Kinetic Theory of Matter (1)
Definition of the Kinetic Model of Matter: The Kinetic Model of Matter states that the tiny particles that make up matter are always in continuous random motion.
Particles are in constant random motion
Kinetic Theory of Matter (2)
Let
Kinetic Theory of Matter (3)
Comparison of the properties of different states:
What is Brownian Motion
Brownian motion is the continuous random motion of small particles in fluid or gas.
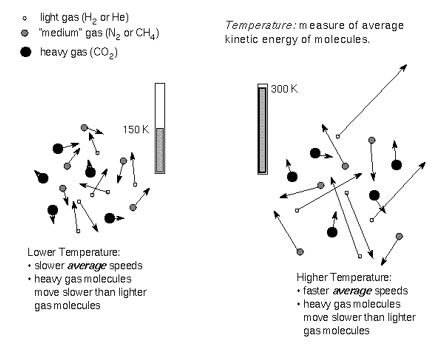
How Temperature Affects the Speed of Particles
If temperature increases, gas particles move at higher speeds. Increasing temperature increases the kinetic energy of each individual particle. This increases the speed at which each molecule travels at.
Relationship between pressure and temperature of a gas
The pressure of a fixed mass of gas is directly proportional to its temperature, assuming that volume is constant. This law is also known as the Gay-Lussacs
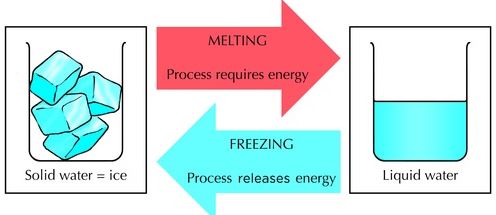
Definition of Melting and Boiling
Melting is the process in which a substance absorbs thermal energy to change from a solid state to liquid state, at a fixed temperature. When a solid melts, it changes from the solid to the liquid state at a certain temperature known as its melting point.
Boiling is the process in which a substance absorbs thermal energy to change from a liquid state to gaseous state, at a fixed temperature. When a liquid boils, it changes from liquid to the gaseous state at a certain termperature known as the boiling point.
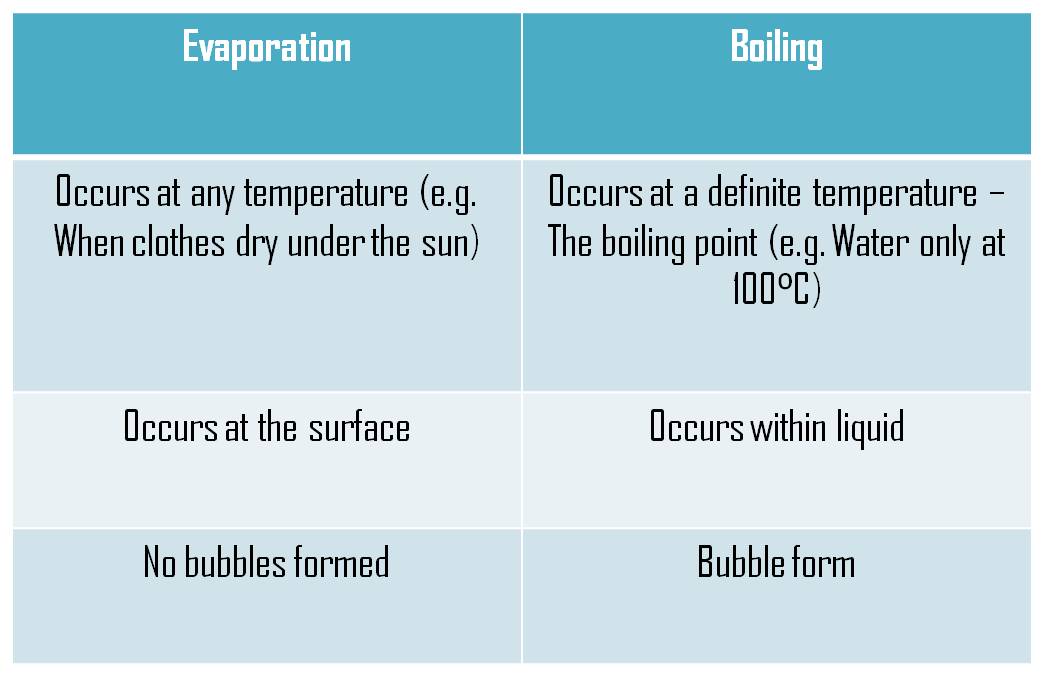
Difference between Boiling and Evaporation
The video below explains boiling, evaporation and vaporisation. How are they different?
Table of differences between boiling and evaporation
Below is a table that states the differences between boiling and evaporation
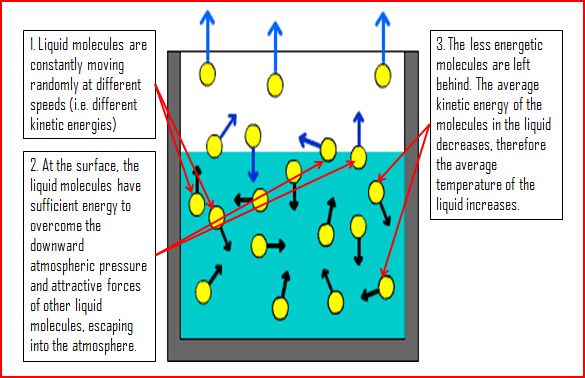
Explain Evaporation by the Kinetic Theory
The diagram below explains evaporation via the kinetic theory.
What is a Thermometer
A thermometer is a device used to measure the temperature of an object. For Liquid-in-glass thermometers, they can contain 2 different liquids: Mercury and Alcohol. The choice of liquid is dependent on the purpose of the thermometer. Mercury thermometwrs have a smaller range and therefore, can be used oto measure a greater range of temperatures. The image below shows an alcohol thermometer.
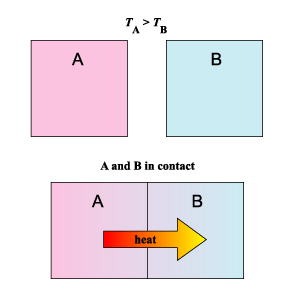
Transfer of Thermal Energy
The transfer of thermal energy or heat always occurs from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature.
Definition of conduction
Conduction is the transfer of thermal energywithout any movement of the medium.
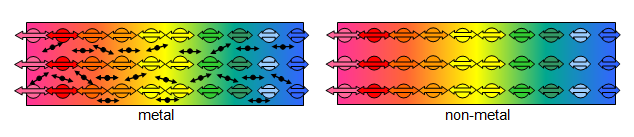
Conduction in solids and metals
In non-metals, collision between neighbouring particles make them vibrate vigorously. The neighbouring region then becomes hot. Thermal energy is transferred without the transfer of particles. In metals, the free electrons gain kinetic energy and move at greater speeds towards cooler regions of the rod. As the move, the collide with atoms, making them vibrate more vigorously. Thermal energy is transferred via the motion of free electrons.
Efficiency in conduction of heat in liquids and gases
In liquids and gases, the particles are spaced farther apart compared with solids. Thus, collision between the particles are less frequent in liquids and gases. Hence they are poor conductors of heat.
Fluids are poor conductors of heat.
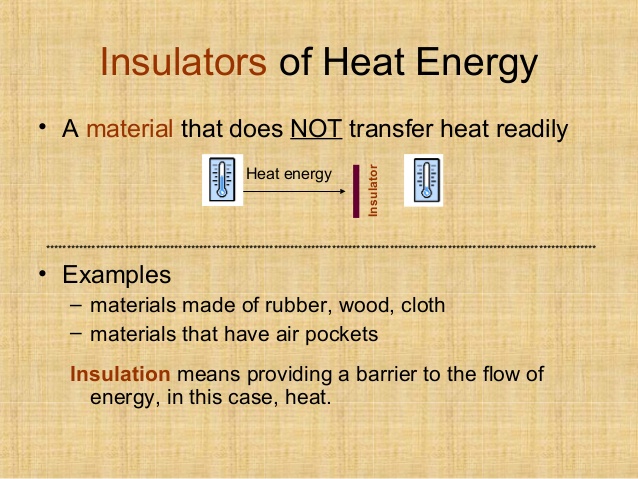
What are Poor Conductors
Poor conductors are also known as insulators.
Uses of insulators
Poor conductors of heat make good materials for coldwear and hot water flasks. They are able to trap air and prevent the quick loss of heat to the environment.
Insulators of heat are mainly used to retain heat (e.g. wool jackets, hot water flasks etc.)
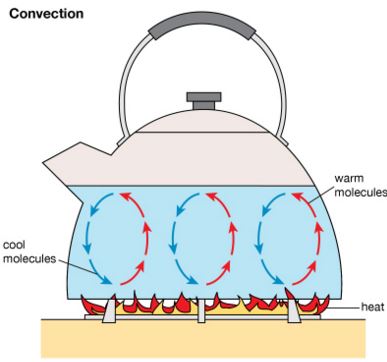
Definition of convection
Convection involves the movement of the fluid particles due to a change in the density of the fluid.
Convection takes place only in fluids i.e. liquids and gases. It requires the bulk movement of fluids that carries the thermal energy.
Convection current arises from a fluid that results from convection.
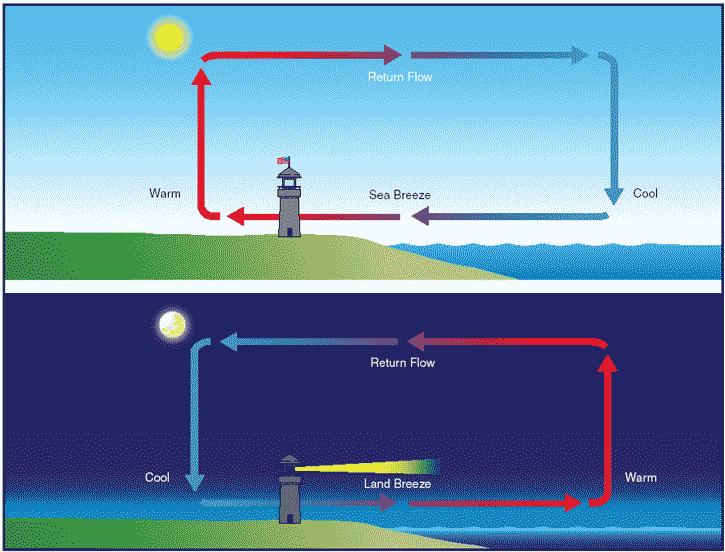
What causes the land and sea breeze?
In the day,the land heats up very quickly and the air above it warms up a lot more than the air over the water. The warm air over the land is less dense and begins to rise. Low pressure is created.
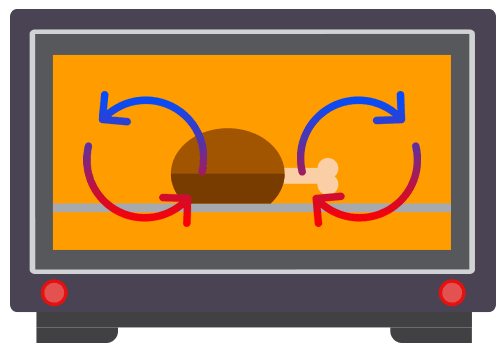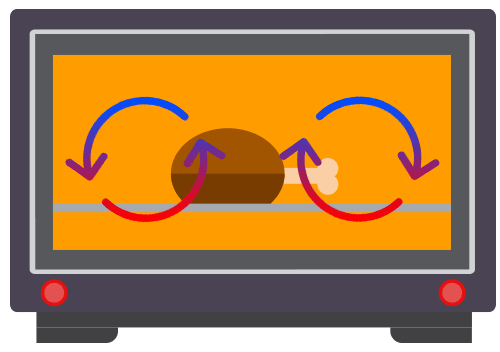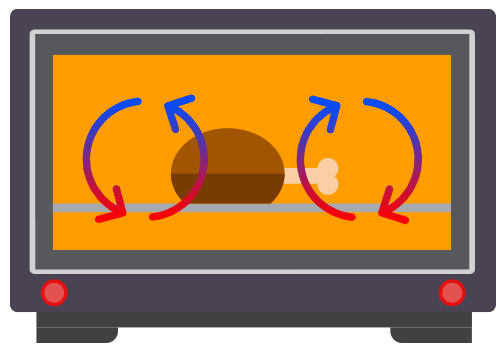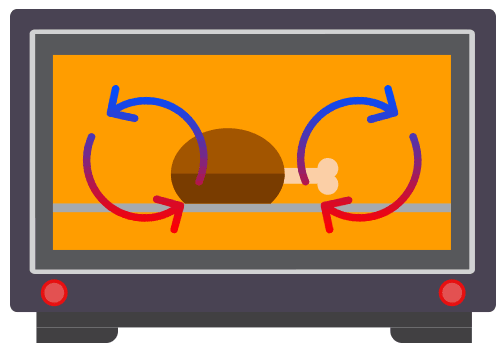
Applications of Convection
Common applications of convection include commonly used in kitchen applicances, such as water heaters, kettles and ovens.
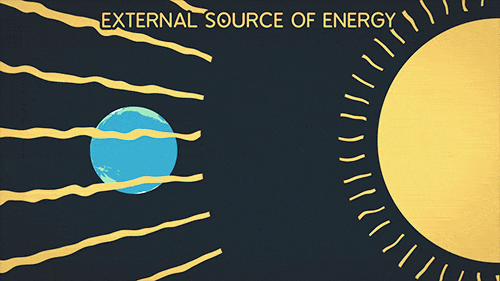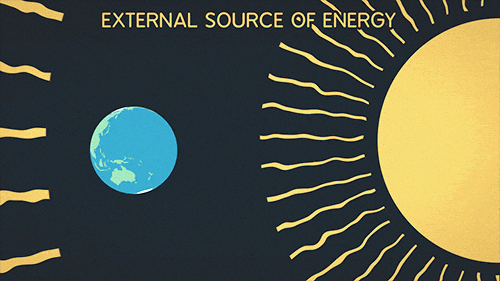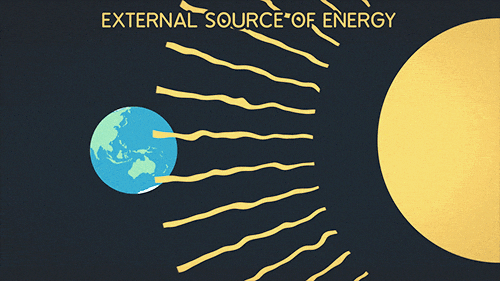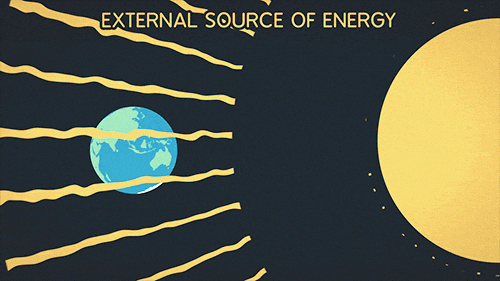
Definition of radiation
Radiation is the transfer of thermal energy via electromagnetic waves.
Factors affecting amount of heat radiation emitted and absorbed:
Temperature, colour of surface
SI unit: Watt (W)
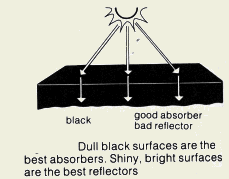
Factors affecting rate of emission and absorption
1) Colour and texture. Dull and black surfaces are better emitters and absorbers than shiny and silvery surfaces.
2) Surface temperature. The higher the surface temperature relative to the surroundings, the higher the rate of emission of infrared radiation.
Uses of good and poor radiators
In colder climates, greenhouses help trap infrared radiation from the sun, plants and soil to ensure a warm, comfortable internal environment for plants to thrive.
The greenhouse effect, which results in thermal insulation of the earth, works in a similar mechanism to that of a constructed greenhouse. Watch the video below to gain a deeper understanding of the background behind such a phenomenon.
How Different Parts of the Flask Prevent Heat Loss or Heat Gain
The air pressure over the water is higher with cold dense air, which moves to occupy the space created over the land. The cool air that comes along is called a sea breeze.