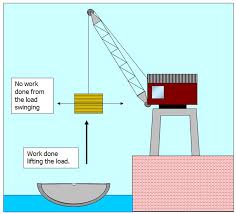
What is Work Done, W?
Work done on an object is the product of the force acting on the object and the distance travelled by the object in the direction of the force.
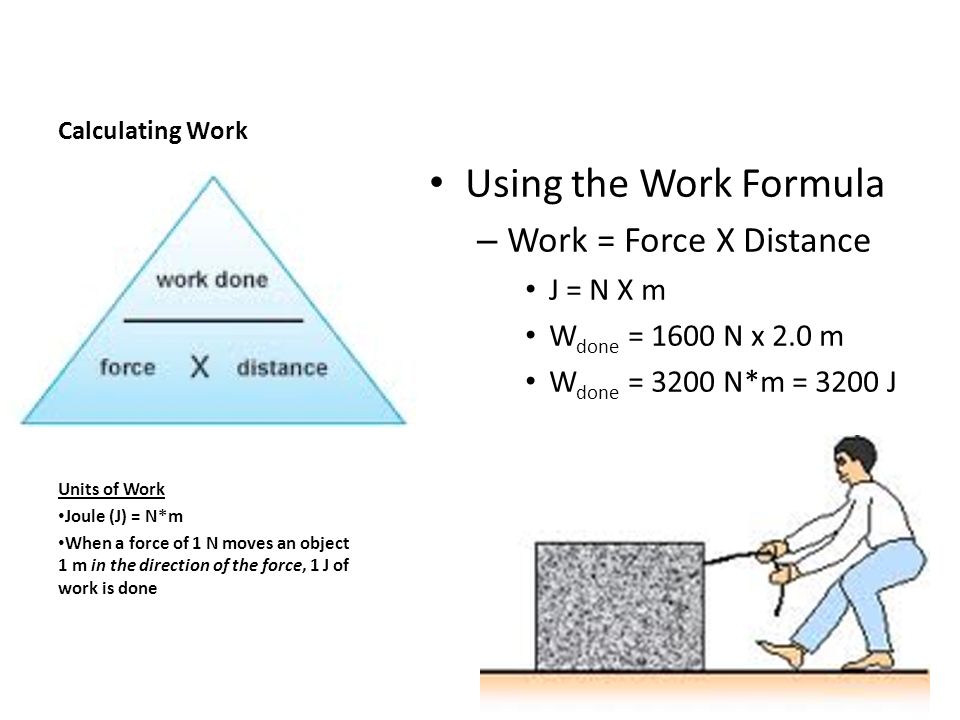
[Supplementary] Work Done formula + Example
Formula of work done:
W = F (Force) x d (Distance)
SI unit: Joules (J)
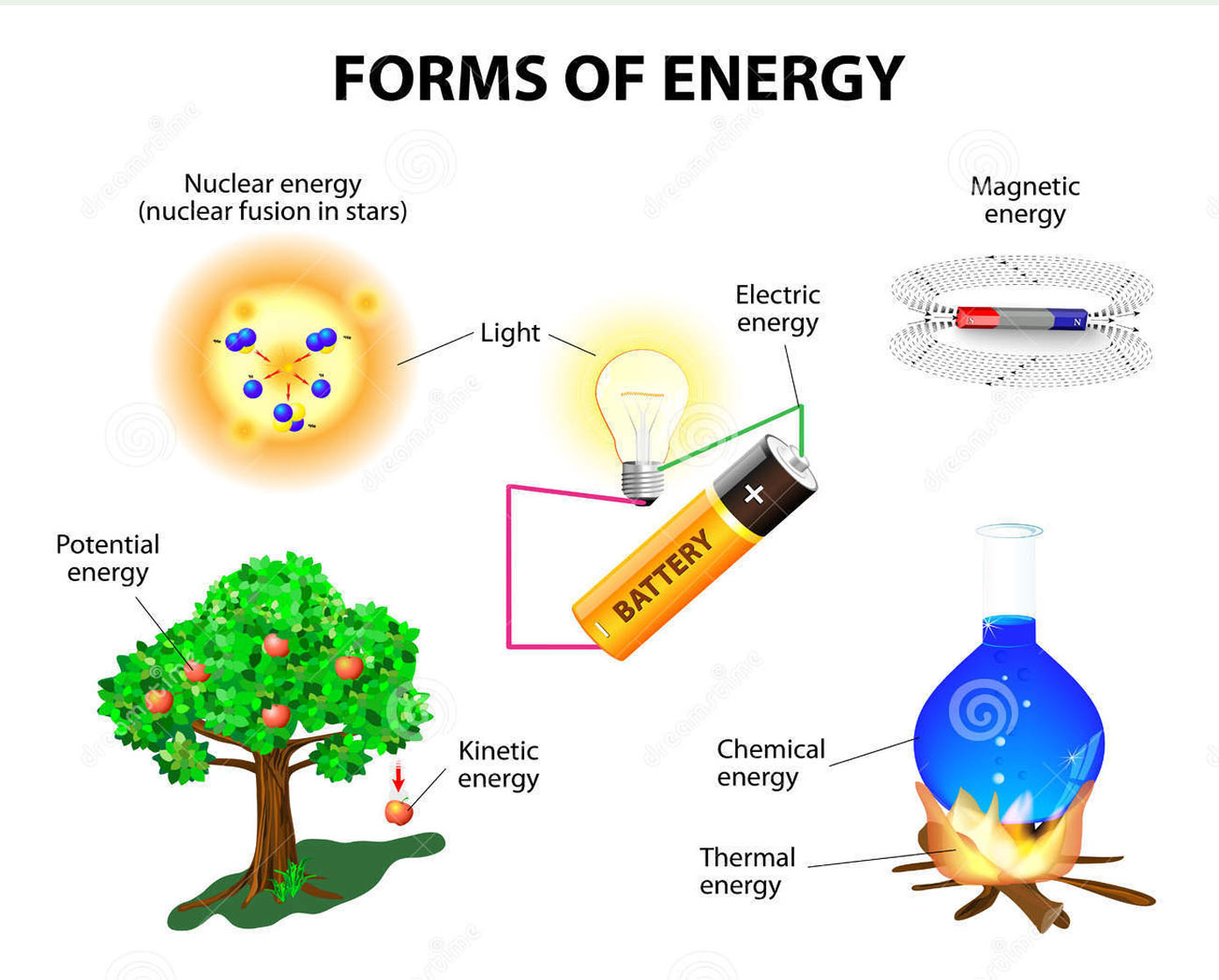
What is Energy
Energy is the ability to do work. Energy is transferred when work is done. An object may have energy due to its motion (kinetic energy, K.E.) or its position (potential energy, P.E.). Energy may be transferred and stored.
Types of Energy
Identify examples of changes in kinetic, gravitational potential, chemical potential, elastic potential (strain), thermal, sound and electrical potential energy that have occurred as a result of an event or process 5 Recognise that energy is transferred during events and processes, including examples of transfer by forces (mechanical working), by electric currents (electrical working), by heating and by waves.
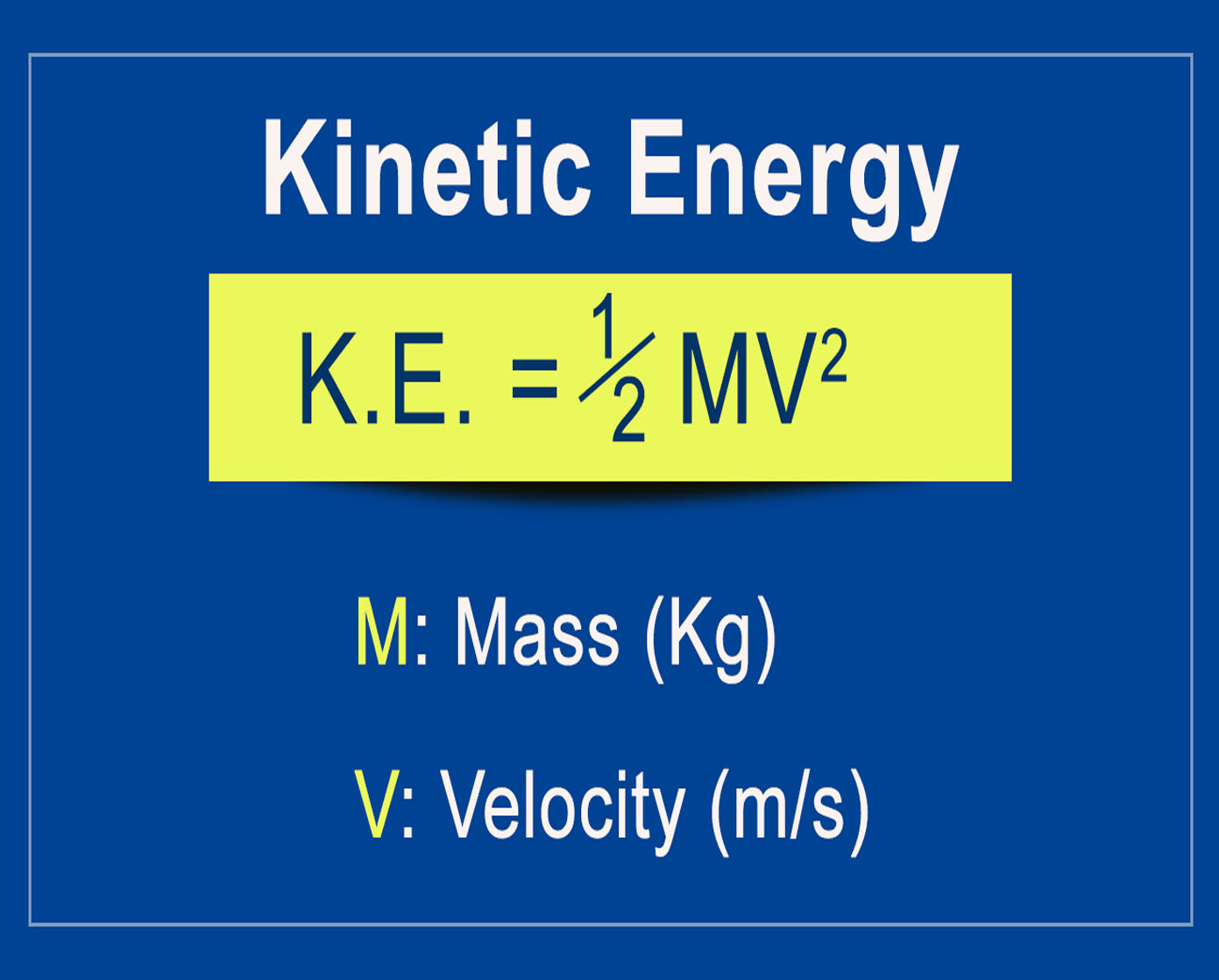
[Supplementary] Kinetic Energy formula
Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion.
Formula of kinetic energy:
Ek = 1/2 mv^2
SI unit: Joules (J)
[Supplementary] Gravitational Potential Energy formula
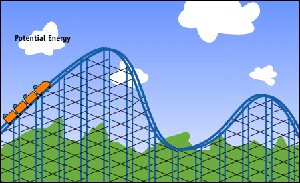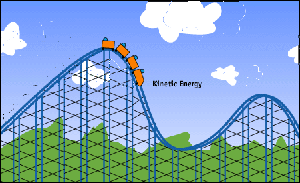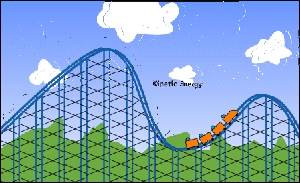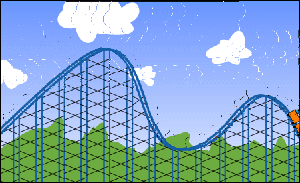
Gravitational potential energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its position in a gravitational field.
Formula of gravitational potential energy: Ep = mgh
Ep = mgh
SI unit: Joules (J)
Potential and Kinetic Energy
How does the amount of kinetic or potential energy vary with the amount of force that is applied to an object? Use the intractive tool to find out!
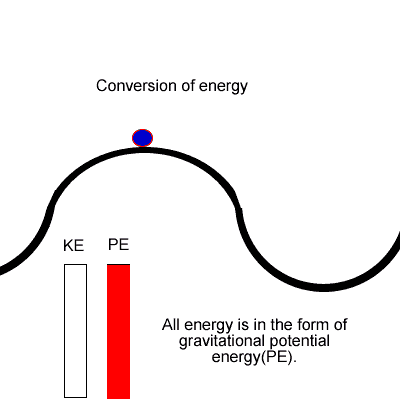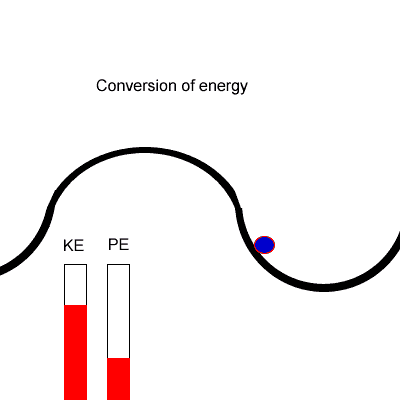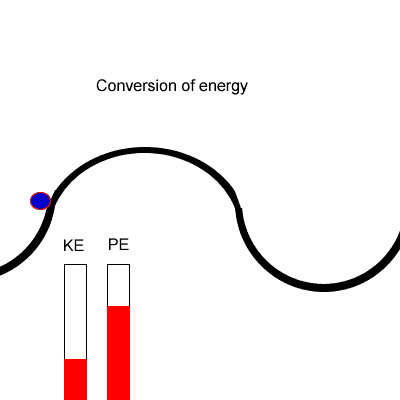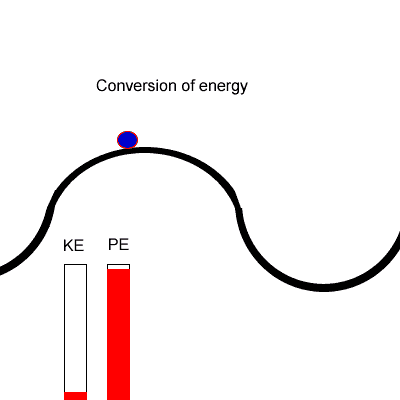
What is Principle of Conservation of Energy?
The Principle of Conservation of Energy states that the total amount of energy in an isolated system is constant.
Principle of Conservation of Energy
In other words, Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be converted from one form to another.
What is Power, P?
Power is the rate of work done.
Formula of power: P = W/t = E/t SI unit: Watt (W)
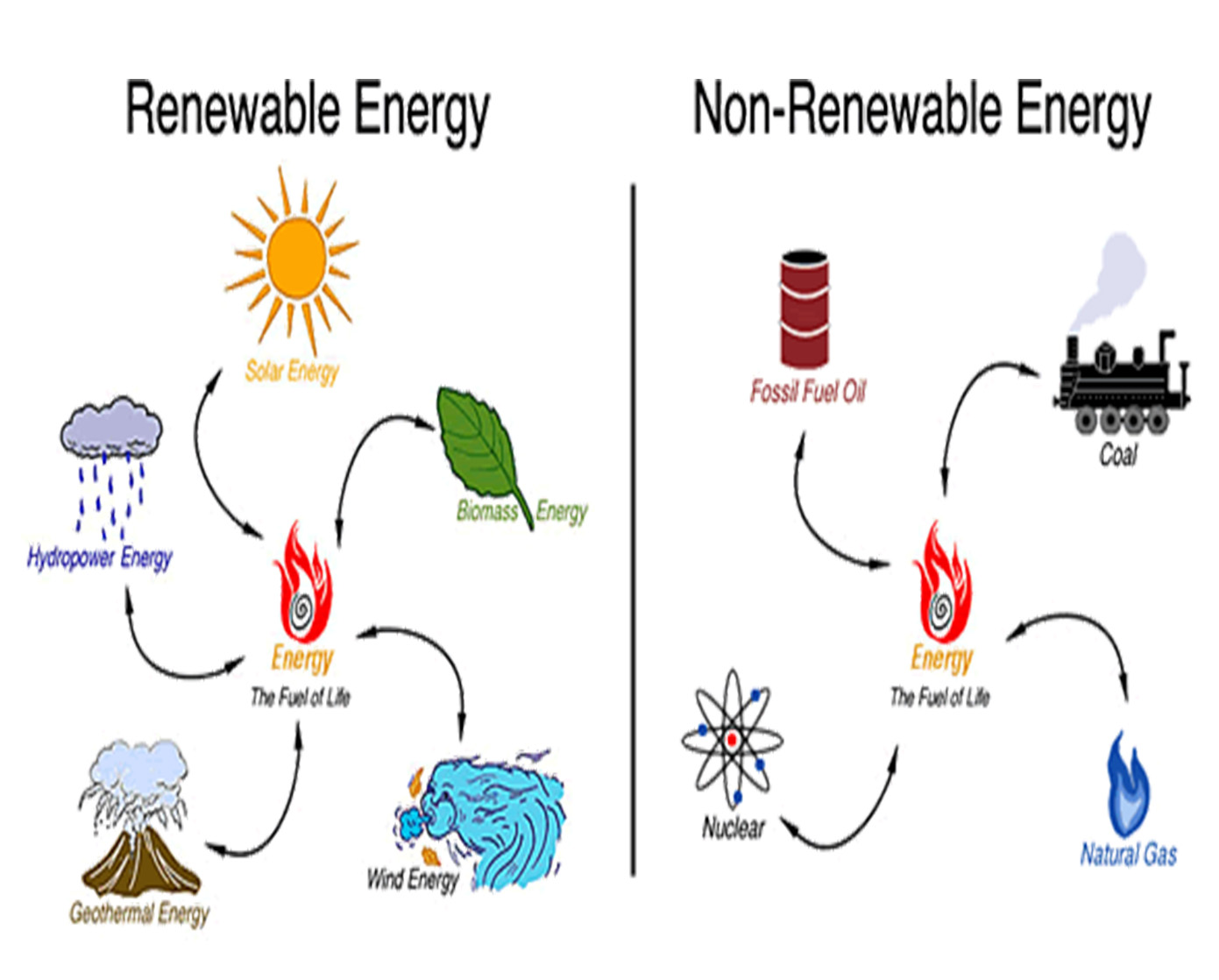
Renewable vs non-renewable resources
Renewable sources of energy, just like it sounds, are resources that theoretically can be used for ever if used at a rate which is consistent with the rate in which it is replenished. Examples include solar, wind and water energy. Every day, the sun comes out and we can indefinitely use its energy
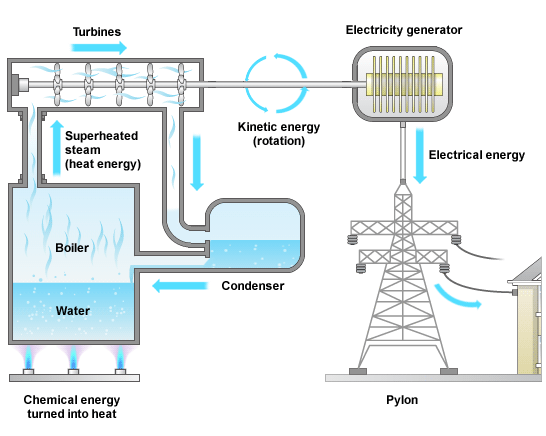
Chemical Energy Stored in Fuels
1. Burn the chemical fuel to produce heat.
2. The heat is then used to heat a liquid such as water which is then turned into steam.
3. The pressure from the steam is used to spin a turbine, and it is this spinning that produces electricity.
Advantages:
Ready made and available
Relatively cheap
Disadvantages:
Gives off pollutants which can be damaging to the environment
Non-renewable
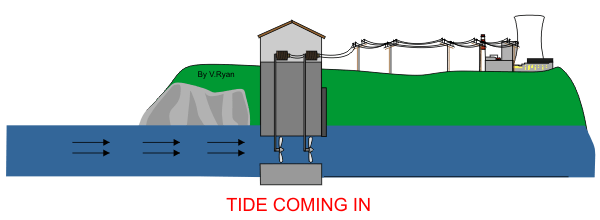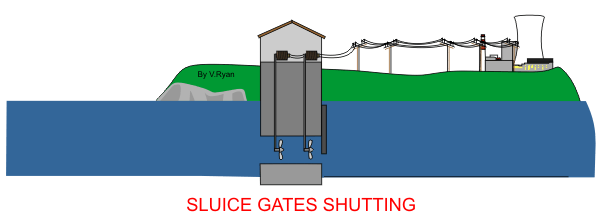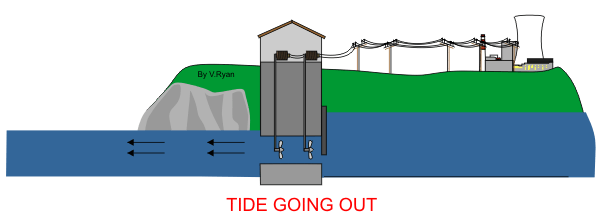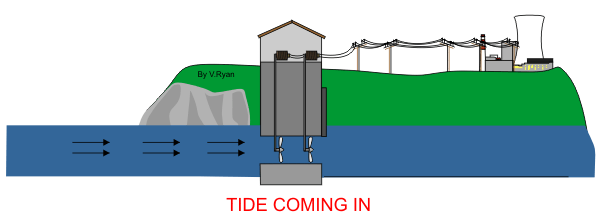
Tides and waves
1. Underwater turbines spin like windmills
2. The turbines are mounted on a gearbox shaft, which generated electricity.
3. Underwater cables then help carry the electricity to the shore.
[Supplementary] The main source of tidal energy is the moon.
Advantages:
Has potential to generate alot of energy
Very reliable as it is quite easy to predict when is there going to be a low and high tide
Renewable, so can be continued to be used for a long time
Little environmental impact
Disadvantages:
Initial costs of building dams are extremely high.
Affects transportation system in the water.
Affect ecosystem surrounding the dam.
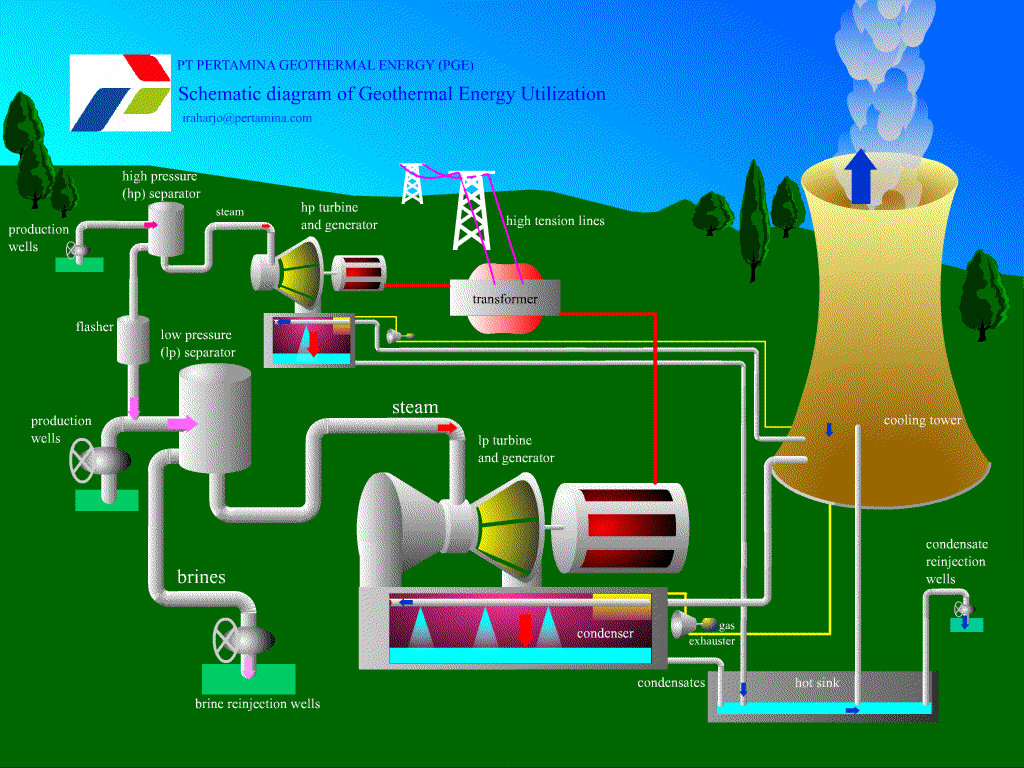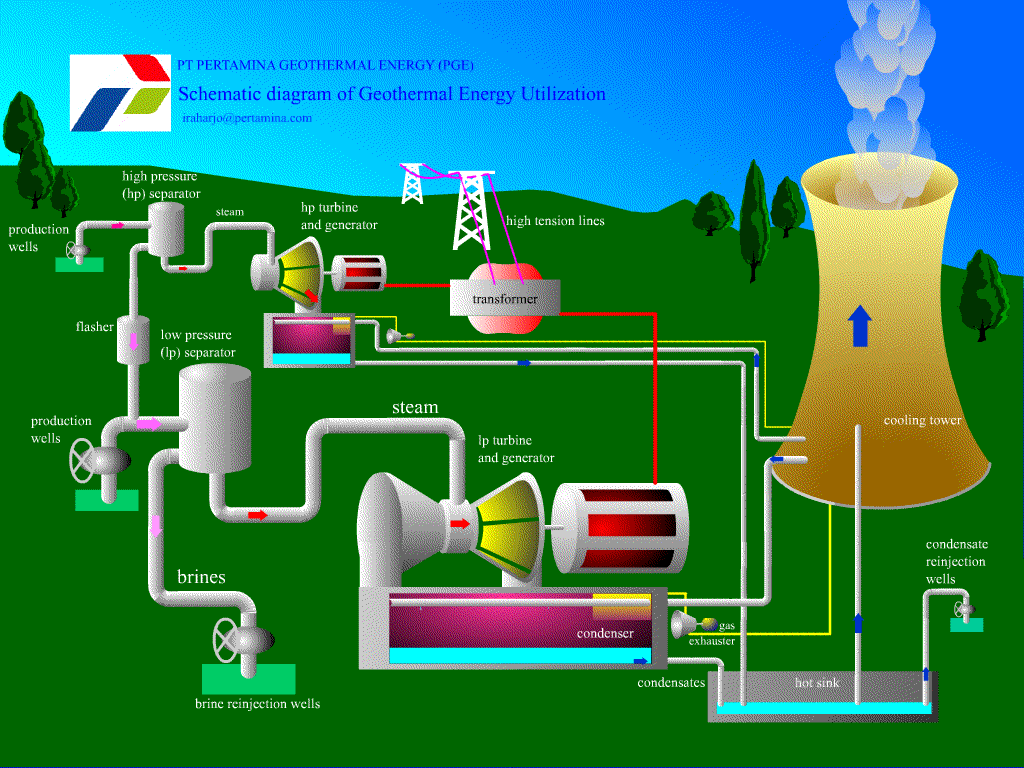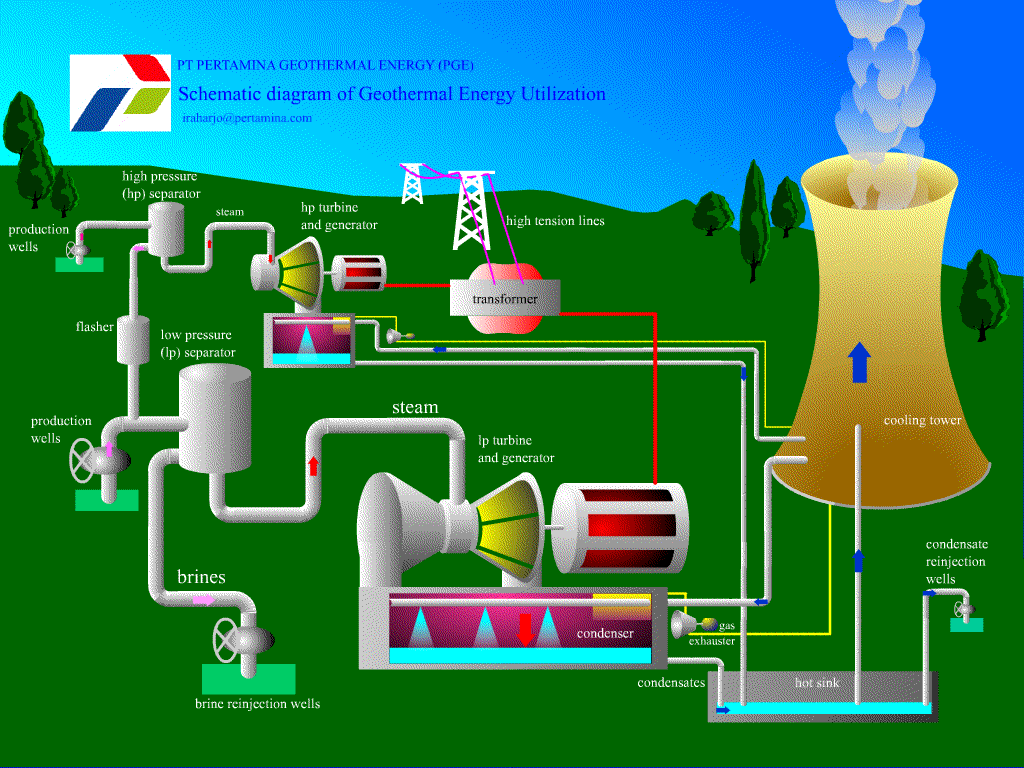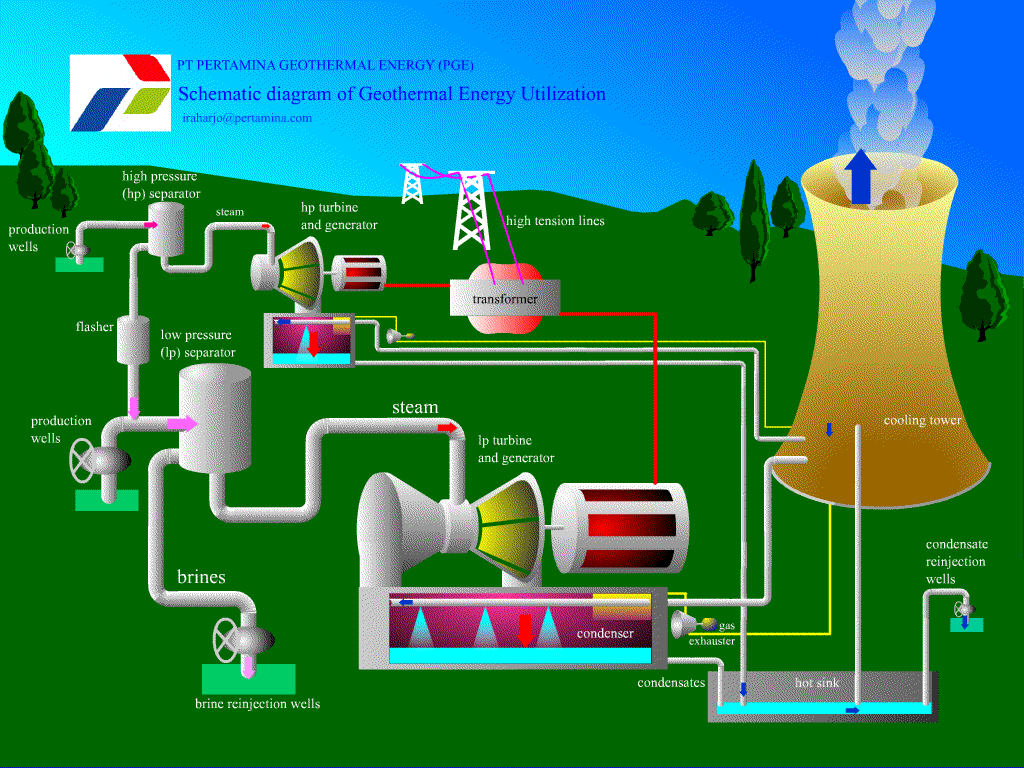
Geothermal Resources
1. Possible to use the natural heat of the earth to generate electricity.
2. Cold water is first pumped underground.
3. The cold water then comes out as steam.
4. This steam can be used for heating or powering turbines to create electricity.
Advantages:
Potentially unlimited supply of energy.
Little impact on the environment.
Renewable
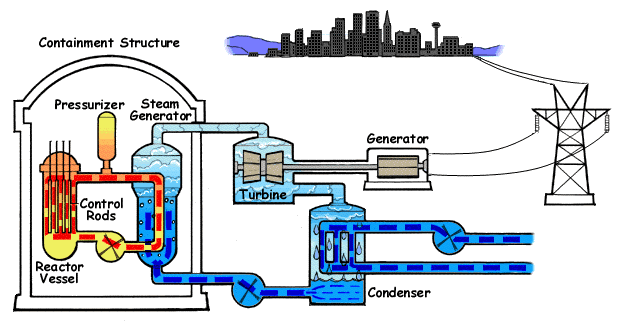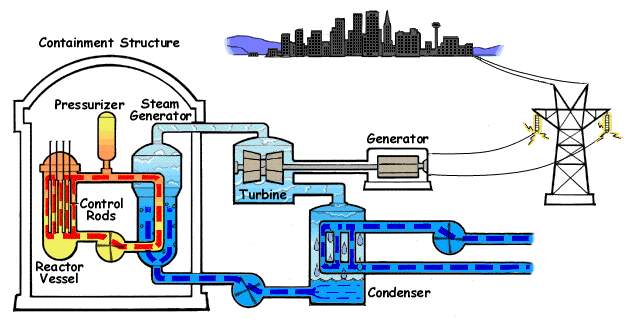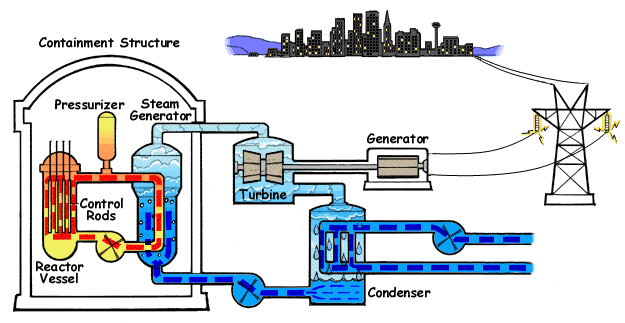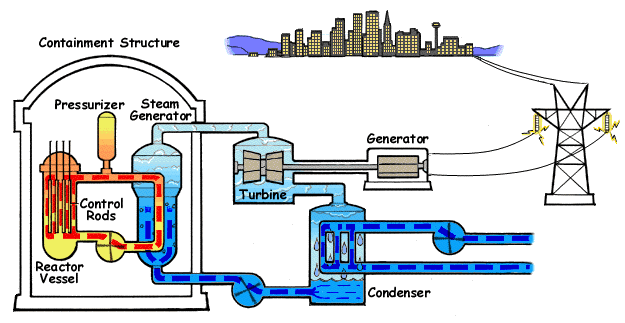
Nuclear Fisison
Electricity can be generated through nuclear fission. During nuclear fission, energy is released, and electricity can be produced in the Nuclear Reactors.
Advantages:
Small amount of radioactive material can release a lot of energy
Relatively cheap
Can last a long time
Doesn
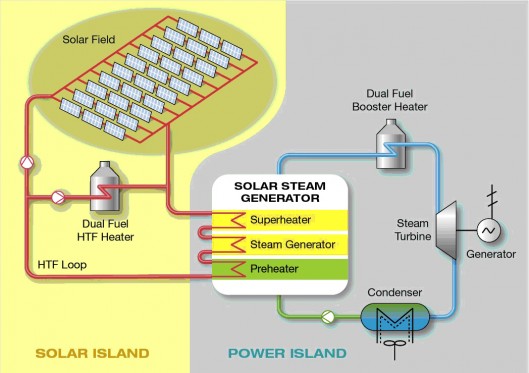
Heat and Light from the Sun
Heat from the sun is trapped in solar panels and subsequently converted into electricity.
Advantages:
Potentially infinite supply of energy
Little environmental impact
Renewable
Disadvantages:
May be costly to install solar panels.
Solar panels may only produce very hot water in very sunny climates, and in cooler areas may need to be supplemented with other energy resources.
Solar panels do not work at night and are subjected to weather conditions eg cloudy days.
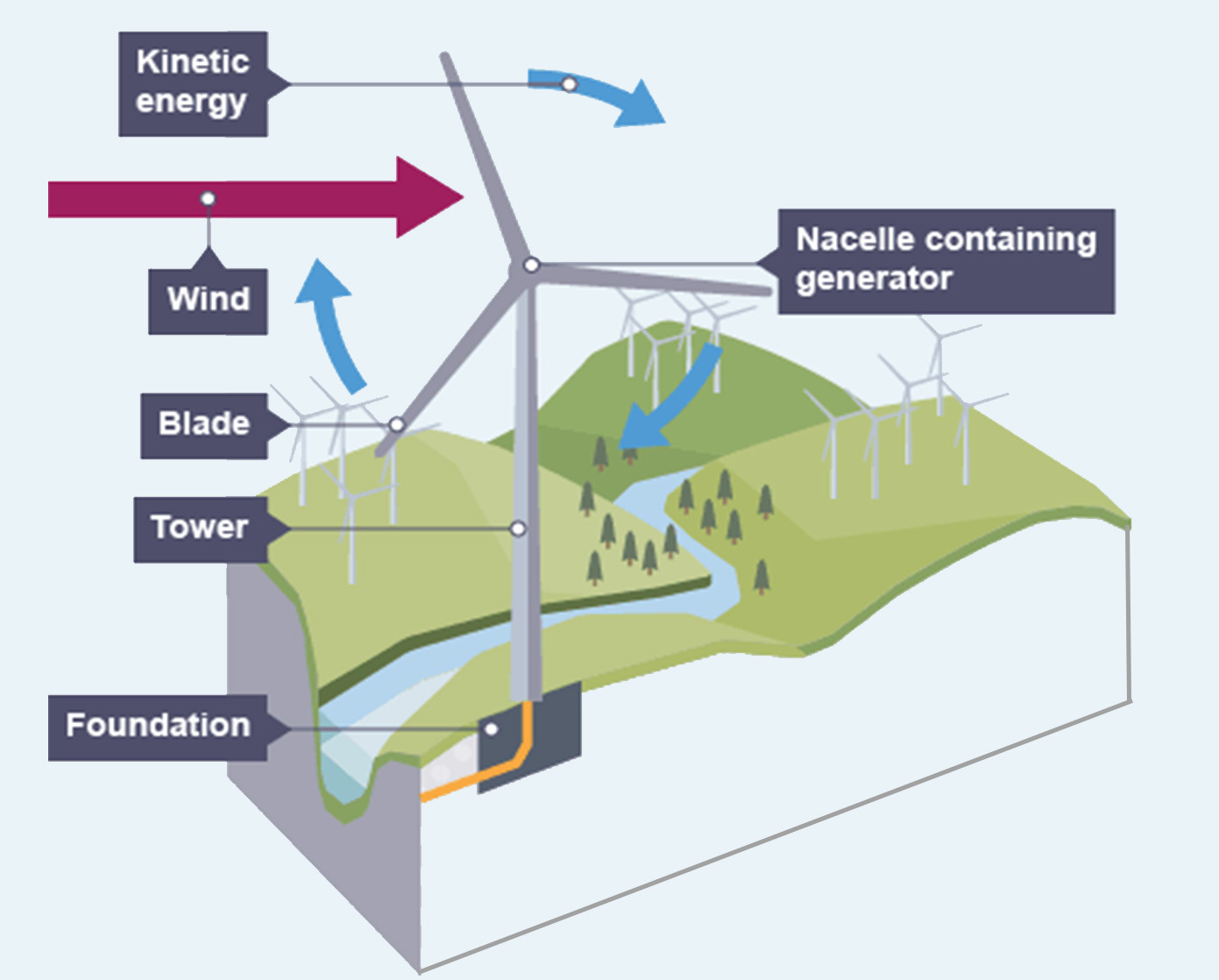
Wind Energy
Wind is produced as a result of giant convection currents in the atmosphere, which are driven by heat energy from the Sun. This means that the kinetic energy in wind is a renewable energy resource - as long as the Sun exists, the wind will too.
Wind turbines use the wind to drive turbines directly. They have huge blades mounted on a tall tower. The blades are connected to a nacelle, or housing, which contains gears linked to a generator. As the wind blows, it transfers some of its kinetic energy to the blades, which turn and drive the generator. Several wind turbines may be grouped together in windy locations to form wind farms.
Advantages:
Wind is a renewable energy resource and there are no fuel costs.
No harmful polluting gases are produced.
Disadvantages:
Wind farms are noisy and may spoil the view for people living near them.
The amount of electricity generated depends on the strength of the wind.
If there is no wind, there is no electricit