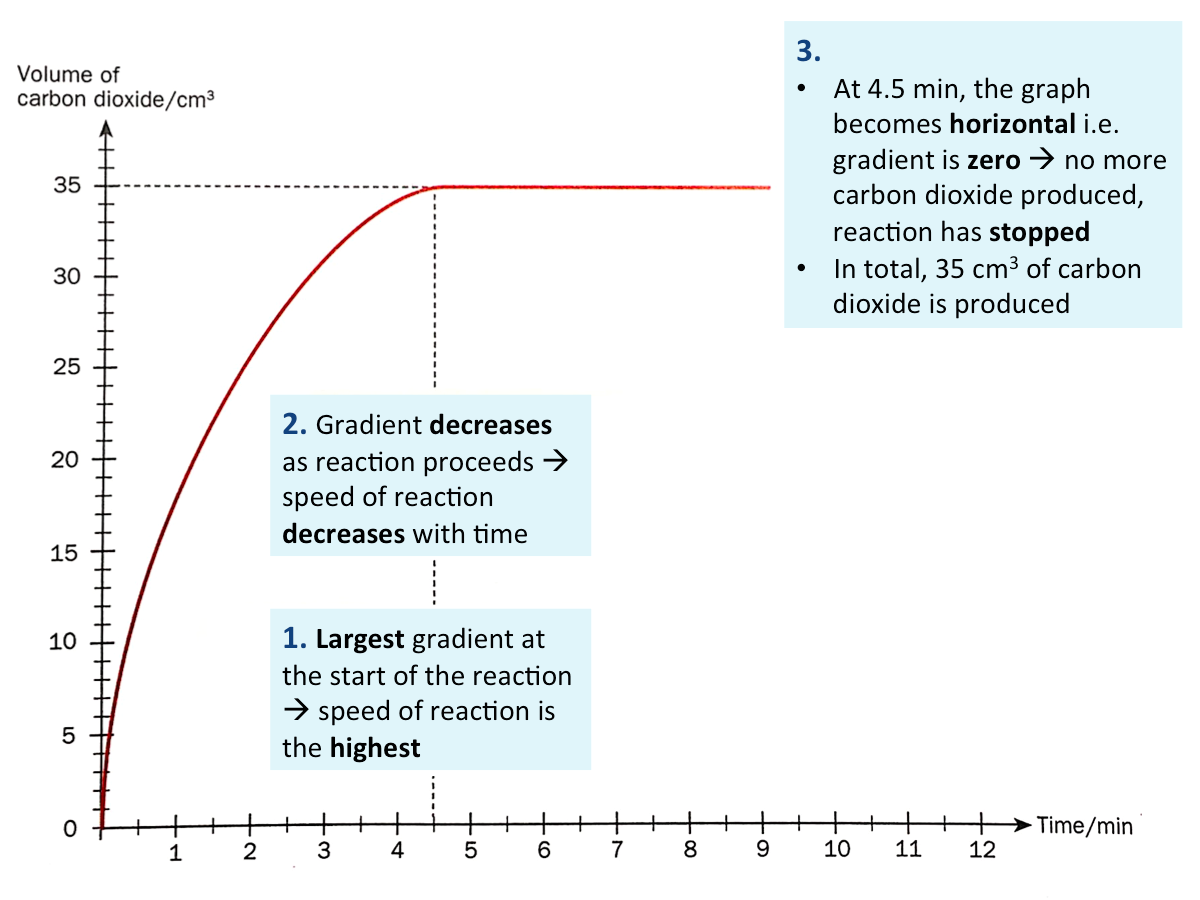
How can we tell the change in speed of reaction from a graph?
Generally, for any reaction, the change in mass or volume of the reactants (or products) can be plotted against time. The gradient at any point of the graph indicates the speed of reaction at a particular time.
The larger the gradient, the higher the speed of reaction.
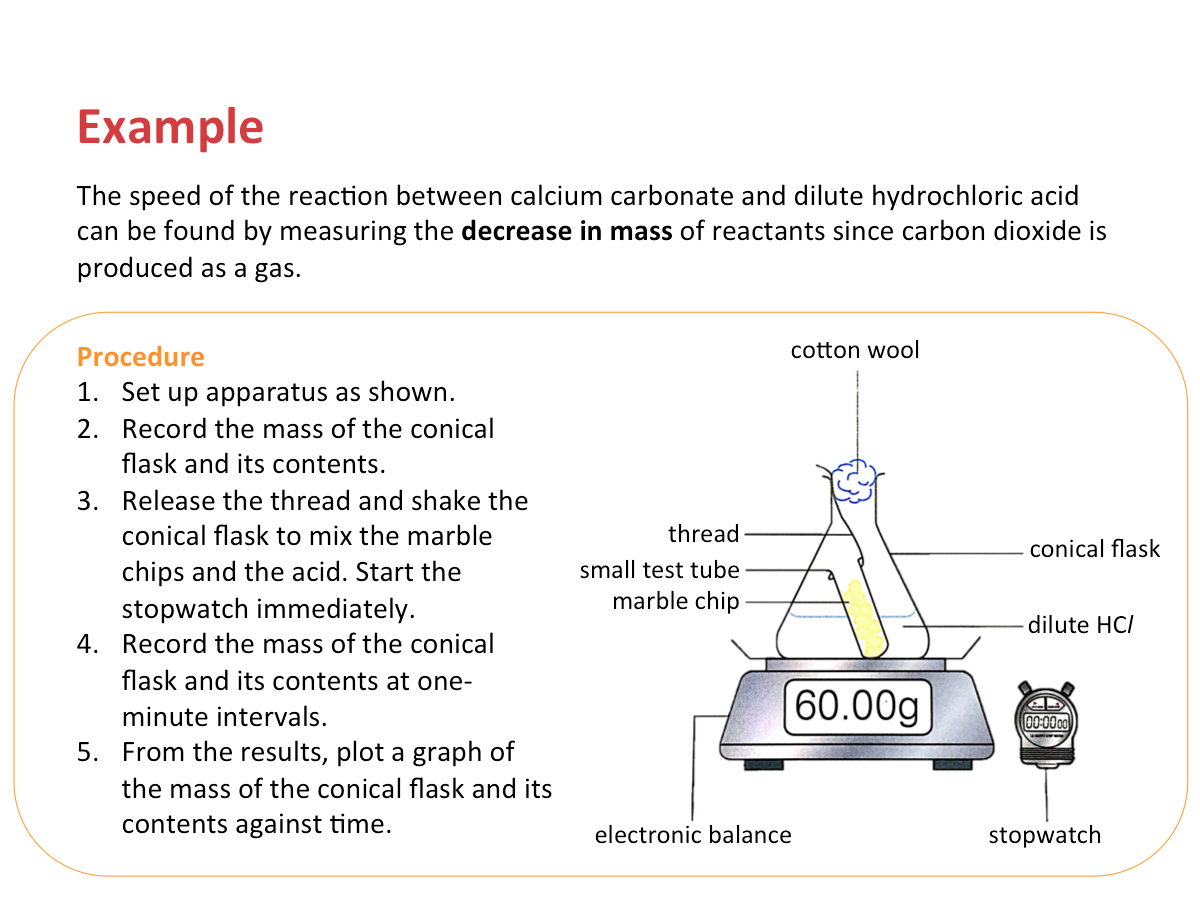
Measuring the Change in Mass
The speed of a reaction can also be found by measuring the change in mass of a reaction mixture in a certain time. For some reactions, such as those that produce gases, it is easier to measure the decrease in mass of reactants instead of the increase in mass of products.
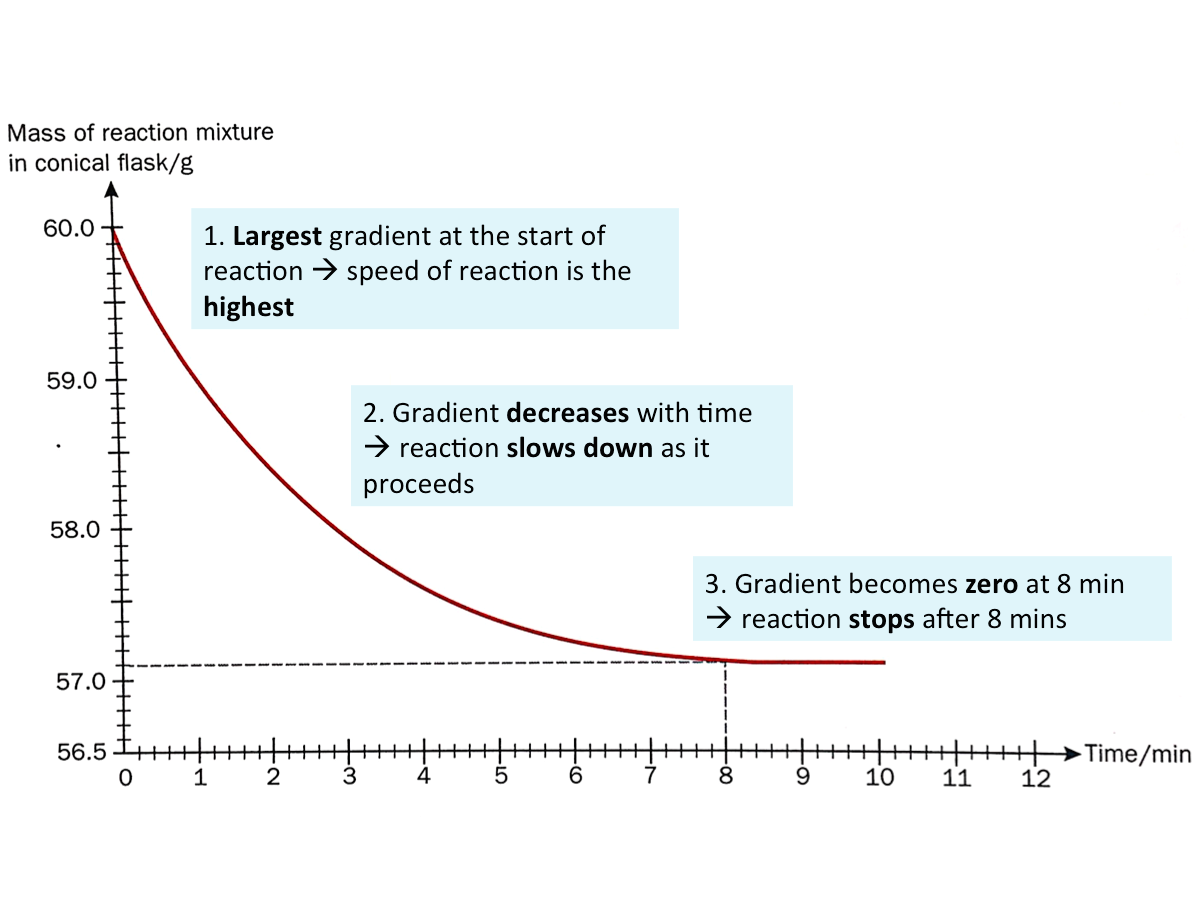
Reading the Graph
The graph below shows the decrease in mass of the reaction mixture in the previous example over time.
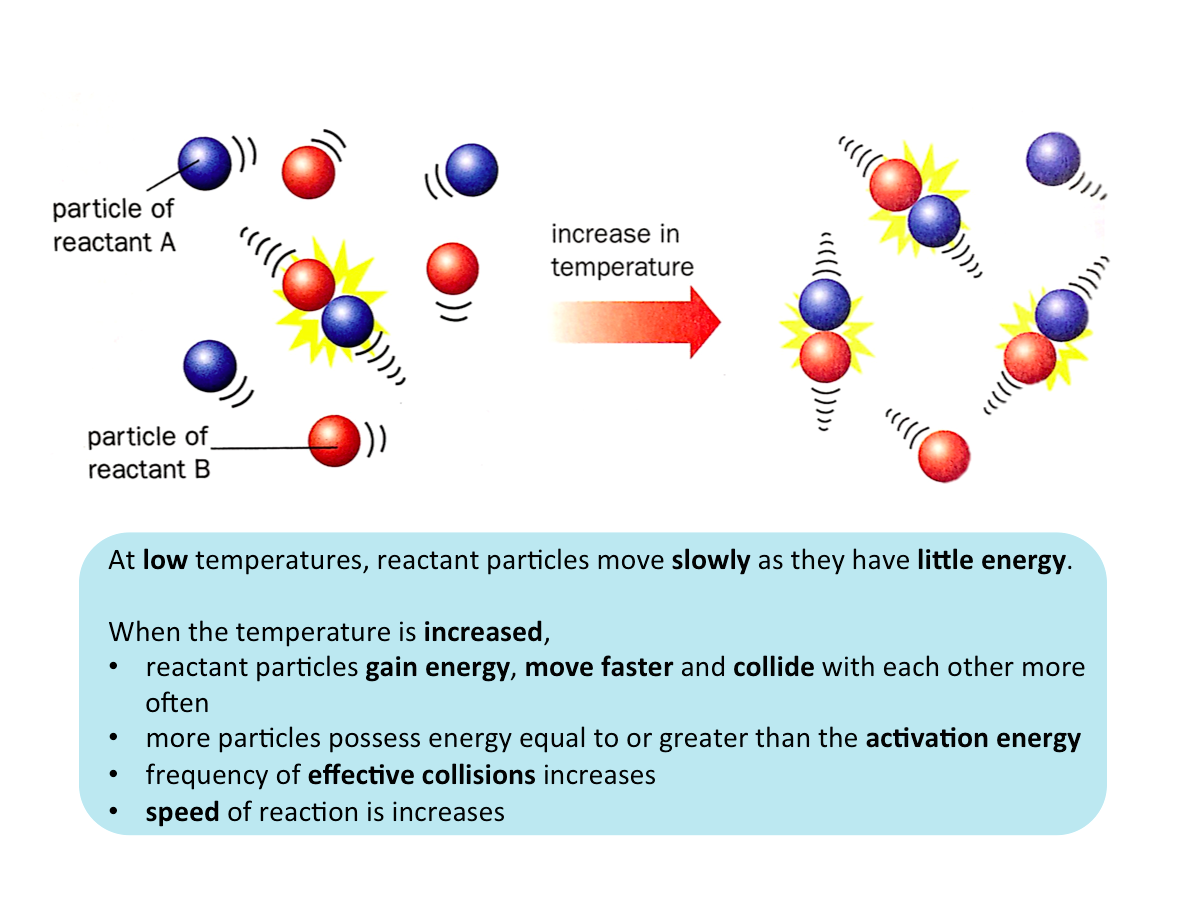
Speed of Reaction anf Effective Collision
In order for a reaction to occur,
- the reactant particles must collide with each other and
- they must collide with energy that is equal to or greater than the activation energy
When the collisions between reactant particles fulfil these conditions, product particles are formed. These collisions are known as effective collisions.
The frequency of effective collisions between reactant particles affects the speed of reaction. An increase in the frequency of effective collisions increases the speed of reaction.
Watch the video below to learn more about effective collision.
Factors That Affect the Speed of a Reaction
Many factors affect the speed of a chemical reaction. These include the
- concentration of the reactants
- pressure at which the reaction occurs (for gaseous reactants)
- particle size or surface area of the reactants (for solid reactants)
- temperature at which the reaction occurs
- presence of a catalyst
Watch the video below to learn more about the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
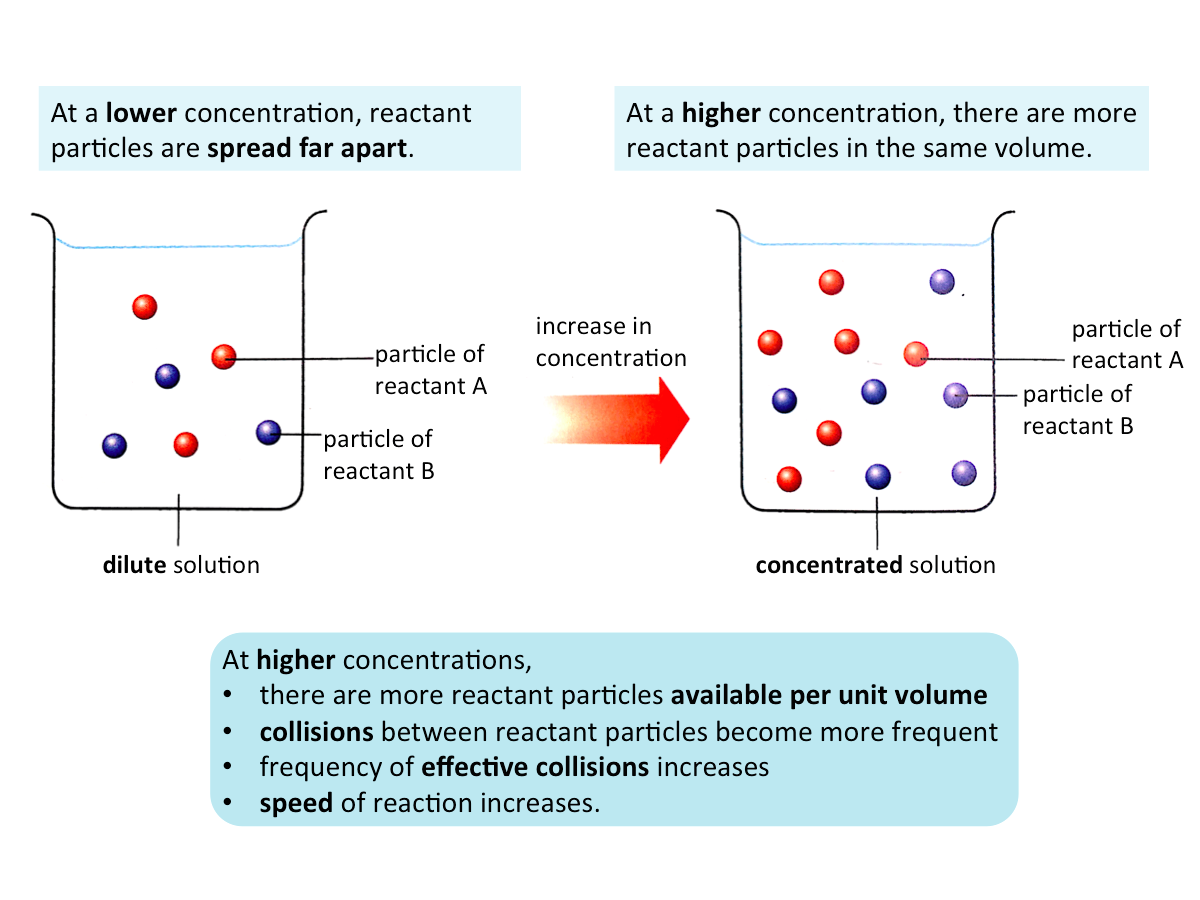
Effect of Concentration on the Speed of Reaction
When the concentration of a reactant is increased, the speed of the reaction increases.
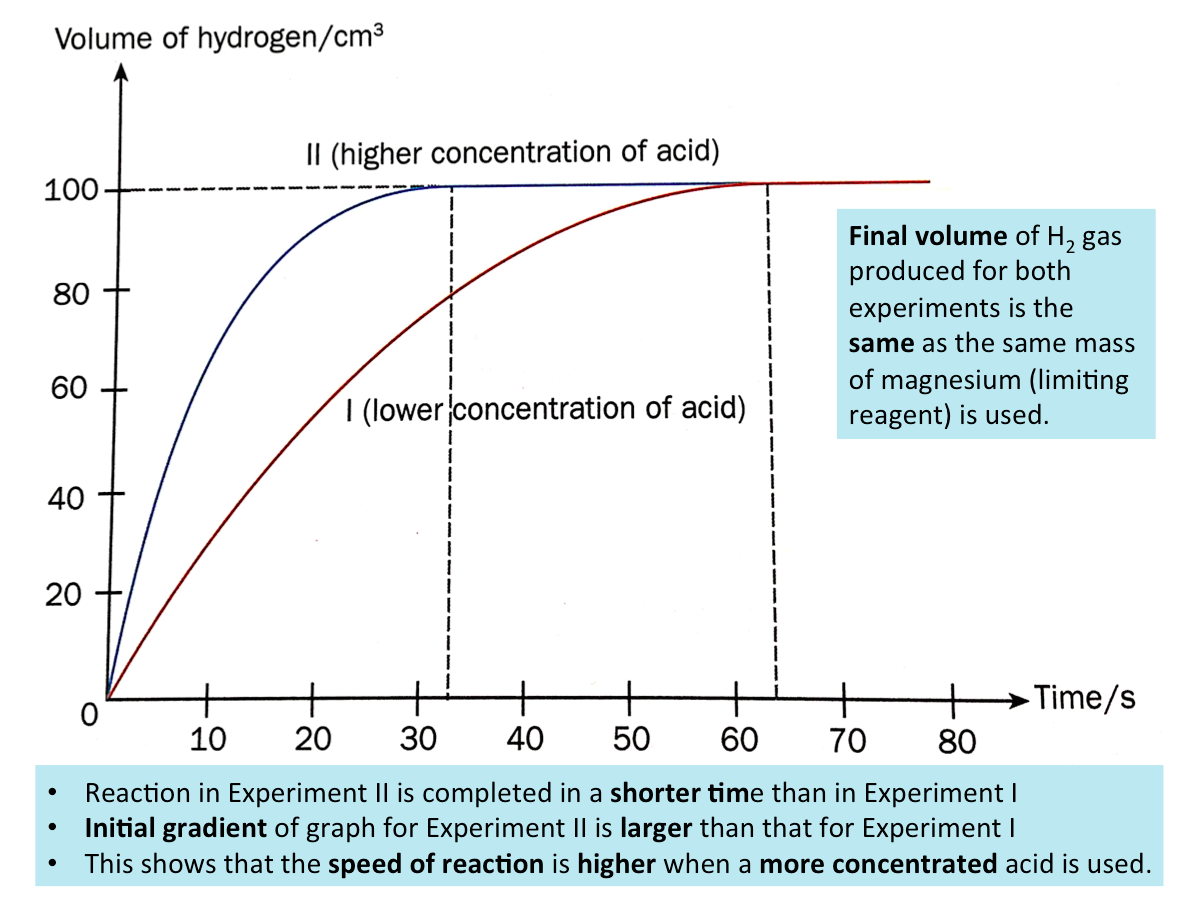
Effect of Concentration on the Speed of Reaction (Example)
To investigate the effect of concentration of a reactant on the speed of reaction, experiments involving the reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid and magnesium are carried out. Two experiments are preformed and all conditions are kept constant other than the concentration of hydrochloric acid. The concentration of hydochloric acid used in Experiment II is twice that of Experiment I.
A graph from the results of the experiment is shown below.
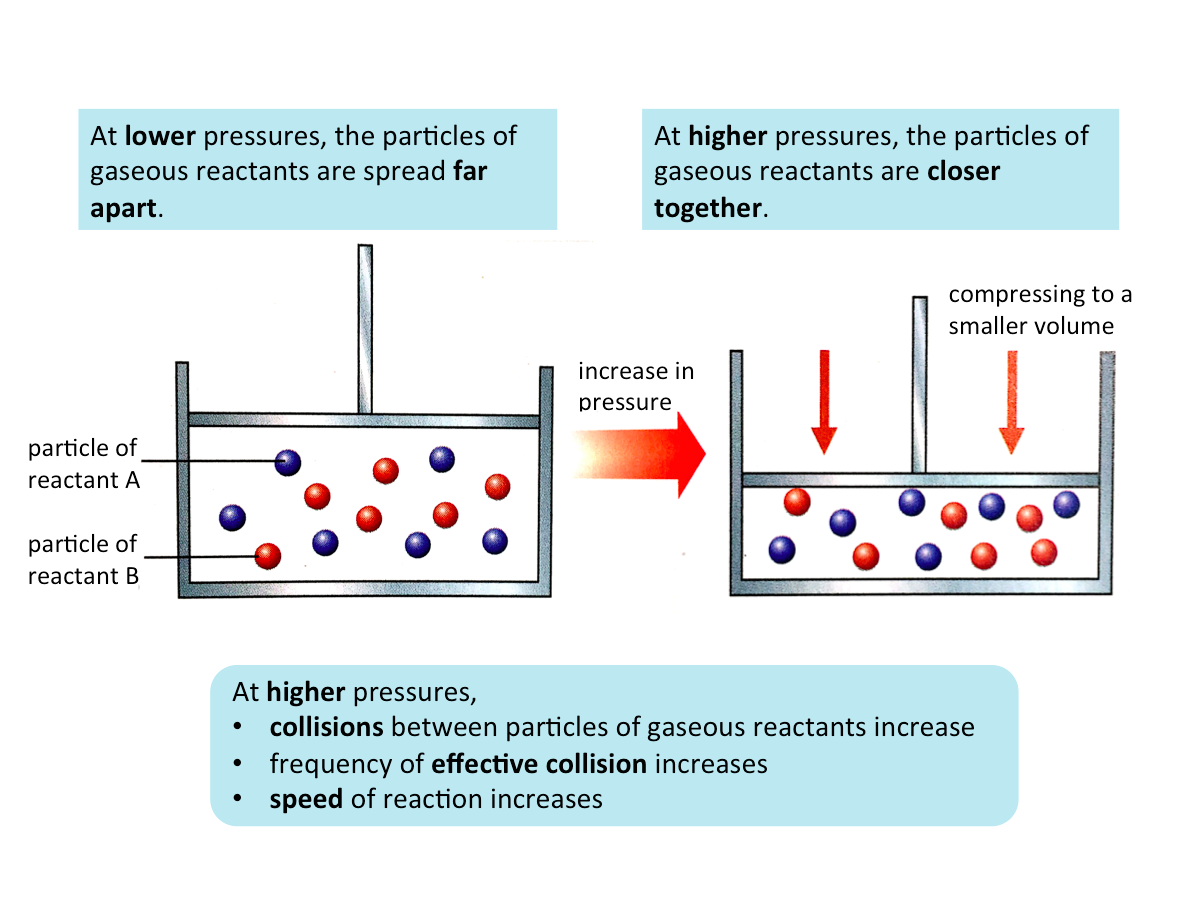
Effect of Pressure on the Speed of Reaction
Pressure significantly affects the speed of reaction in chemical reactions that involve gases.
When the pressure of a gaseous reactant is increased, the speed of the reaction increases.
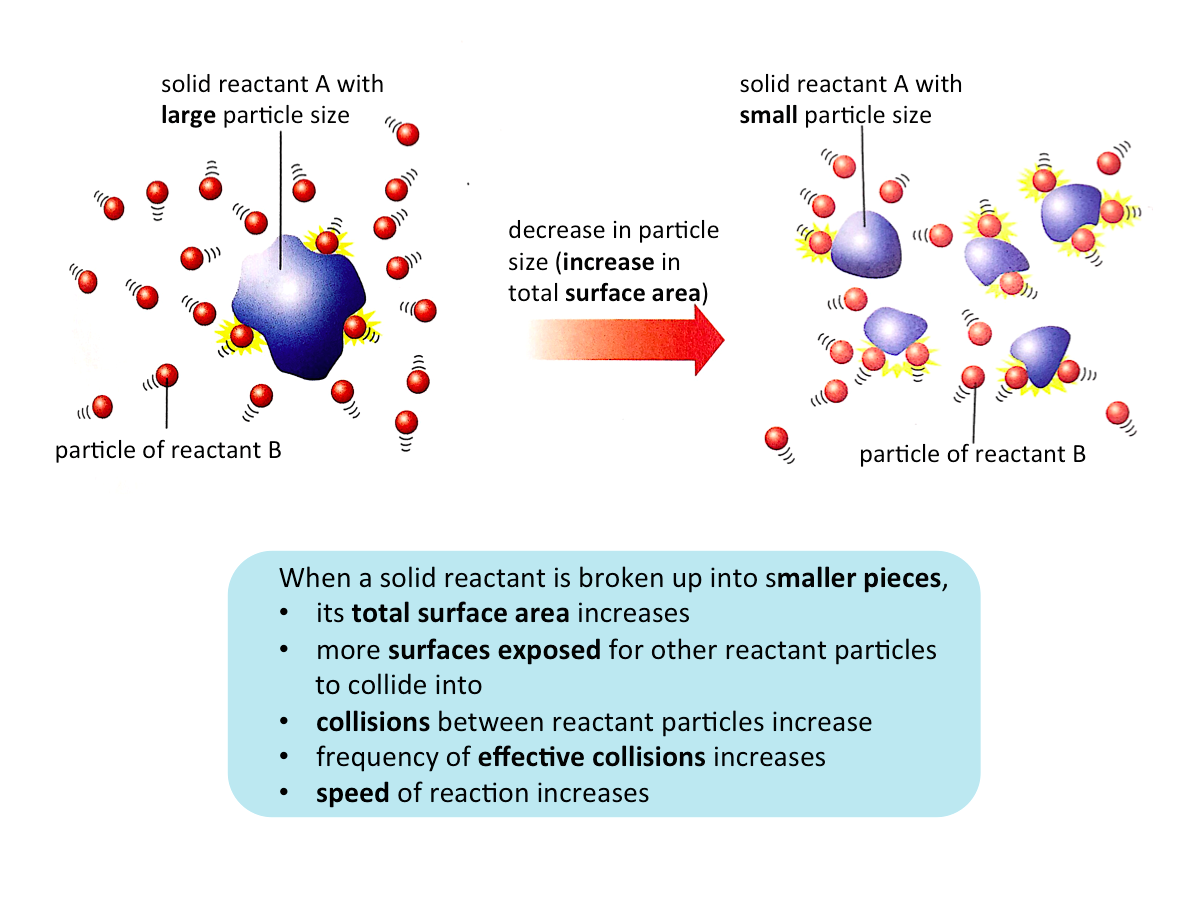
Effect of Particle Size on the Speed of Reaction
When the surface area of a solid reactant is increased (i.e. the particle size is decreased), the speed of reaction increases.
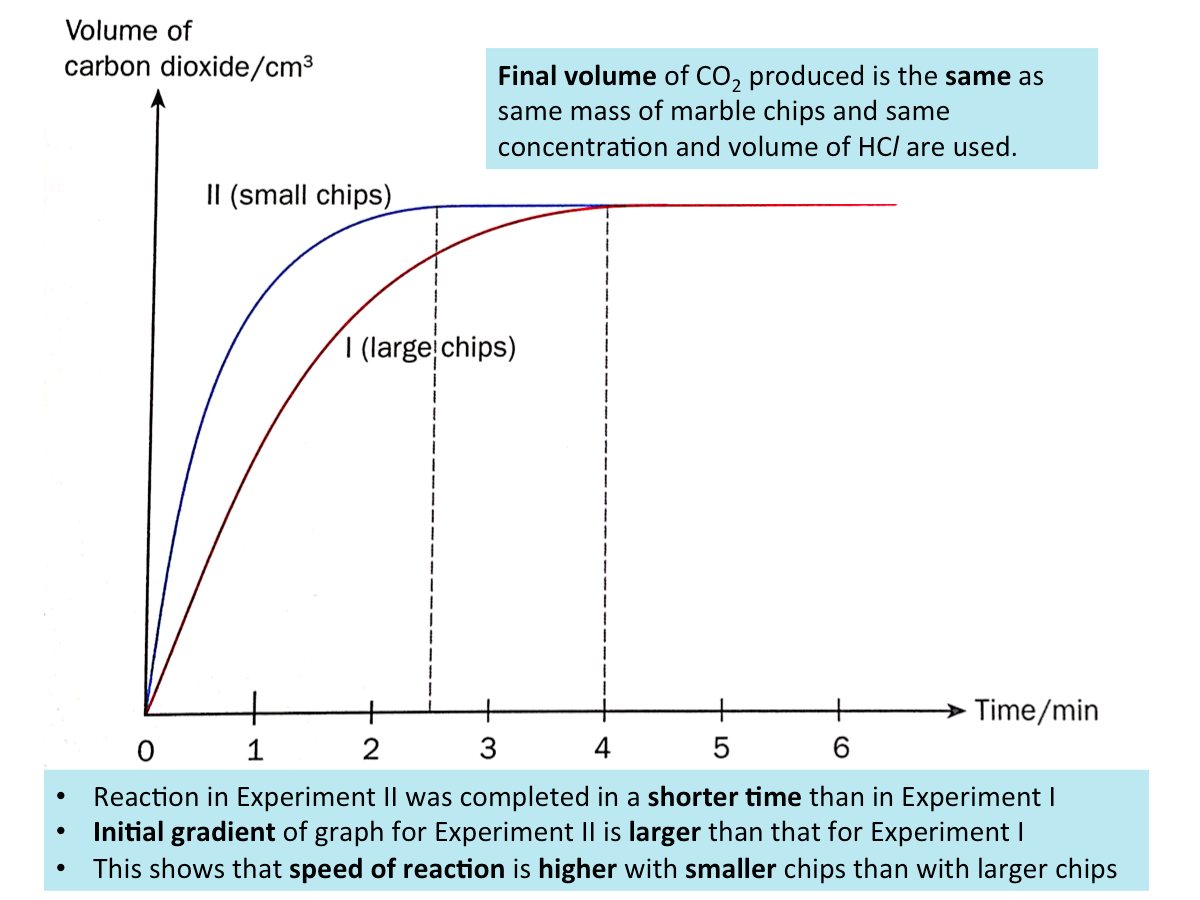
Effect of Particle Size on the Speed of Reaction (Example)
Consider the reaction between marble chips (calcium carbonate) and dilute hydrochloric acid.
calcium carbonate + dilute hydrochloric acid ? calcium chloride + water + carbon dioxide
We can investigate the effect of particle size on the speed of reaction by reacting a fixed concentration and volume of hydrochloric acid with
I. large marble chips (large particle size)
II. crushed marble chips (small particle size)
The volume of carbon dioxide gas produced is measured at regular time intervals.
A graph from the results of the experment is shown below.
Effect of Particle Size on the Speed of Reaction (Video)
Watch the video below to learn more about how surface area affects the rate of reaction.
Effect of Temperature on the Speed of Reaction
When the temperature of a reactant is increased, the speed of the reaction increases.
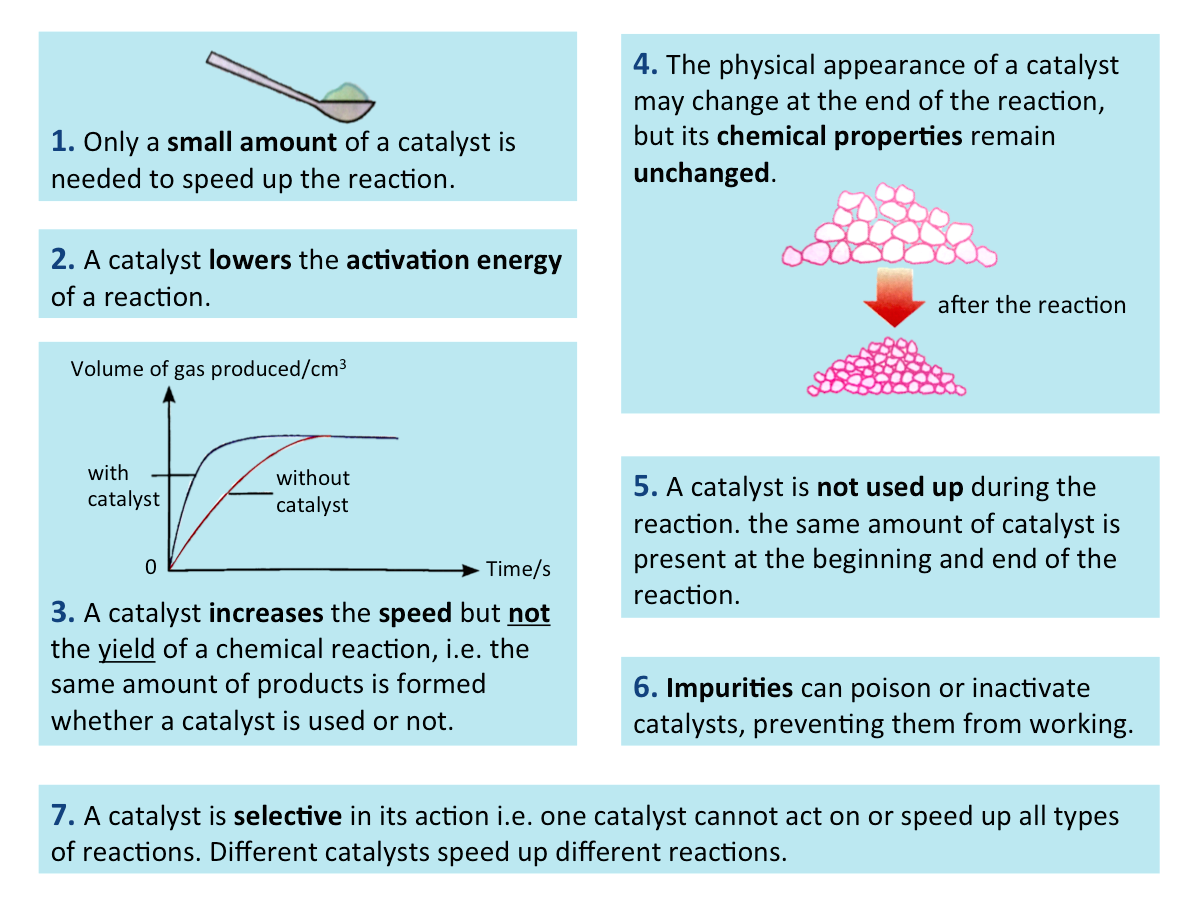
Characteristics of a Catalyst
A catalyst is a substance which increases the speed of a chemical reaction and remains chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction.
A catalyst has the following characteristics:
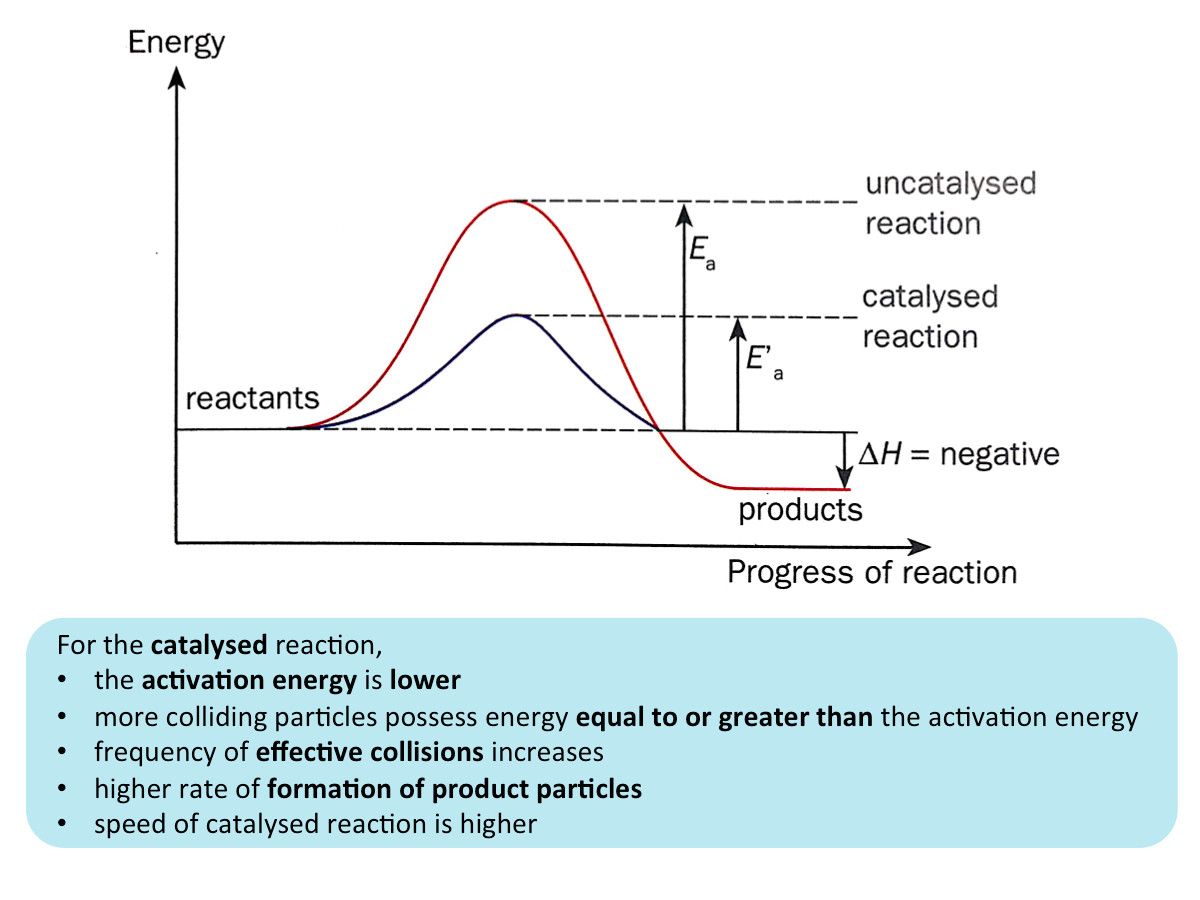
Catalyst and Activation Energies
Catalysts increase the speed of reaction by providing an alternative pathway for the reaction to proceed. The catalysed reaction has a lower activation energy than the reaction without the catalyst.
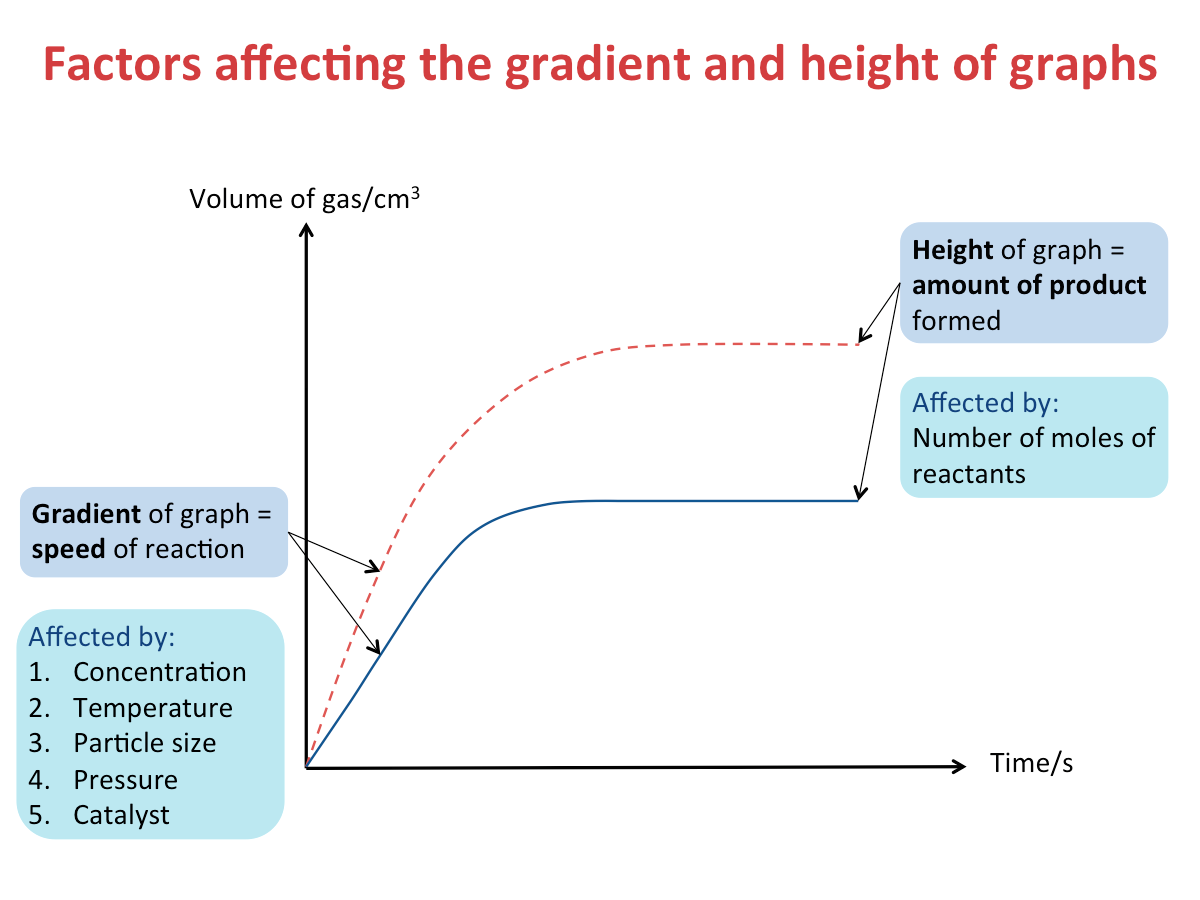
Factors Affecting the Gradient and Height of Graphs
The figure below shows the different factors that affect the gradient and height of graphs.
What is oxidation?
Oxidation has taken place if a substance
- Gains oxygen
- Loses hydrogen
- Loses electrons
- Increases its oxidation state after a reaction.
Oxidation occurs when a substance gains oxygen.
What is reduction?
A reduction reaction is the reverse process of an oxidation reaction.
Reduction has taken place if a substance
- Loses oxygen
- Gains hydrogen
- Gains electrons
- Decreases its oxidation state after a reaction
Reduction occurs when a substance loses oxygen.
What is a redox reaction?
A redox reaction is a chemical reaction which involves the oxidation of a substance and the reduction of another substance.
Test
Try these questions out and click on Reveal Answer to check!
Oxidation - Loss of Hydrogen
Oxidation occurs when a substance loses hydrogen.
Reduction - Gain of Hydrogen
Reduction occurs when a substance gains hydrogen.
Oxidation - Loss of Electrons
Oxidation occurs when a substance loses electrons.
Reduction - Gain of Electrons
Reduction occurs when a substance gains electrons.
Oxidation State
When a substance loses or gains electrons, its oxidation state changes. We can determine if oxidation or reduction has taken place by studying the oxidation states of the reacting atoms.
The oxidation state is the charge an atom of an element would have if it existed as an ion in a compound.
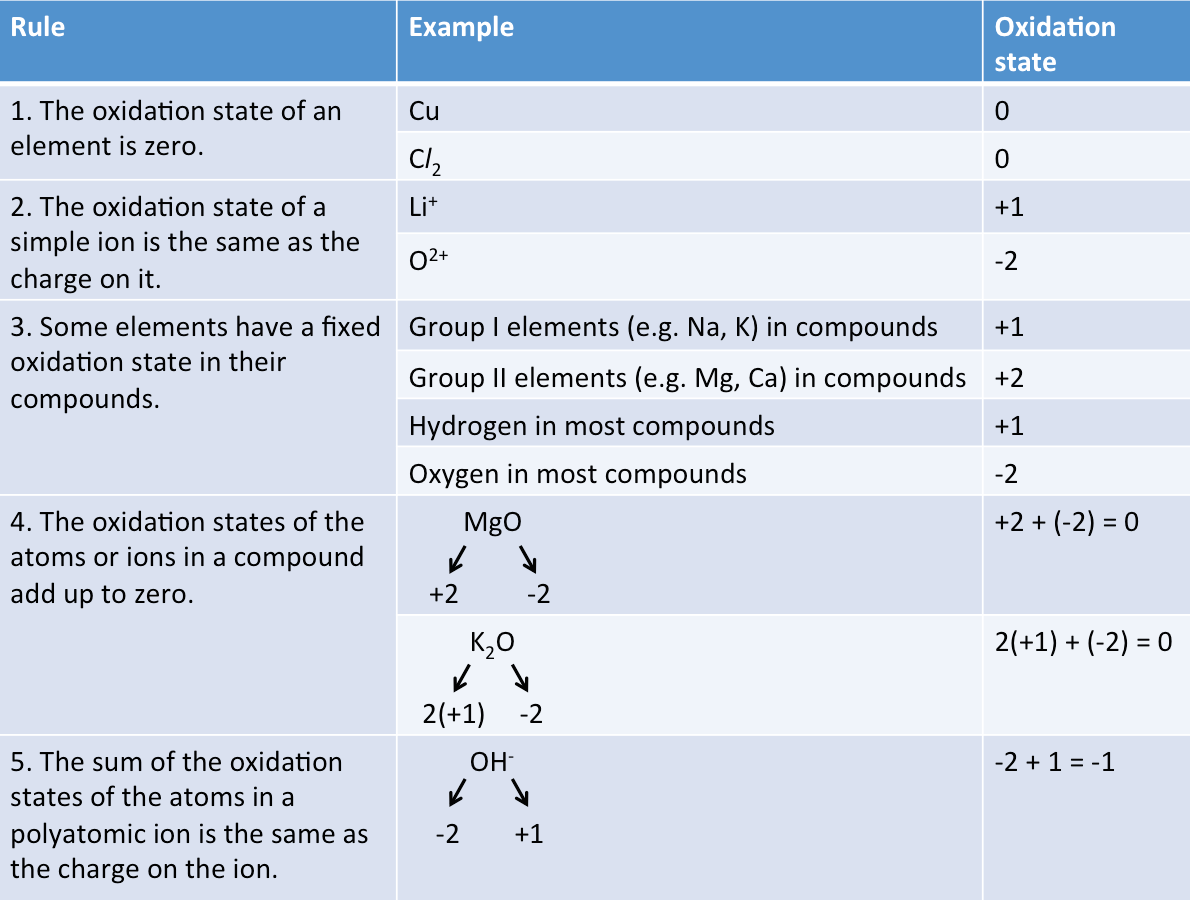
How do we determine the oxidation states of atoms in a substance?
The table below shows the rules for working out the oxidation states of atoms and ions.
Test
Try these questions out and click on Reveal Answer to check!
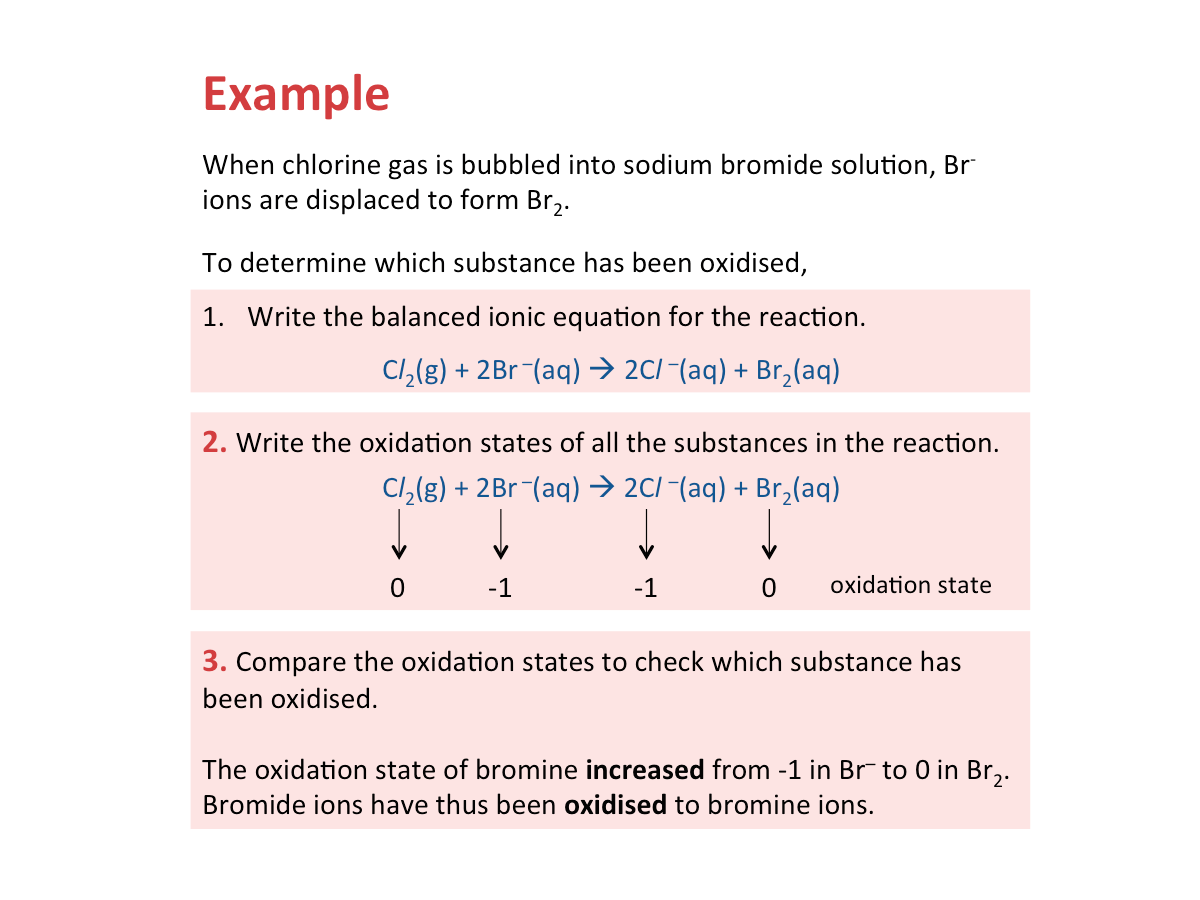
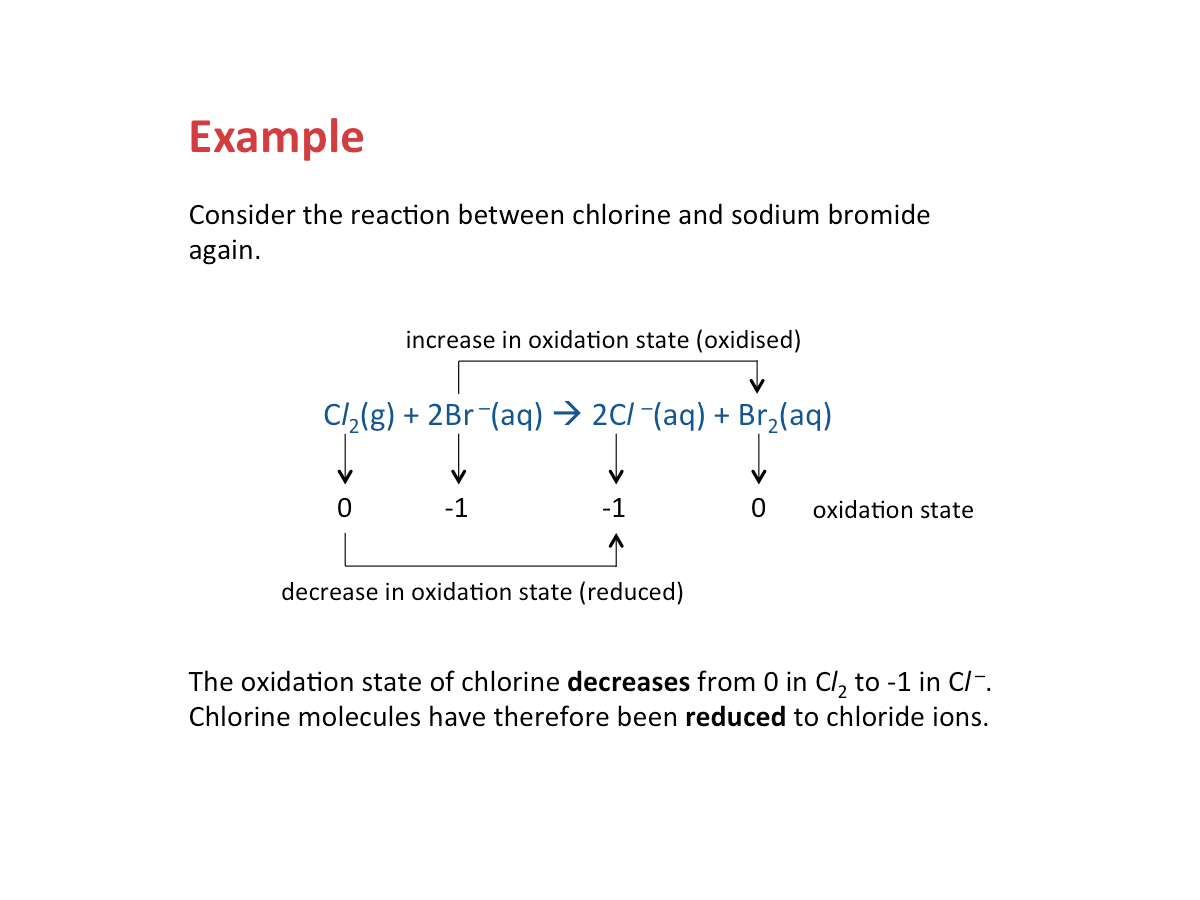
Oxidation - Increase in Oxidation State
When a substance loses electrons, its oxidation state increases and it is oxidised.
Oxidation occurs when the oxidation state of a substance increases.
Reduction - Decrease in Oxidation State
Reduction occurs when the oxidation state of a substance decreases.
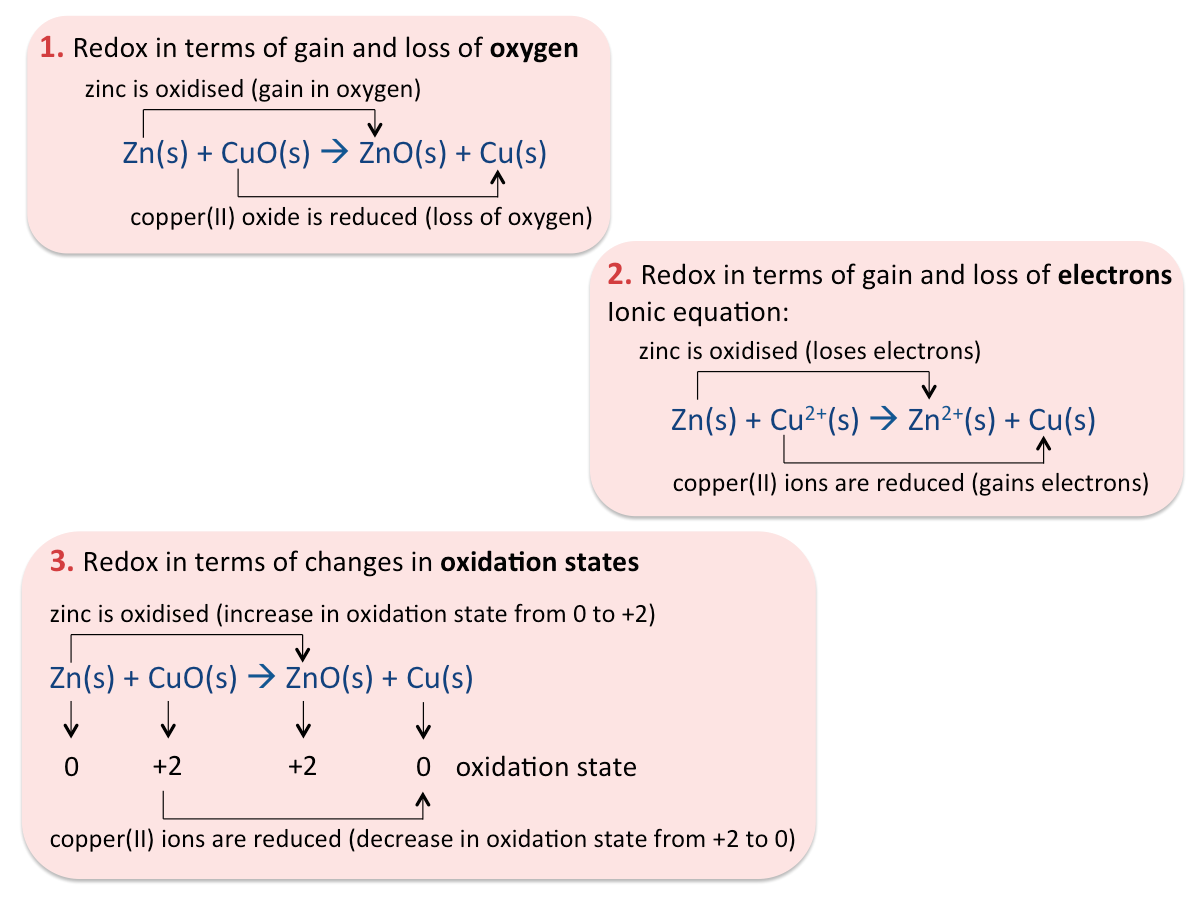
Has a redox reaction taken place?
The three ways of determining if a reaction is a redox reaction are shown below.
Test
Try these questions out and click on Reveal Answer to check!
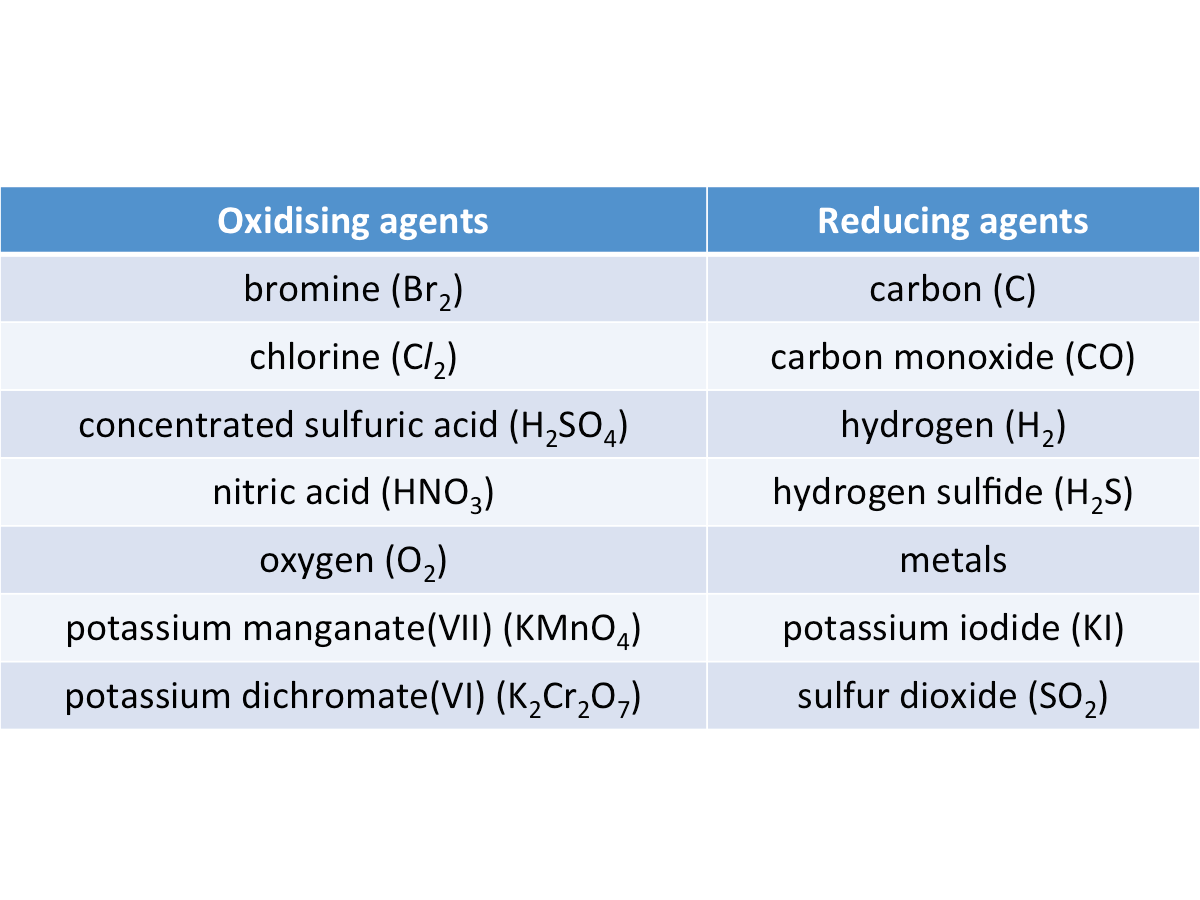
What are oxidising and reducing agents?
An oxidising agent is a substance that causes another substance to be oxidised.
An oxidising agent is reduced in the process.
A reducing agent is a substance that causes another substance to be reduced.
A reducing agent is oxidised in the process.
The table below shows some common oxidising and reducing agents.
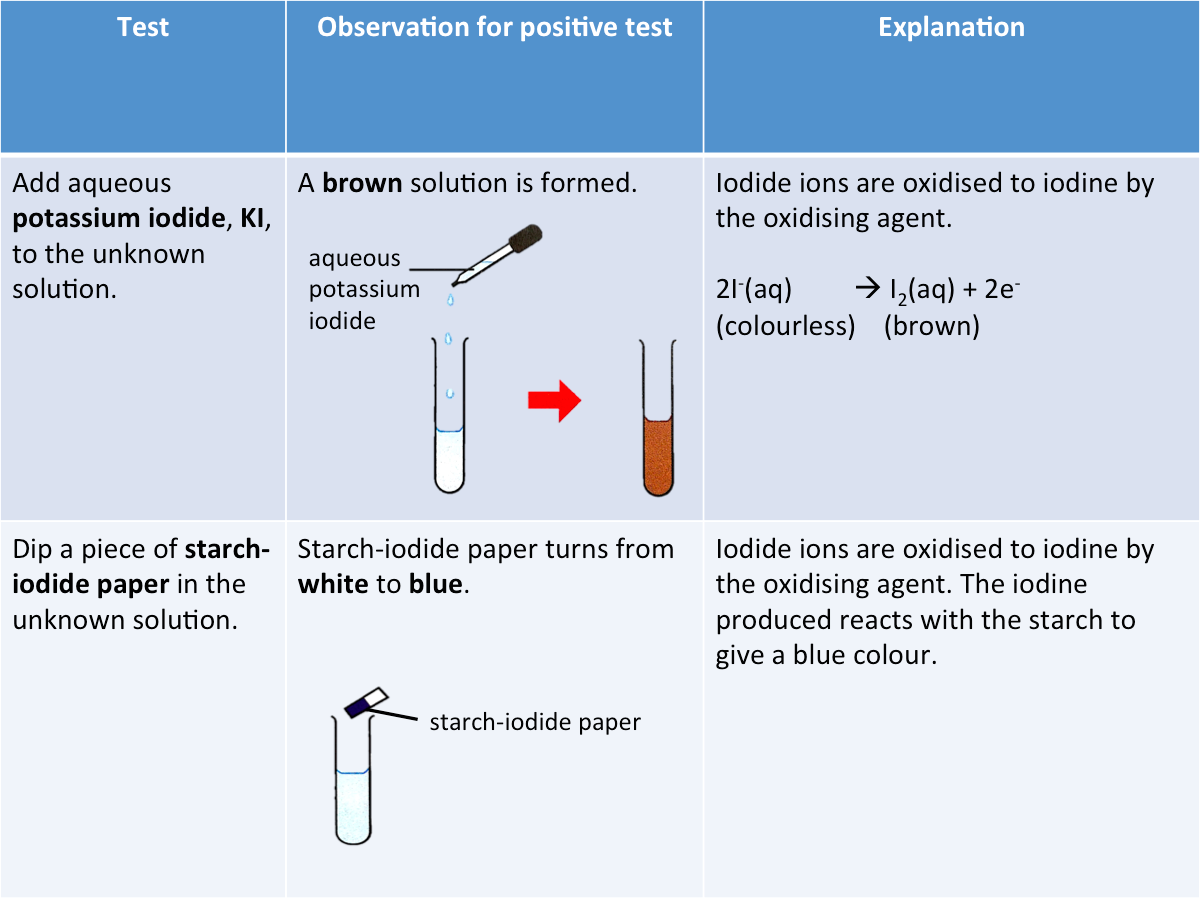
Testing for an Oxidising Agent
Aqueous potassium iodide, KI, or starch-iodide paper can be used to test for the presence of an oxidising agent.
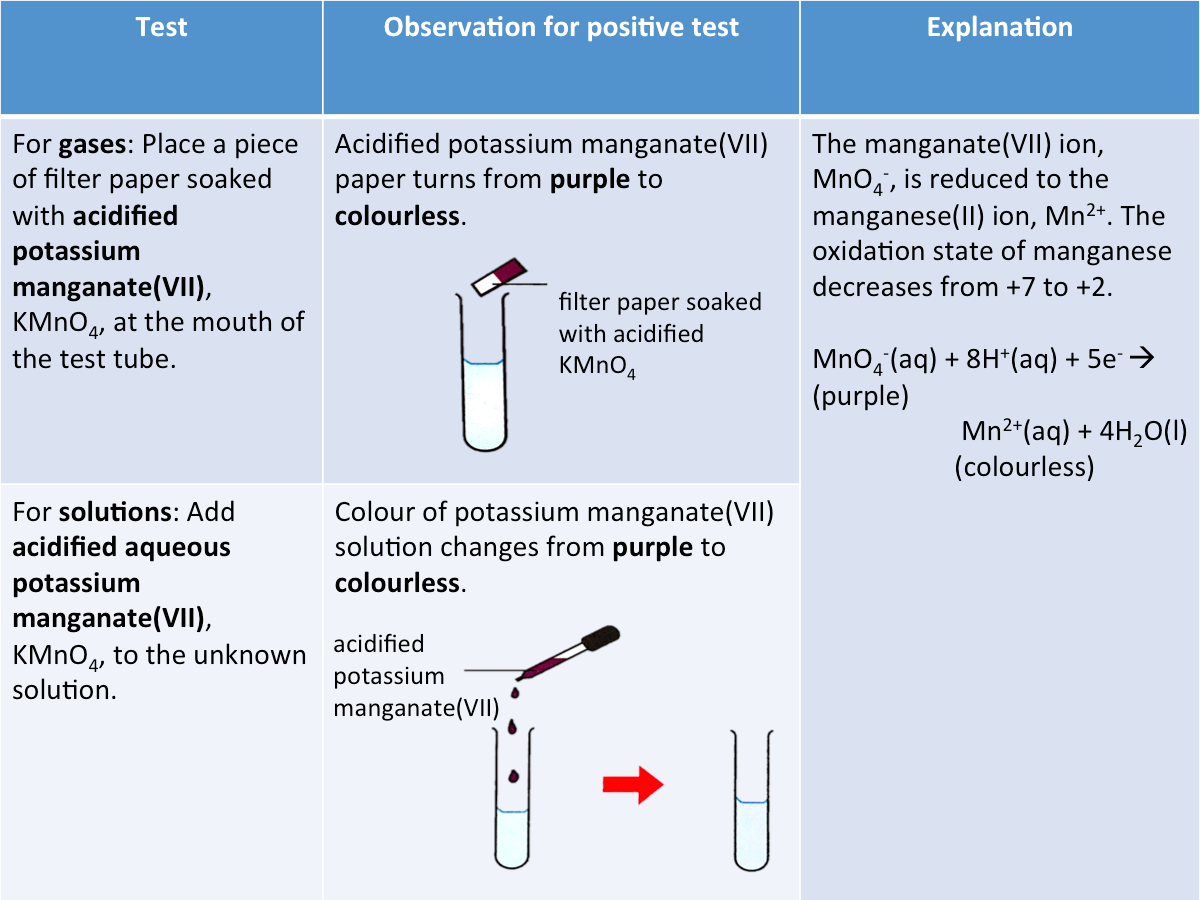
Test for a Reducing Agent
Acidified potassium manganate(VII) can be used to test for the presence of a reducing agent.
Chapter Summary (Video)
Refer to the video below for a summary of the chapter.