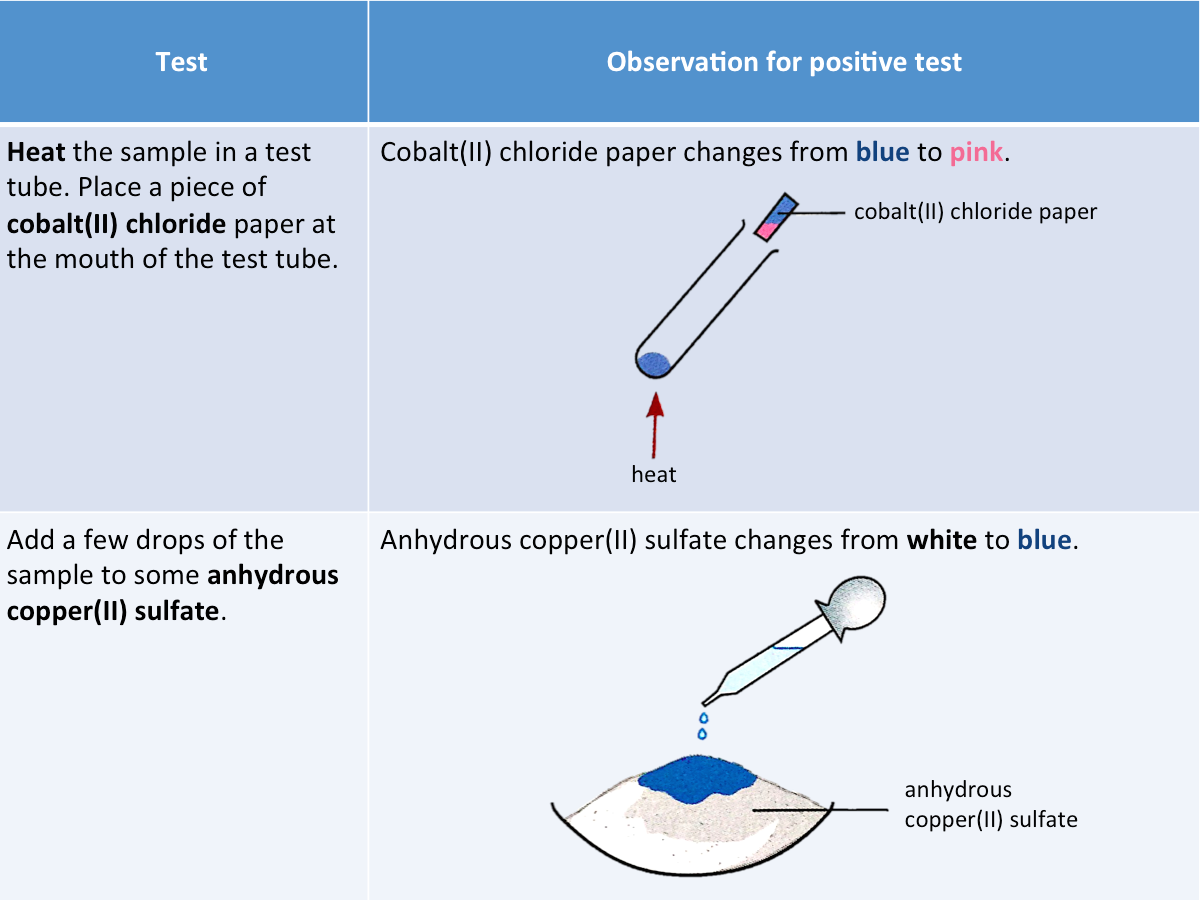
How is water identified?
When a hydrated salt is heated, the colourless liquid that condenses near the top of the test tube is most likely to be water.
The two chemical tests that will confirm the presence of water are shown in the table below.
The Atmosphere
The Earth is surrounded by a layer of air called the atmosphere. The atmosphere acts as a blanket to protect the Earth from the Sun and maintain the Earth temperature.
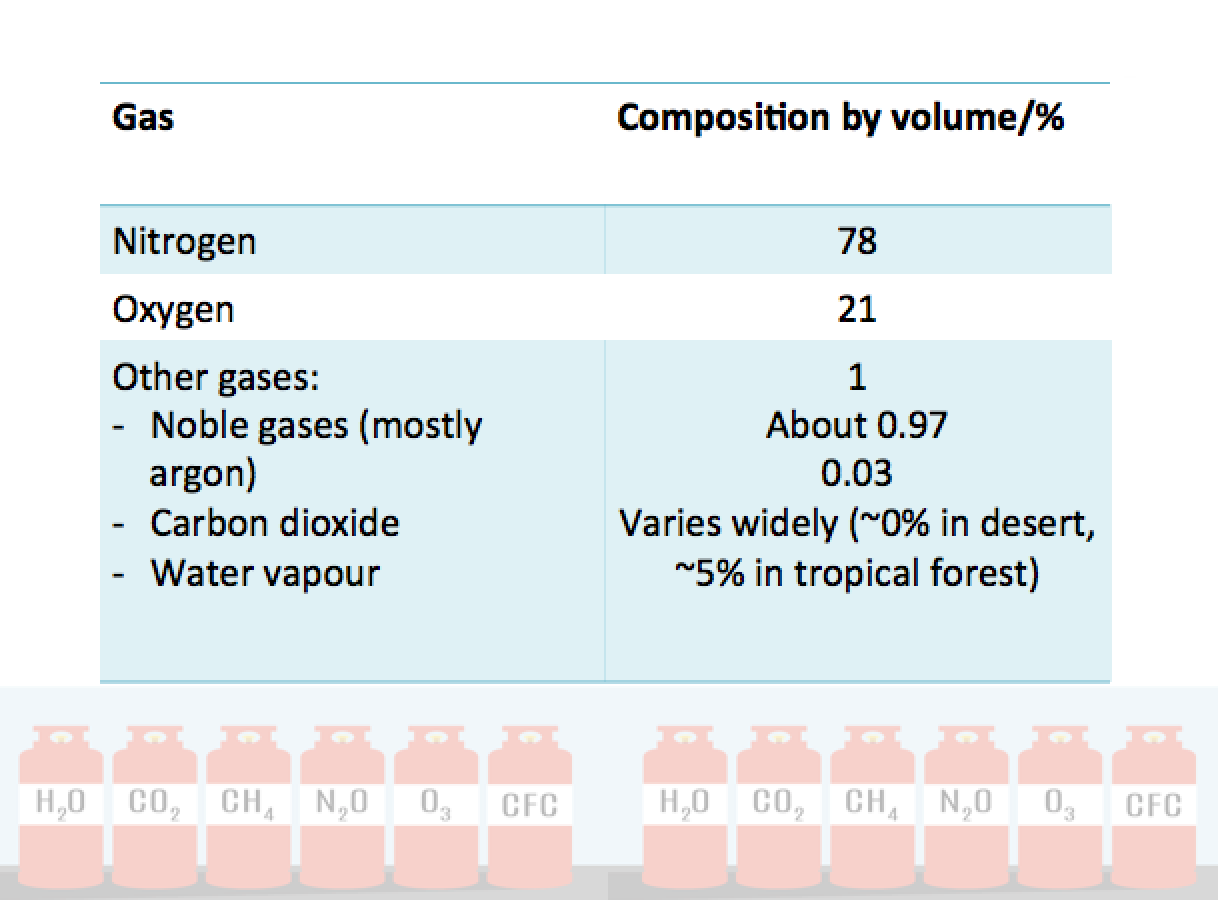
What does air consist of?
Air is a mixture of several gases. It contains elements and compounds. Its composition varies from time to time and place to place. The table below shows the composition by volume of gases in a typical sample of clean, dry air.
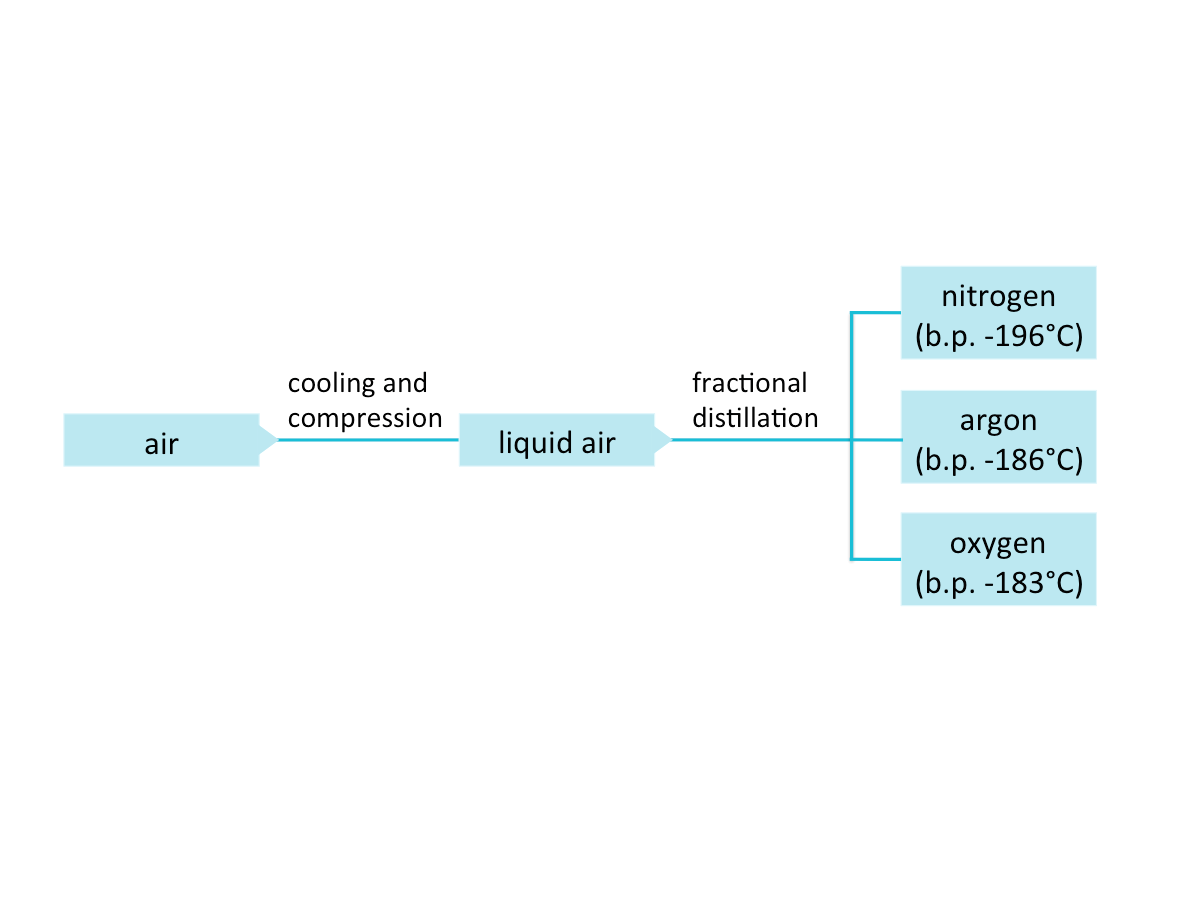
How can we separate air into its constituent gases?
Air can be separated into its constituent gases by the fractional distillation of liquid air. Air is first cooled and compressed into a liquid, which is then separated into fractions by fractional distillation. In fractional distillation. the liquid with the lowest boiling point distils over first.
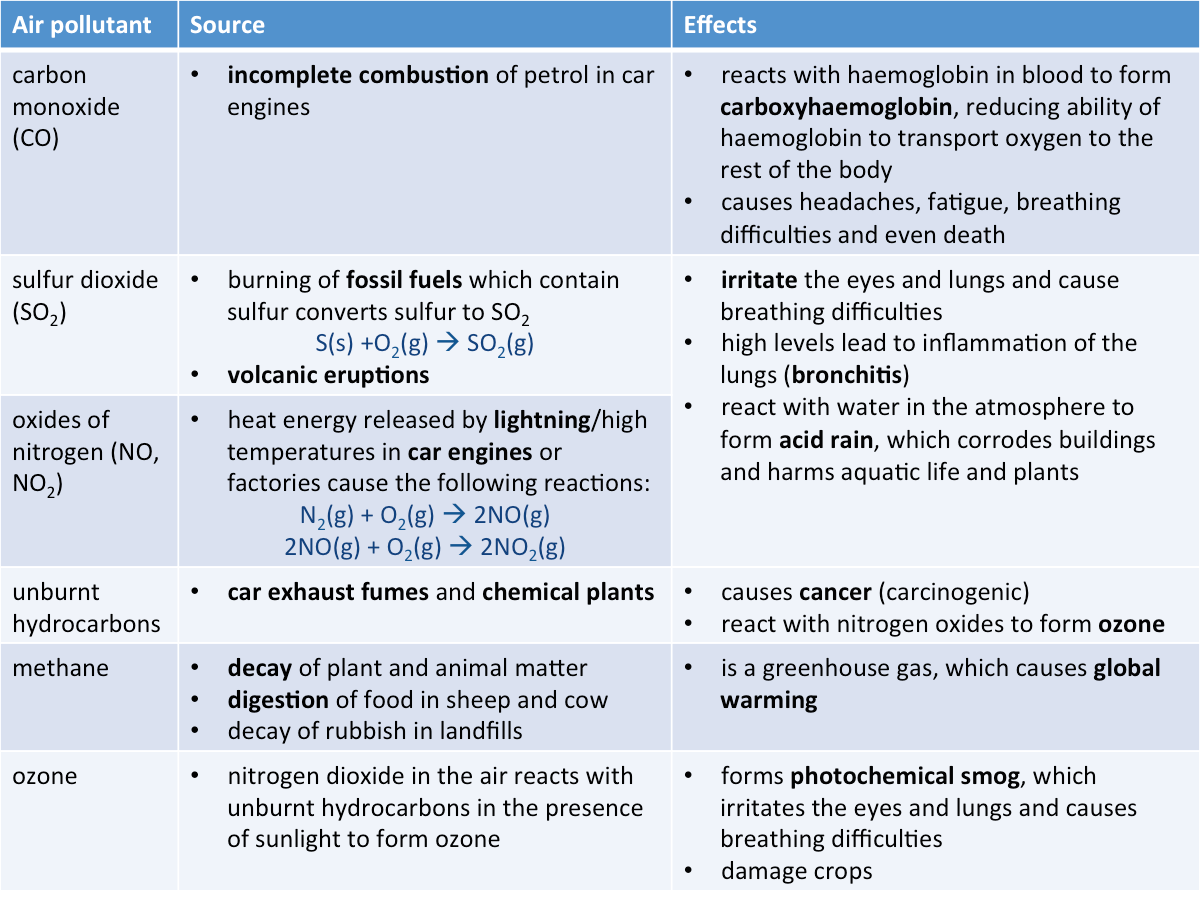
Sources and Effects of Air Pollutants
Air pollution is the condition in which air contains a high concentration of chemicals that may harm living things or damage non-living things.
The table below shows the sources and effects of some common air pollutants.
Formation of Acid Rain
Click on the numbers below to find out more about how acid rain is formed!
Effects of Acid Rain
The figure below summarises the effects of acid rain.
The Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle is the mechanism that maintains the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Watch the video below to learn more about the carbon cycle.
The Carbon Cycle (cont.)
To maintain a constant amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, the rate of removal of carbon dioxide must be balanced by the rate of return of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere.
The table below shows the processes involved in the carbon cycle.
The Greenhouse Effect
Carbon dioxide and water vapour allow visible radiation from the Sun to reach the Earth surface, but trap some of the infrared radiation emitted by the Earth. Heat energy is thus retained in the atmosphere, producing a warming effect called the greenhouse effect.
Greenhouse gases are gases that trap radiation. Some examples of greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and water vapour. Without these greenhouse gases, the Earth surface temperature would be around -40
Global Warming and its Consequences
Global warming is the increase in the Earth average temperature due to the build-up of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The possible consequences of global warming are shown below.