Hazards of Electrostatics
Electrical charges accumulate on moving objects such as trucks and cars. This is due to the friction between the road and the vehicle. When a sudden discharge occurs, it may ignite a spark and result in an explosion. This is the reason why trucks carrying flammable items like fuels always have a chain trailing behind. This ensures that the charge that could potentially build up is neutralised by electrons from the ground. This process is called "earthing".
Likewise, a lightning bolt that strikes a building could lead to devastating consequences. Hence, lightning rods are assembled at the top of bulding to channel the energy from the lightning to the ground.
Lightning: Build-Up of Static Electricity
The build-up of static electricity in the natural world is one of the reasons why lightnings occur. Watch the video below to gain a deeper understanding of how static electricity can be dangerous.
Man-made disasters due to Static Electricity
Why do some flammable liquids explode when on a vehicle?
Methods to prevent these hazards
In most instances, an Earthing System is used. This principle of neutralising a charge is also practised in vehicles.
Practical Uses of Electrostatics
Photocopiers, Spray Painting, Electrostatic Precipitators are all examples of machinery that apply the principle of electrostatics. Watch the video below for a deeper understanding.
Powder Painting
Static electricity also applies to the technique of spraypainting, or powder painting.
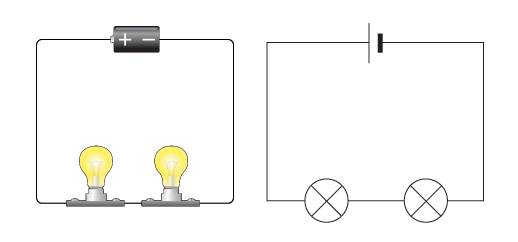
Definition of a Series Circuit
A series circuit is one where the components are connected one after another in a single loop, and has only one path through which electrical charge can flow through.
Current in a Series Circuit
In a series circuit, the current at any point of the circuit is the same.
The current in series circuit is the same when measured at any 2 different points.
Potential Difference in a Series Circuit
In a series circuit, the sum of the potential difference across each component is equal to the potential difference across the whole circuit.
Formula: V(all) = V1 + V2 + V3 +
Resistance in a Series Circuit
In a series circuit, the effective resistance R is the sum of all the resistances
Formula: R(all) = R1 + R2 + R3 +
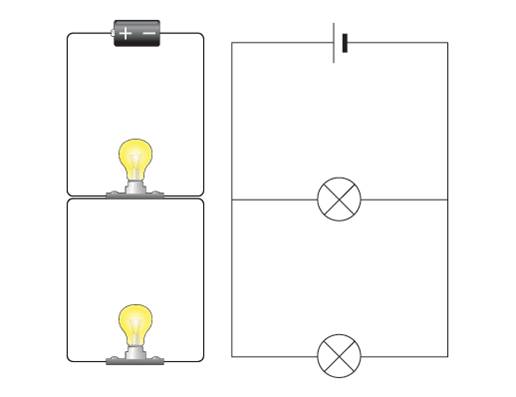
Definition of a Parallel Circuit
A parallel circuit is one where the components are connected to the e.m.f. source in two or more loops, and has more than one path through which electric charge can flow.
Current in a Parallel Circuit
In a parallel circuit, the sum of the individual current in each of the parallel branches is equal to the main current flowing intoor out of the parallel branches.
The main current in parallel circuit is equal to the sum of all the individual circuits.
Potential Difference in a Parallel Circuit
In a parallel circuit, the potential difference across separate parallel branches is the same.
Potential Difference SAME across all branches
Resistance in a Parallel Circuit
In a parallel circuit, the reciprocal of the effective resistance of the resistors in a parallel, 1/R, is equal to the sum of the reciprocal of all the individual resistors.
Formula: 1/R(all) = 1/R(1) + 1/R(2) + 1/R(3) +
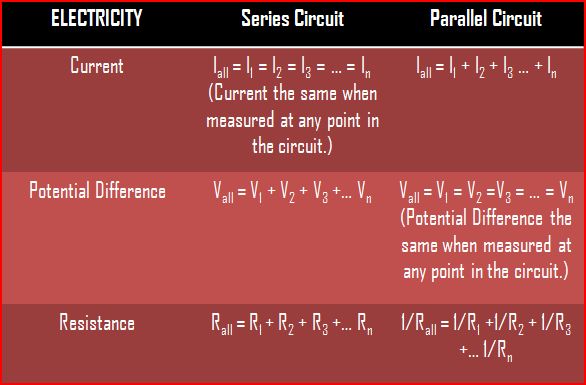
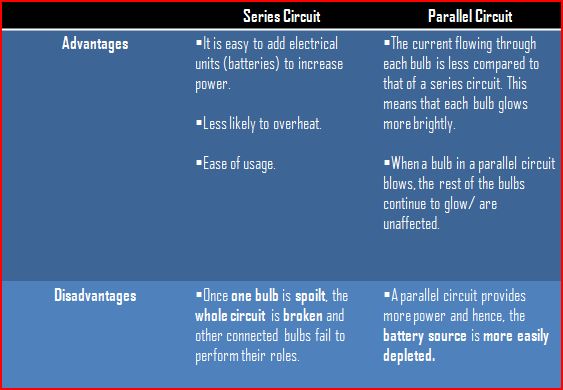
Comparison Table of Series and Parallel Circuit
The table below shows a comparison between a circuit in series arrangement and another in parallel.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Series and Parallel Circuit
The table below compares the advantages and disadvantages of using a series and parallel circuit.
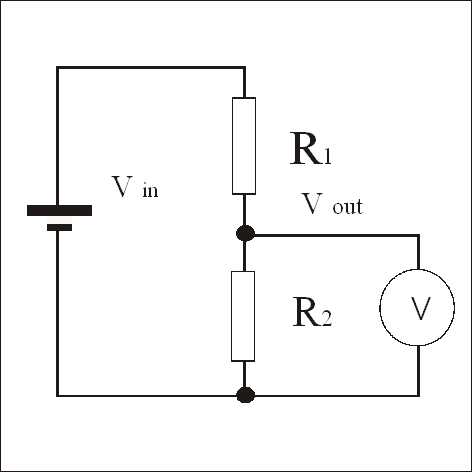
Definition of Potential Divider
A potential divider is a line of resistors connected in series. It is used to provide a fraction of the voltage source to another part of the circuit.
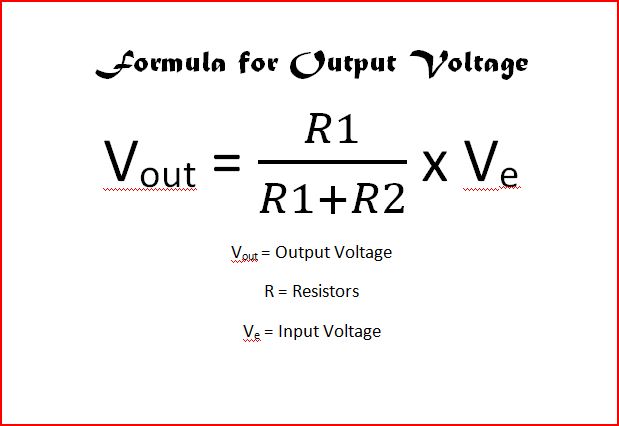
Formula for Output Voltage
The formula for output voltage is shown below:
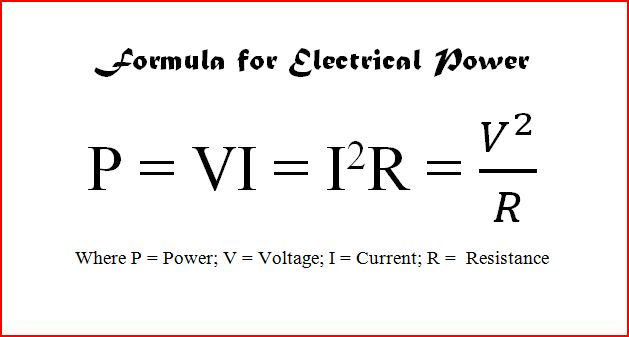
Formula for Electrical Power
As mentioned in the earlier topics, electricity is the energy released when charged particles such as electrons move. As such, the energy that is released can be utilised as a useful form of energy, and can be converted from one form to another to perform useful tasks. The formula for energy is listed below.
SI unit for Power
The SI unit for power is Watts. This is commonly seen on many electrical appliances like the iron, television and electric stove.
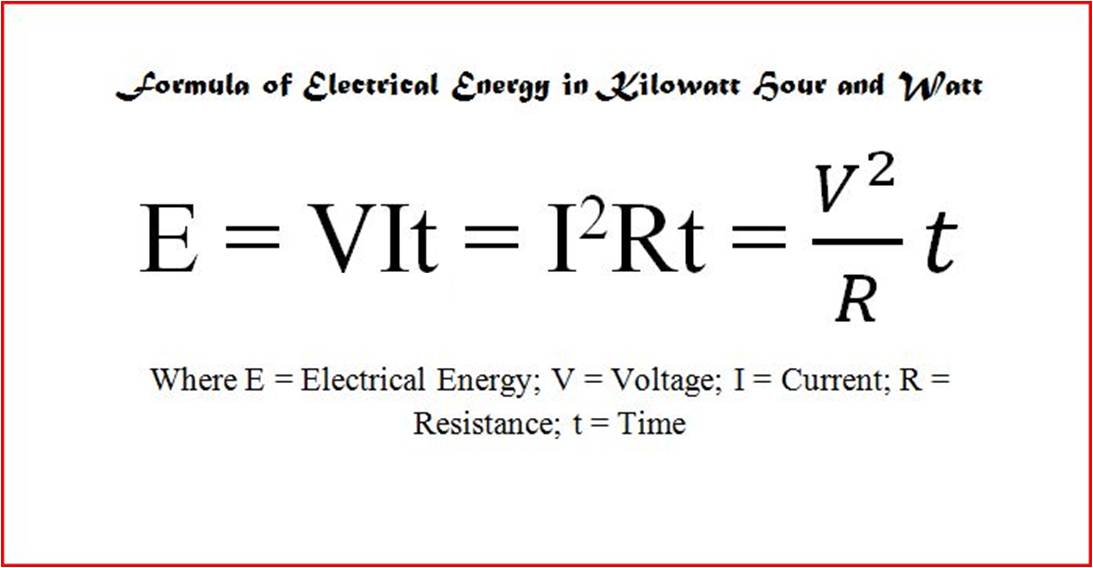
Formula for Electrical energy in Kilowatt Hour
We can also measure the electrical energy E used in time t.
Practicality of the measure kWh
In most households in Singapore, electricity consumption is measure in terms of kilowatts per hour. This is then multiplied by the cost of producing that amount of electricity, which is dependent on the price of natural gas and oil.
Dangers of Electrcity during Misuse
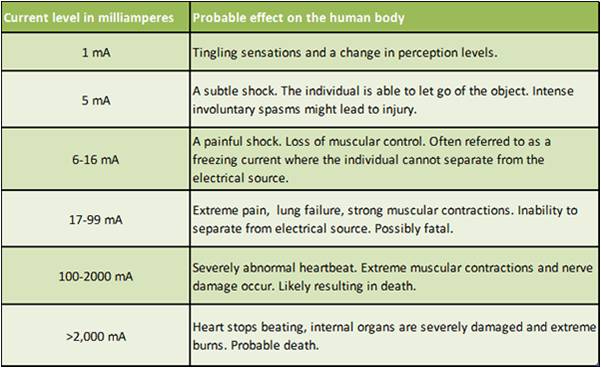
Electricity is a useful tool, it can also result in accidents such as major burns and even death. Here are some instances of electricity, when misappropriately handled, can lead to such accidents:
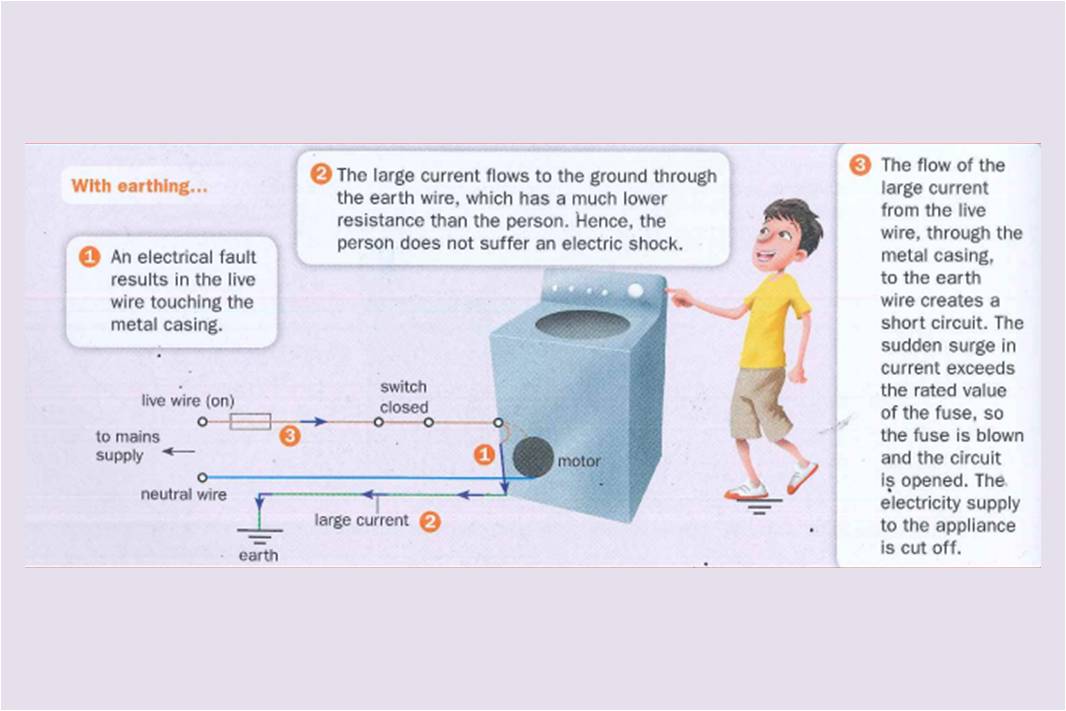
1. Damaged Insulation - When the wire casing that insulates the metal waire is damaged, direct contact with a live wire can lead to electrocution and death.
2. Overheating Cables - Overloaded power sockets.When an unusually large current flows through the wires, the power socket is overloaded and that heats up the cables. Otherwise, inappropriate usage of wires can lead to overheating. (Remember: resistance is inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area.A thinner wire has a higher resistance and can overheat at a faster rate.)
3. Damp environments - When water is in contact with electricity and the human body, it provides a conducting path for the current, resulting in a case of electrocution.
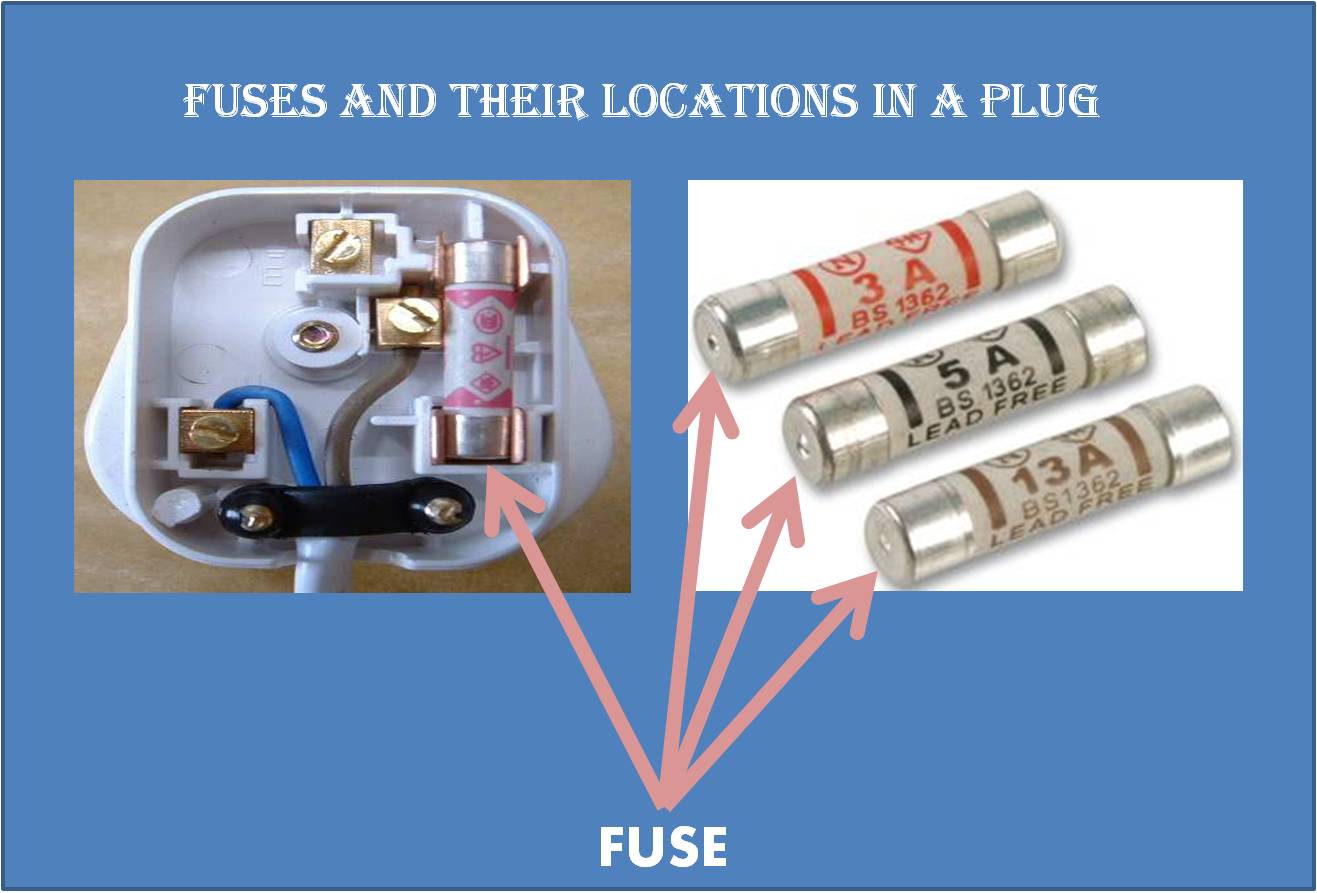
Definition of a Fuse
A fuse is a safety device that is connected to a live wire. A fuse has different fuse ratings, which indicates the maximum value of current that can flow through before the fuse blows. In general, thicker wires conduct larger currents and hence, require a a fuse with a higher rated value.
The followiing points should be considered when choosing an appropriate fuse:
1.A rated value that is slightly higher than the current of the electrical appliance draws under normal operating conditions.
2. Should be connected to a live wire so that the current to the appliance iscut off when the large current melts the fuse.
3. Main power supply must be switched off when replacing a fuse
Definition of a Circuit Breaker
A circuit breaker is a safety device that automatically switches off when an unusually large amount of current flows through it. Without circuit breakers, a suden durge in current will damage home appliances or even start a fire.
Definition of a Switch
A switch in a safety device that is meant to break or complete an electrical circuit. It is usuallt connected to both the live and neutral wire, so as to complete or break the circuit.
A Switch helps to complete the circuit.
Different types of Wires
In most circuits, there are 3 types of wires. These 3 wires all perform a function to ensure the safe and efficient use of a circuit.
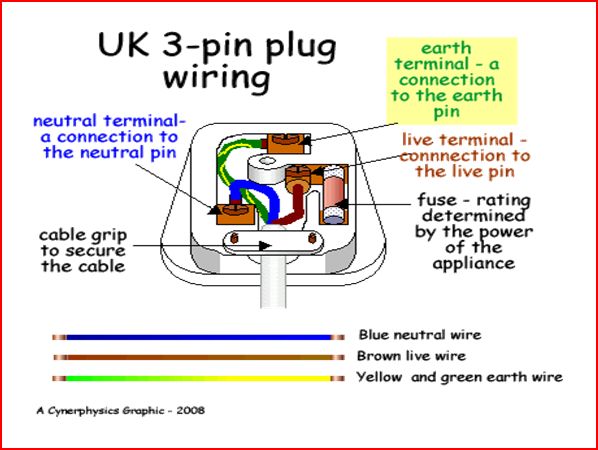
1. Live Wire (Usually RED or BROWN) - The live wire is the wire that is connected to a high voltage and delivers the current to the appliance. This is the wire that connects circuit breakers, fuses and switches.
2. Neutral Wire (Usually BLUE) - The neutral wire helps to complete the circuit by providing a return path to the supply for the current. It is usually placed at ZERO volts.
3. Earth Wire (Usually GREEN) - The Earth Wire is a low resistance that connects the live wire to the ground. In an event that there is a surge in the current, the larger current and the live wire touches the metal casing, electricity would flow through the earth wire instead of the person
Three-Pin Plug
In a 3-pin plug, each of the pins are actually connected to each of the wires, as shwn in the diagram below.
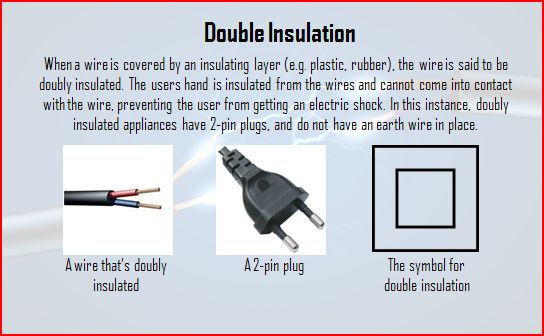
Definition of Double Insulation
In double insulation, this occurs in household appliances that use 2-pin plugs. Hence, the do not require an earth wire. This is done by insulating the internal components of the applicances and also insulating the internal components from the external casing. Such appliances usually do not have metal casing (replaced with plastic).
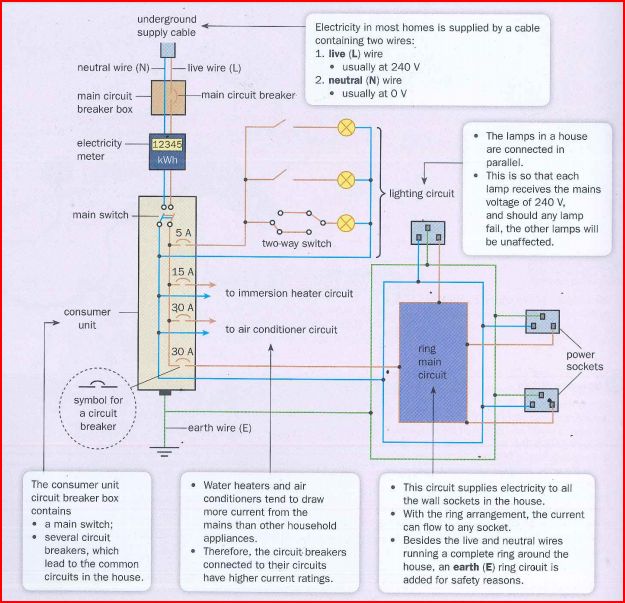
Wiring and Power System in a household
The image below shows how the electrical system is set up in a house. In high-rise buildings, such a system is repeated multiple times for each unit.
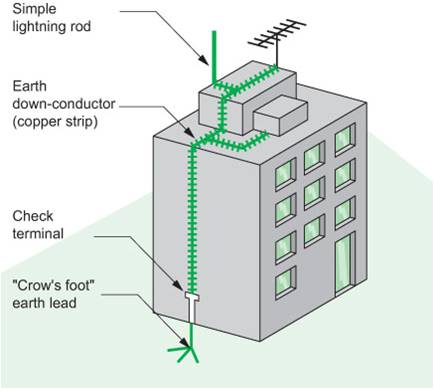
Lightning Conductor
At the top of every building there is a lightning conductor. The lightning conductor has an earthing function, in which it helps to channel all electrical energy from a lightning strike into the ground by providng a path of least resistance into the ground. Hence, it helps to prevent a power surge in the power supply. The earth wire also appears at all sockets in a house. Failure to channel the electrical energy from a lightning strike into the ground can result in fires due to an electrical surge. Watch the news clip below to understand the importance, function and consequence of not installing a lightning rod/ conductor.