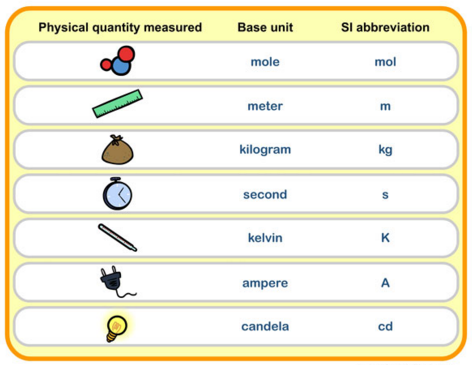
Base Quantities, SI Units and Symbols
A physical quantity is a quantity that can be measured, and consists of a numerical magnitude and a unit.
Length, metre (m) (ruler)
Time, second (s) (digital/analogue clocks)
Mass, kilogram (kg)
Temperature, kelvin (K)
Electric current, ampere (A)
Amount of substance, mole (mol)
Luminous intensity, candela (cd)
Volume of Irregularly-shaped Objects
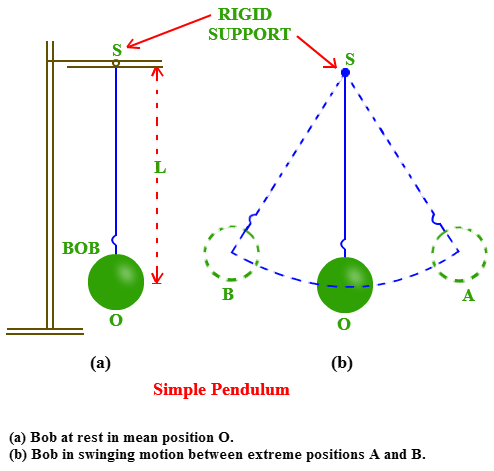
Period, T
A period is the time taken to complete one full oscillation.
Independent of: amplitude of oscillation and the mass of the bob
Dependent on: length of the pendulum and the acceleration due to gravity
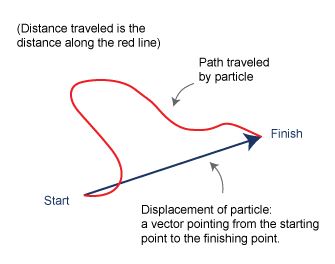
Definition of Displacement VS Distance
Displacement is the measurement of distance from one reference point to another point in a certain direction.
Distance is the total length covered between two points.
Both have SI unit: metre (m).
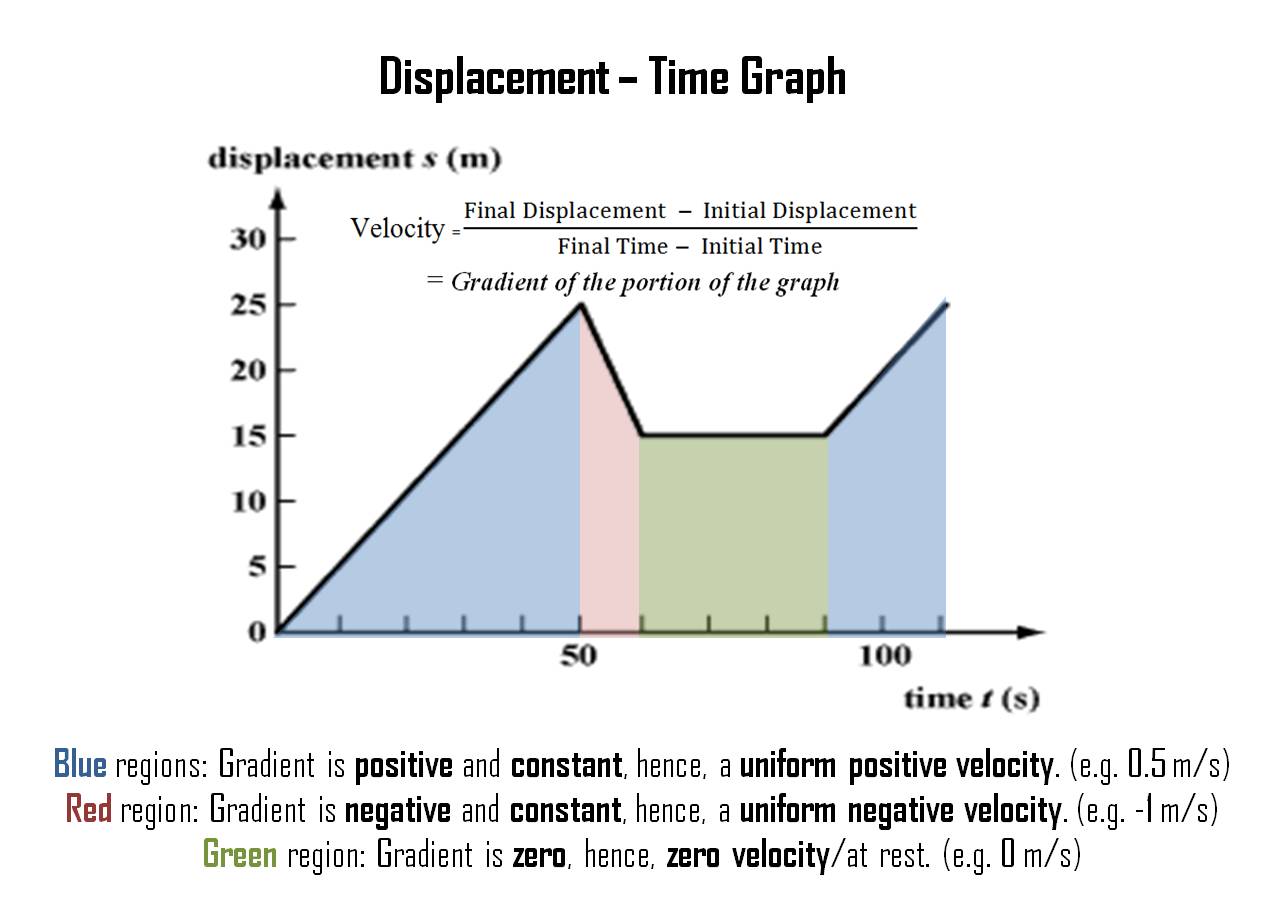
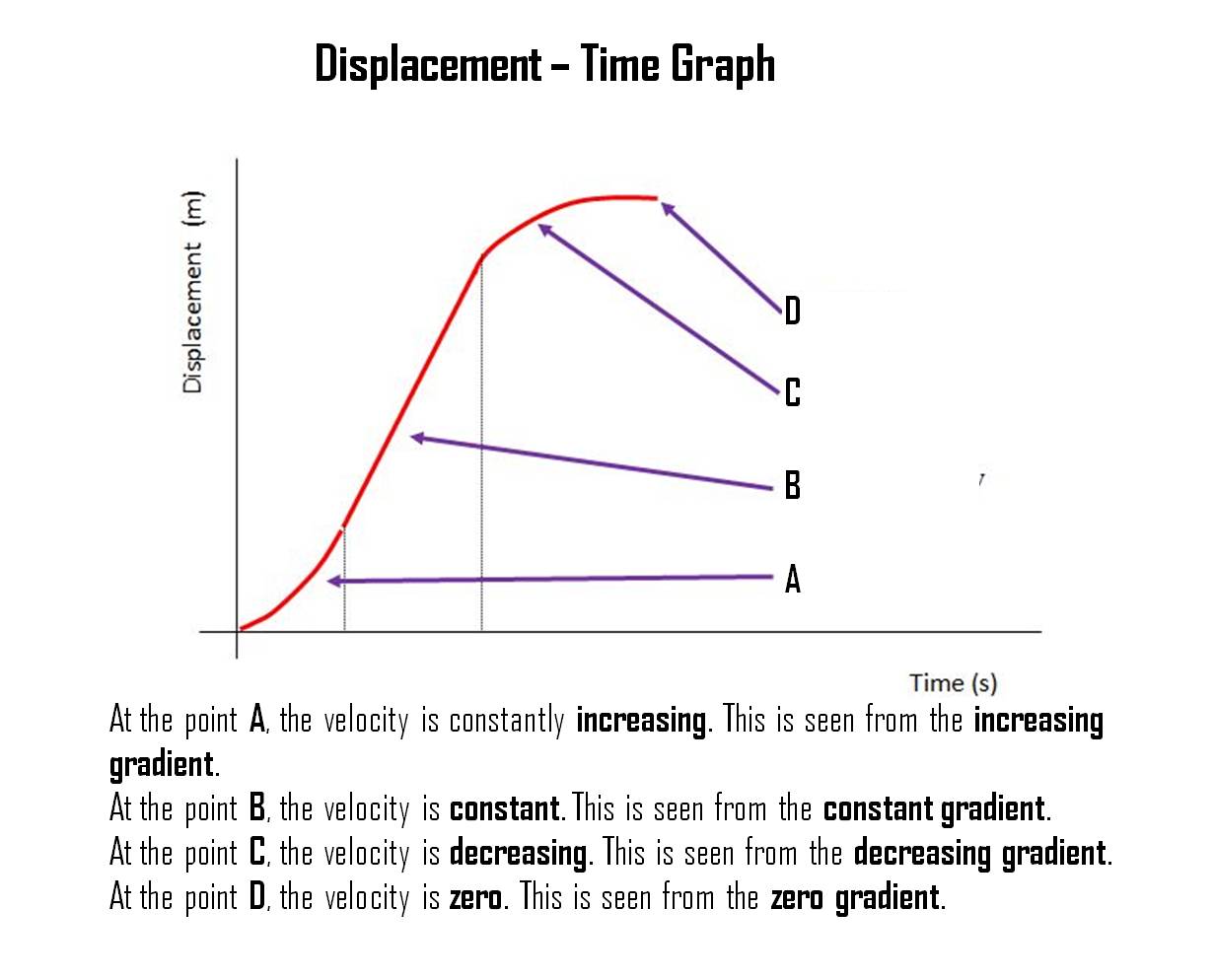
Understanding a Displacement-Time Graph
Looking at the graph below, do you know how to explain it? Study the diagram below.
Understanding a Displacement-Time Graph (2)
The diagram below shows another type of displacement-time graph. Notice how the gradient at each point of the graph indicates the velocity of the object.
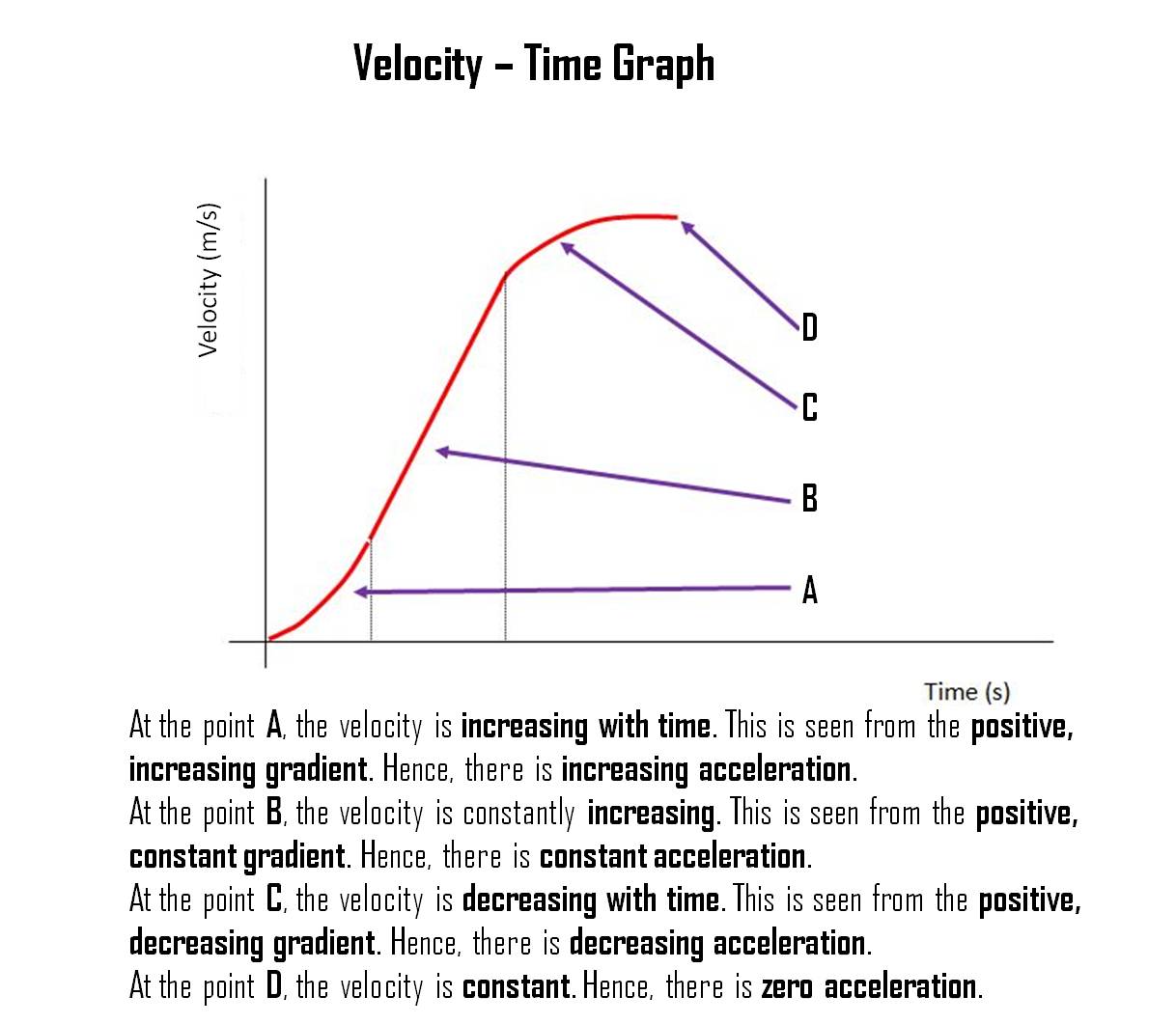
Understanding a Velocity-Time Graph
Looking at the graph below, do you know how to explain it? Study the diagram below.
Understanding a Velocity-Time Graph (2)
The diagram below shows another type of displacement-time graph. Notice how the gradient at each point of the graph indicates the acceleration of the object.
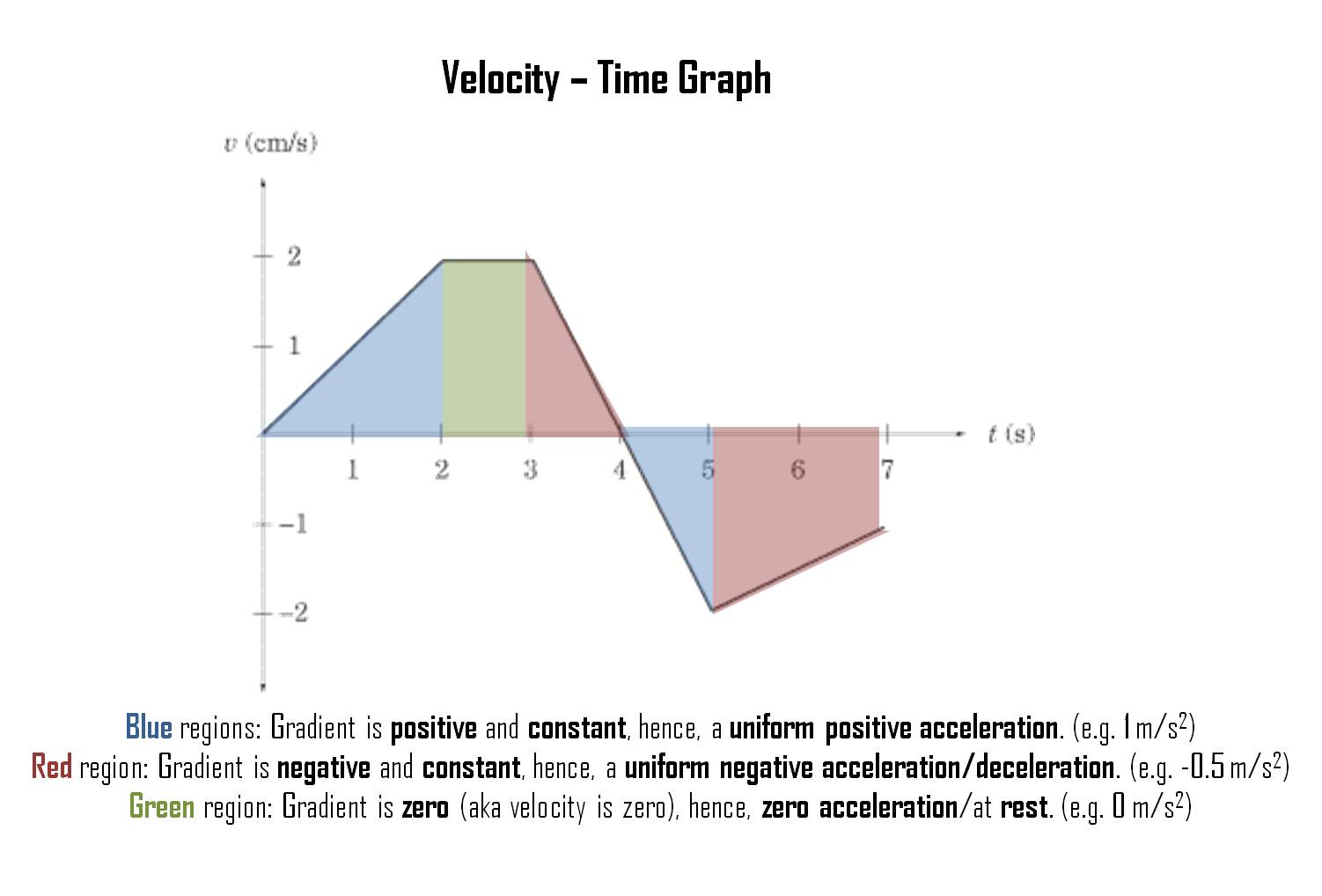
How to Understand the Graphs
Graphs of motion:
What do the gradients mean?
What do the areas under the graphs represent?
Definition of Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. It is seen in this formula:
ACCELERATION = FINAL VELOCITY - INITIAL VELOCITY/TIME
if it is deceleration, the final value will be a negative
SI unit: metre per square second (ms^-2).
Try out the question to test your understanding:
Force and Motion Interactive Tools
Newtons Laws are applied regularly in our daily lives. Use the interactive tool below to see some examples of how they are applied.
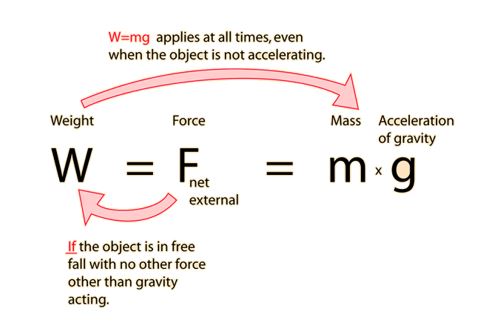
Weight
Weight is a force action on any object with mass.
Formula for weight: W = mg where W = weight, m = mass of object, g = acceleration due to free fall.
What is Mass, m
The mass of an object is a measure of the amount of matter in the object.
Mass is the amount of matter in an object
What is Gravitational Field Strength, g
Gravitational field strength is the gravitational force acting per unit mass.
Formula of gravitational field strength (g):
= gravitational force (Fg) / mass (m)
*note that g measured on the surface of the Moon is only one-sixth of that of the Earth.
What is Weight
Weight is the gravitational force acting on an object.
Difference between Weight and Mass
May the following video provide you guys with a simplified explanation!
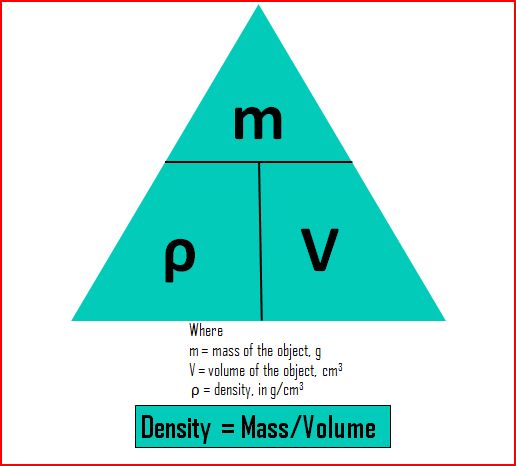
What is Density
Density of an object is its mass per unit volume.
What Happens to Objects with Density Less/More than that of Water?
An object that is denser than water would sink while one that is less dense than water will float when placed in the water.
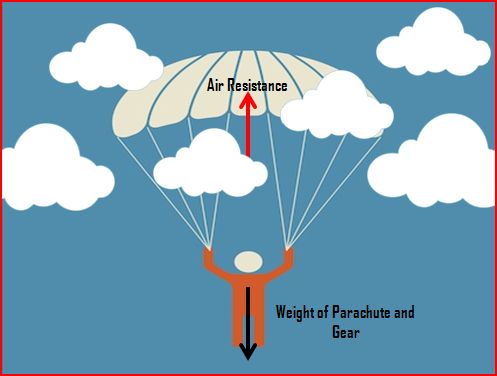
Air Resistance
Air resistance refers to a frictional force that opposes the motion of moving objects as a result of friction with the surrounding air. It increases with the speed of the moving object and also the surface area. Similarly, increasing the density of air increases air resistance. It is also known as the drag force, and the drag force changes with the different media that the object is travelling in.
Newton
Newtons First Law states that an object will continue in its state of rest or uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force.
When forces are balanced, the velocity of an object is constant.
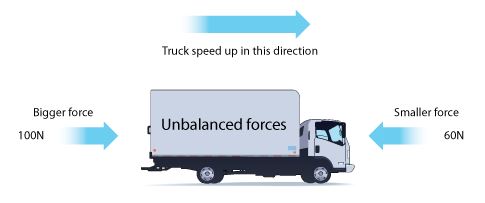
Effects of Unbalanced Forces
When forces are unbalanced, acceleration is non-zero and velocity is not constant.
Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
When forces are balanced, the is no movement of the object. However, an imbalance in the forces would lead to movement.
[Supplementary] Hooke Law
When an elastic object such as a spring is stretched, the increased length is called its extension. The extension of an elastic object is directly proportional to the force applied to it:
F = k x
F is the force in newtons, N
k is the spring constant in newtons per metre, N/m
x is the extension in metres, m
This equation works as long as the elastic limit (the limit of proportionality) is not exceeded. If a spring is stretched too much, it will not return to its original length when the load is removed.
Friction
Friction is a force that opposes motion between two objects in contact.
Friction is a force that opposes the motion of 2 objects in contact
Using velocity-time graphs to find the resultant force
In the previous chapter, we used a velocity-time graph to determine the acceleration of a moving object. (Remember: Gradient = acceleration). Consequently, using the formula F = ma, we can also derive the resultant force exerted by the object.
Look at the diagram below, assuming that the velocity at t = 2s, the acceleration is 1 m/s^2. Assuming that the object is a ball of 10g is rolling at that force, the resultant force is 10 x 1 = 10N.
Ways to Reduce Friction
Use ball bearings, use lubricants (such as oil and grease), or designing the shape of the vehicle to be streamlined.
Friction Interactive Tool
As mentioned, friction is the force that opposes motion. When two objects are rubbed together you produce heat as a result of the friction that exists between both objects. Use the interactive tool below to understand how this worls.
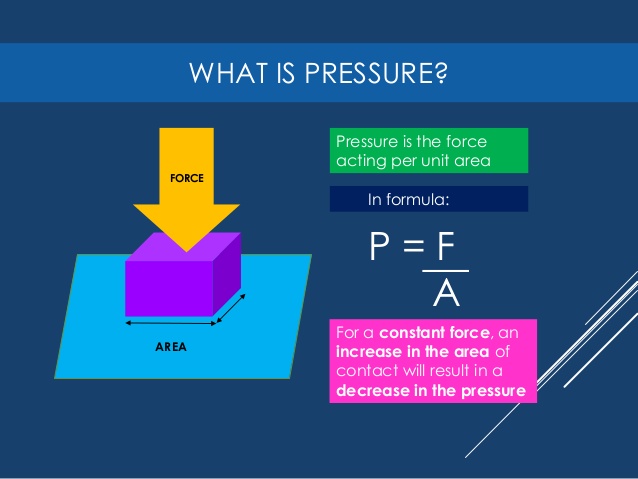
What is Pressure, p?
Pressure is the force acting on a surface divided by the area of the surface.