Definition of Electric Charge
An electrical charge is generated when electrons are removed or added to an atom.
When an electron is removed, it is positively charged.
When an electron is added, it is negatively charged.
In both instancces, the atom becomes an charged and is termed as an ion.
What is the Law of Electrostatics
The Law of Electrostatics states that:
Like charges Repel, Unlike charges Attract.
What happens when surfaces are rubbed together
When surfaces are rubbed together, there is an acquisition of electrical charges . The electrons are unable to move about freeley in the material and henc, remain at the surface where the material has been rubbed. These materials are called electrical insulators. Refer to the introductory video above for a deeper understanding of how electrical charging works.
When objects are rubbed together,the electrons move around enabling a gain in charge.
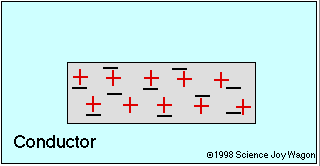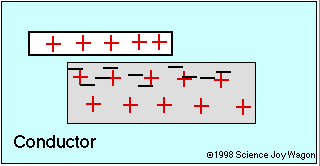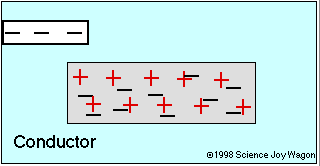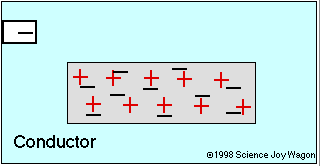
Electrical Conductors and Insulators
An electrical conductor is an object that allows charged particles to move around.
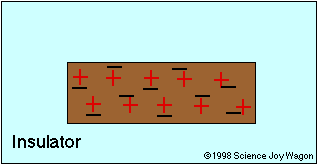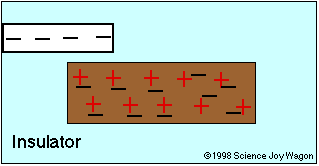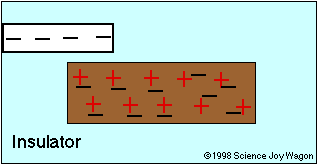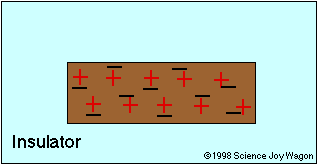
An electrical insulator is an object that does not allow the free movement of charged particles
Conductor
Insulator
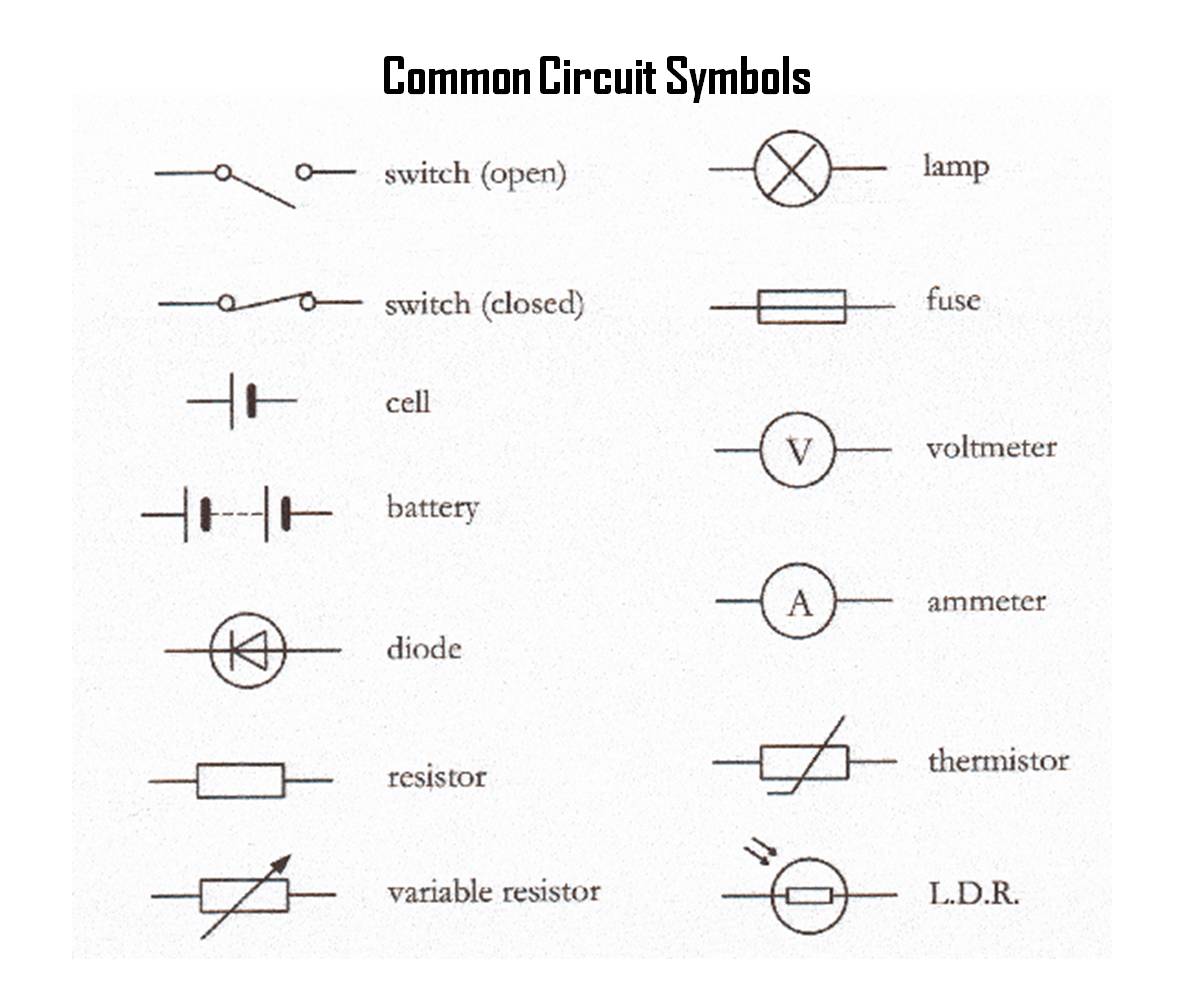
Circuit Symbols
Before we can learn about currents and circuits, we need to be familiar with the common circuit symbols.
Definition of Electric Current
An electric current refers to the rate of flow of electric charge through a conductor. Watch the video below!
Formula for Current
To calculate current or any of its components, we use the following formula.
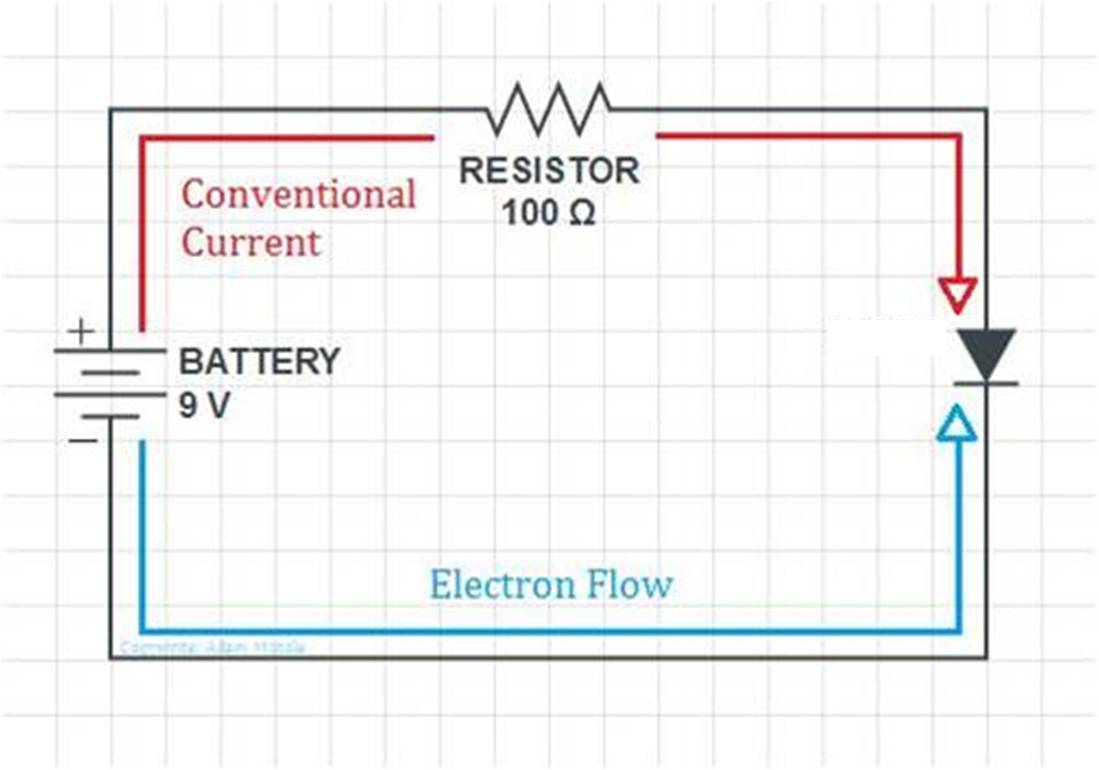
Difference between Conventional Flow and Electron Flow
Before the discovery of electrons, scientists believed that an electric current consisted of moving positive charges. These positive charges flowed from the positive to negative terminal, and was termed as conventional current. However, in reality an electri current is caused by the flow of electrons. These electrons flow from a the negative to positive terminal. Such a movement si known as the <>.electron flow.
Apparatus to measure the amount of current
The instrument used to measure the amount of current is the ammeter, and is used to measure the strength of an electric current in an electric circuit. The amount of current is then indicated by the needle on the ammeter.
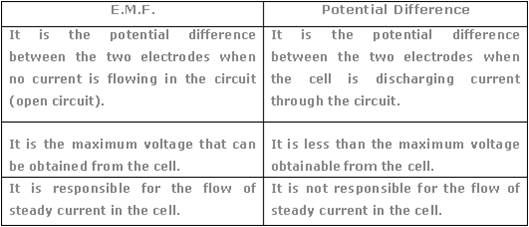
Definition of Electromotive Force (e.m.f.)
The electromotive force refers to the energy given out by a source (cell) in moving one coulomb of charge round the complete circuit. The following formula is essential in aiding you to find the magnitude of the e.m.f. or the electrical energy of a electric source.
E (e.m.f.) = W (work) / Q (charge) = W (work) / I (charge) x t (time)
NOTE: Since Q (charge) = I (current) x t (time), then e.m.f. = W/It as well.
The formula for potential difference is similar to that of the electromotive force. However, the difference lies in whether the cellis discharging or not discharging electricity.
V (potential difference) = W (work done) / Q (charge) = W (work done) / I (current) x t (time)
Definition of Potential Difference
So what exactly is the difference between the electromotive force and potential diffrerence? The potential difference is the work done across the conductor (bulb) in moving one coulomb of charge across it.
Apparatus to measure potential difference
The apparatus that is used to measure potential difference is a voltmeter. It is similar to an ammeter, only that it measures the amount of voltage, not the current.
Definition of Resistance
The resistance of a material refers to the ratio of the potential difference across the material to the current flowing through it.
Formula for Resistance
Resistance, Current and Potential Difference are all related in a single equation, V (voltage) = I (current) x R (resistance, in Ohms)
The SI unit for resistance is Ohm. One ohm is the resistance of a component when a potential difference of one volt applied across a component drives a current of one ampere through it.
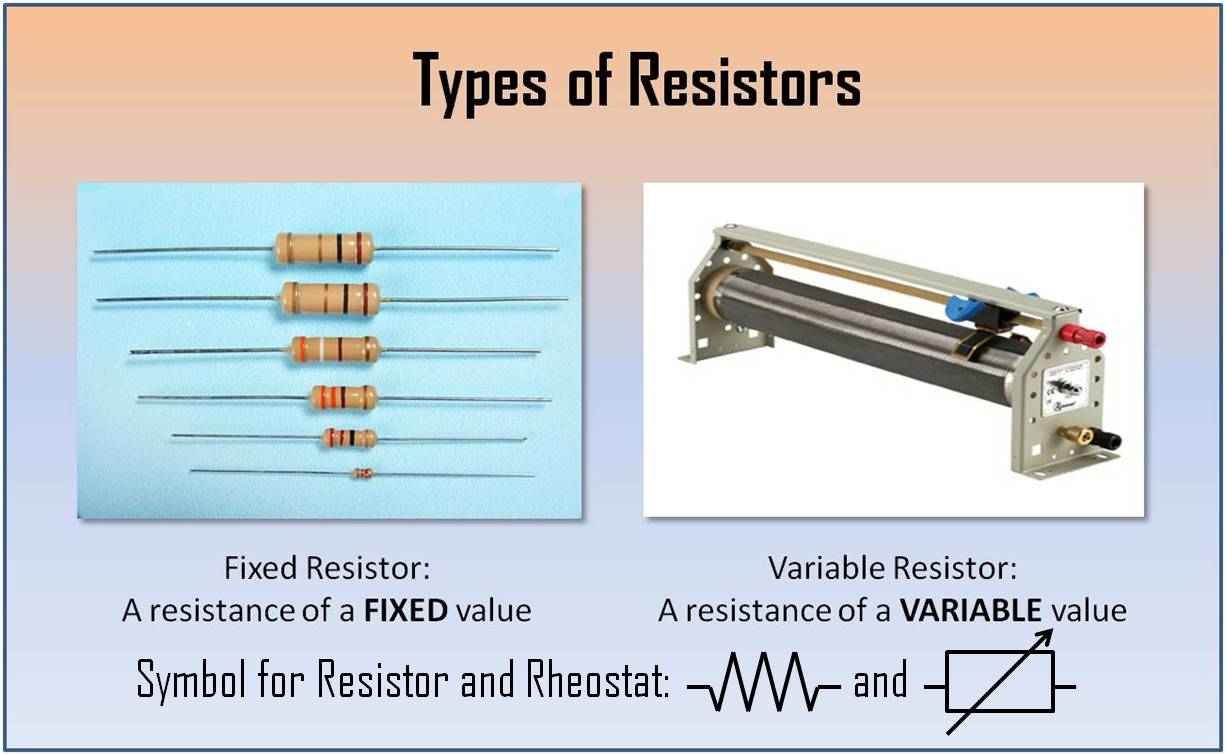
What is a Resistor
A Resistor refers to a conductor in a circuit that is used to control the size of the current flowing in a circuit. The amount of ohms varies between each resistor, ranging from a few ohms to seversal million ohms. There are two kinds of resistors: fixed and variable resistors. A variable resistor is also known as a rheostat.
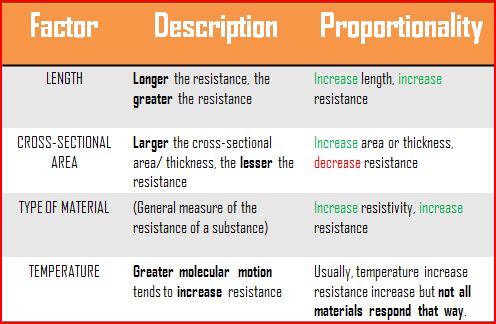
[Supplementary] Factors affecting resistance
There are 3 main factors that affect the resistivity of a material:
1. Cross Sectional Area of the item used
2. Length of the material used
3. Temperature
[Supplementary] Formula for Resistance of a Wire
The formula for resistivity is:
[Supplementary] Resistance of Wire Interactive Tool
Use the interactive tool below to understand how denisty, length, area and resistance are related in the equation.