Definition: Balanced Diet
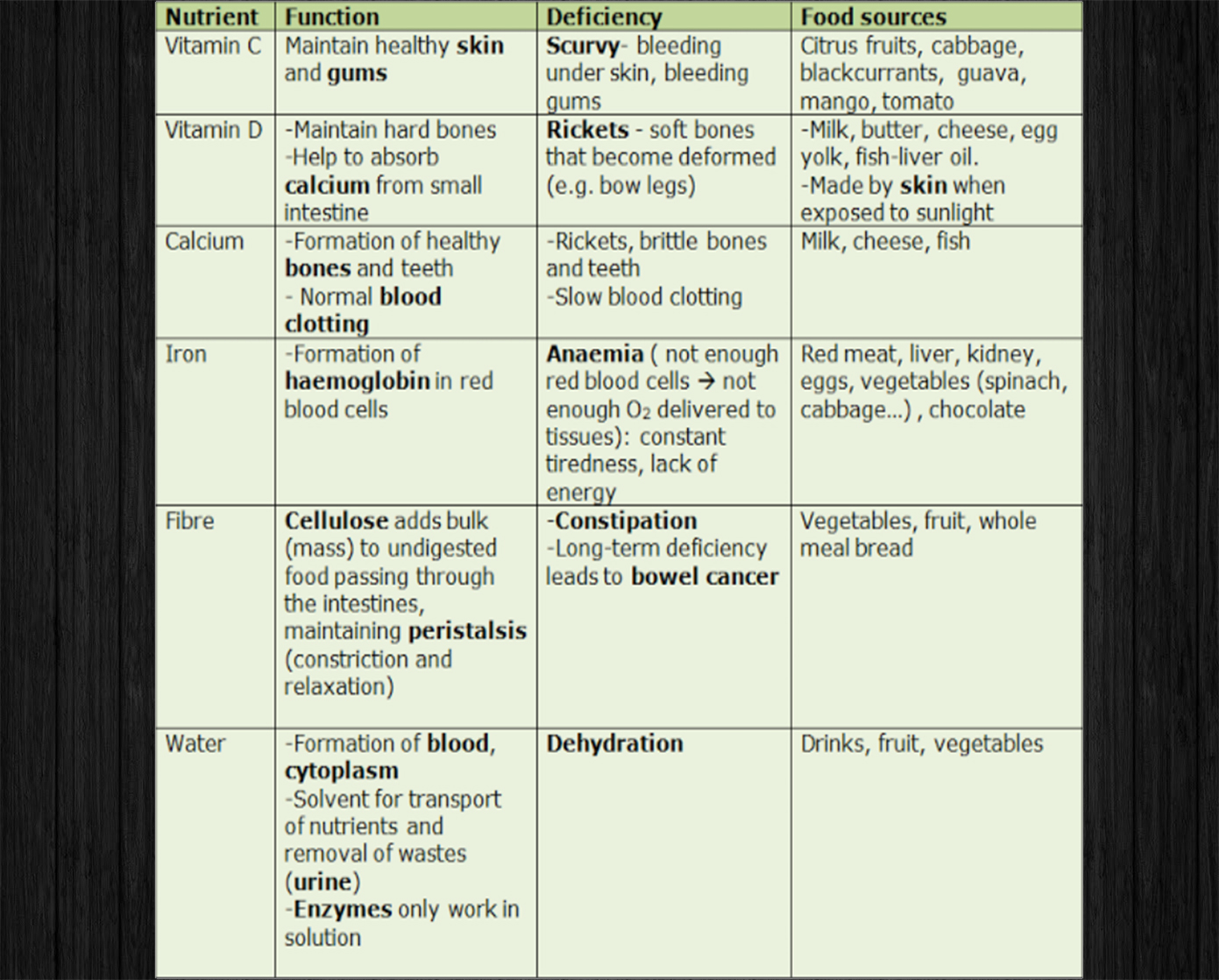
A balanced diet should contain carbohydrate, fat, protein, fibre, vitamins, minerals and water. Note that fibre cannot be digested: it used to form
A balanced diet is a diet that contains all the main nutrients in the correct amounts and proportions to maintain good health.
[Supplement] Dietary Needs for different people
A balanced diet for different people are slightly different, because our energy requirements differ from person to person.
Gender
Males usually use more energy than females due to their larger body frames and higher metabolism rates.
Age
Humans tend to use more and more energy as we age, until we stop growing. However, children need a higher proportion of proteins than adults do.
Pregnancy
Pregnant women require extra nutrients for the development of the foetus as compared to normal women.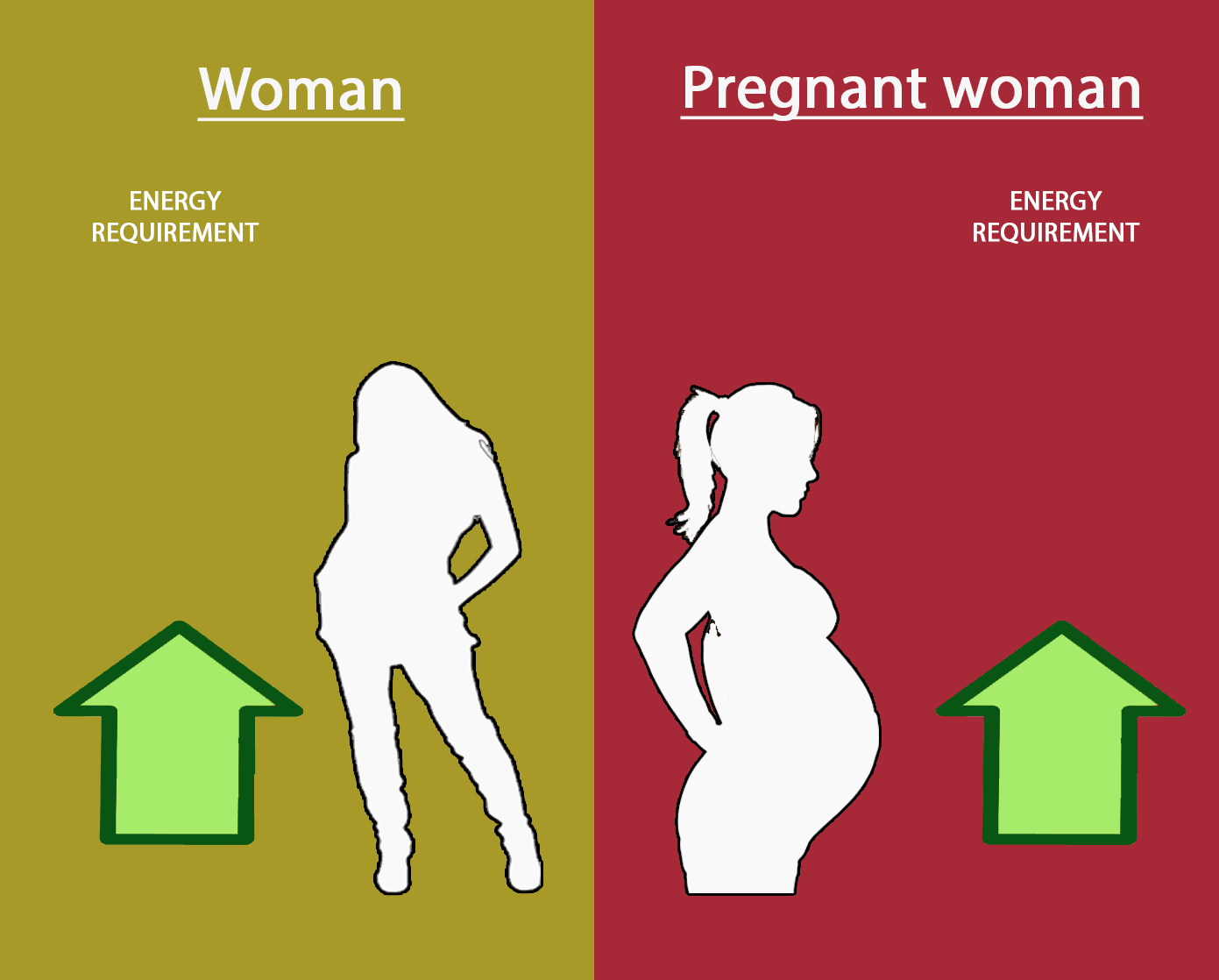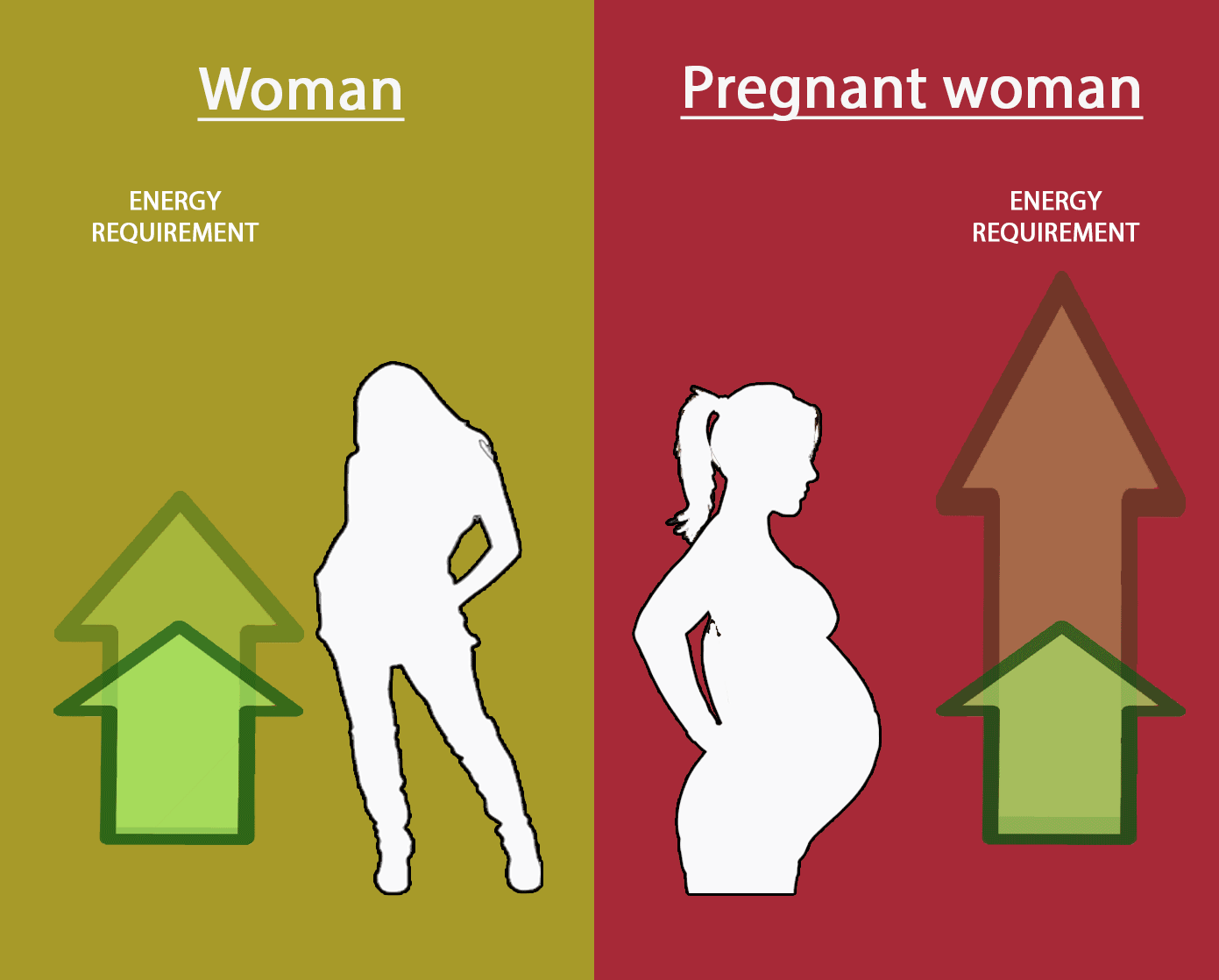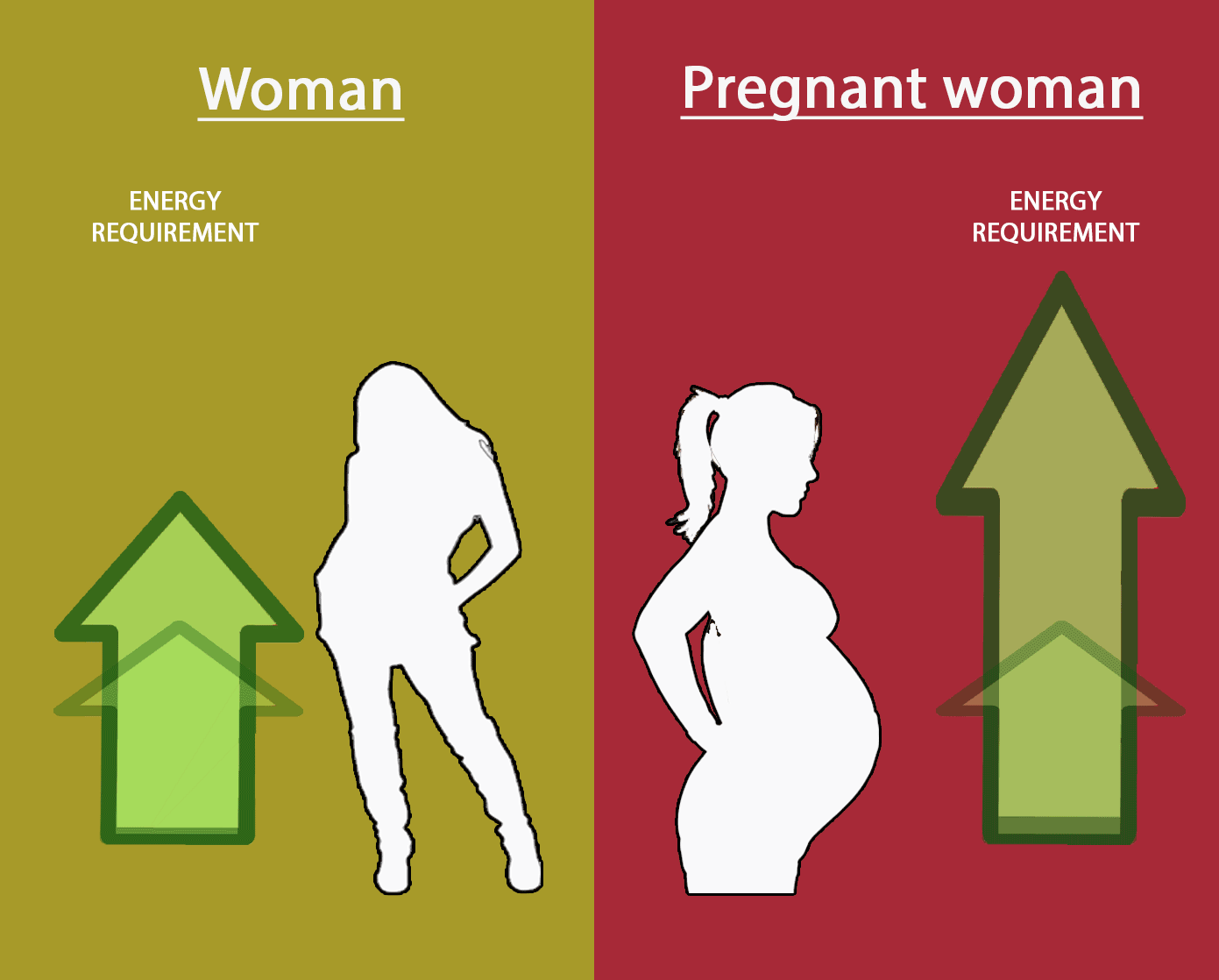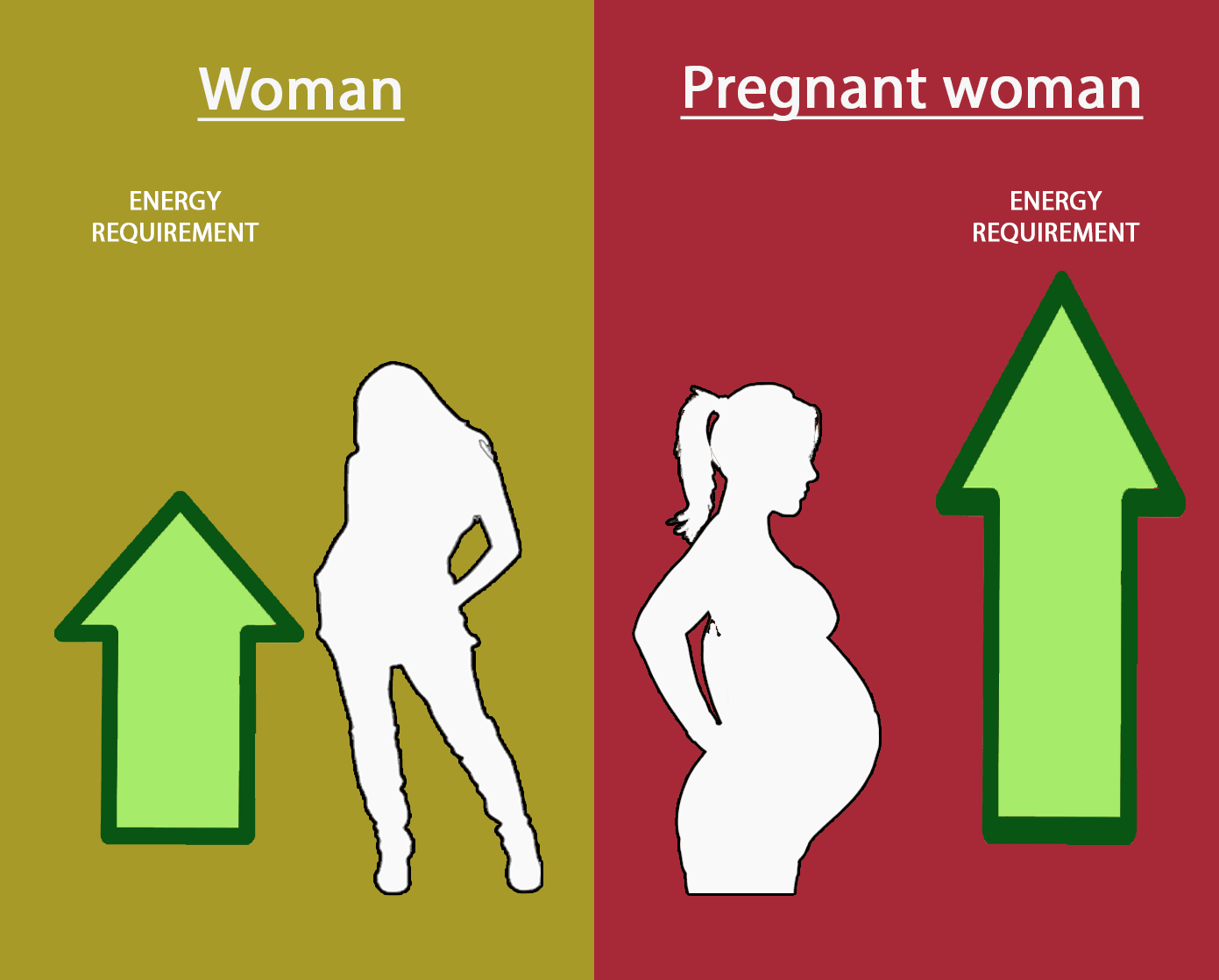
Malnutrition
Malnutrition is the result of not eating a balanced diet. There may be:
- wrong amount of food: too little or too much
- incorrect proportion of main nutrients
- lacking in one or more key nutrients
Such wrong proportion of nutrients e.g. too much carbohydrates (starchy foods) and a lack of protein can lead to Kwashiakor, also known as Childhood protein-energy malnutrition in young children.
Effects of Malnutrition
Obesity
When too much food is injested, it can lead to obesity.This can lead to several diseases such as diabetes, strokes, etc.
Coronary Heart Disease
Too much saturated fat in the diet results in high cholesterol levels. Cholesterol stick to the walls of arteries, gradually blocking them, leading to coronary heart disease.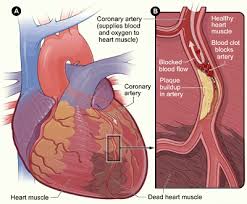
Starvation
Starvation is caused by consuming too little food and it can lead to intense weight loss, organ damage and in serious cases, death. Extreme slimming diets can result in anorexia nervosa.
Constipation
Being unable to defecate can be extremely painful.
Dietary importance
Lacking key nutrients such as vitamin, mineral and fiber can lead to diseases.
Definition: Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption and Egestion
nutrients.
[Supplement] Definition: Mechanical Digestion vs Chemical Digestion
Alimentary Canal
Significance of chemical digestion
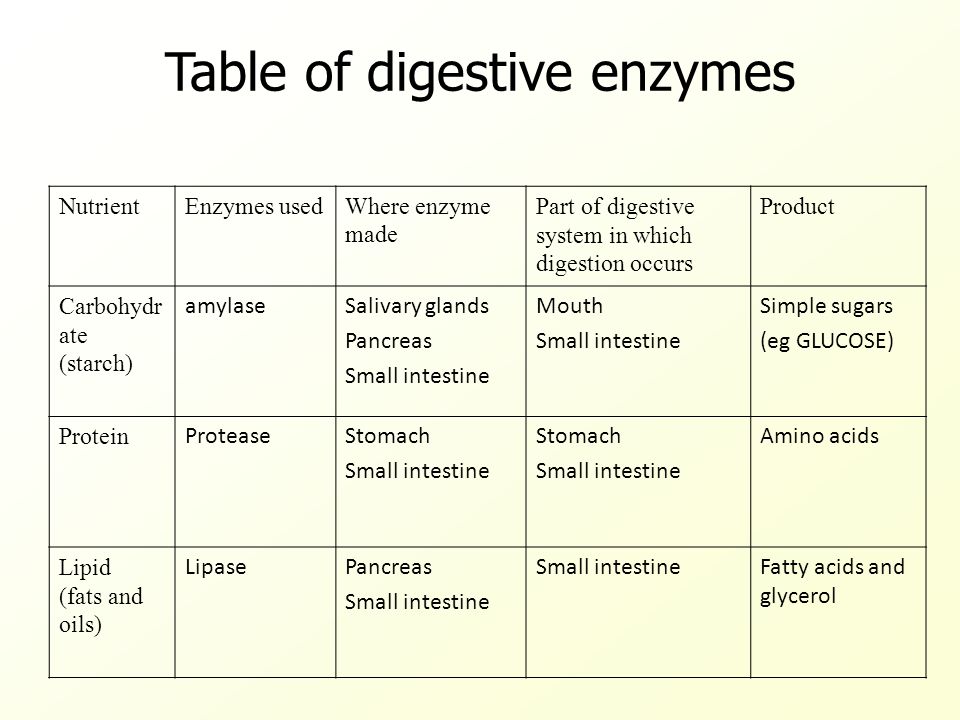
Chemical digestion in the alimentary canal helps in producing small, soluble molecules that can be absorbed.
Function and location of enzymes in alimentary canal
Hydrochloric Acid
Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid, killing bacteria in food and giving an acid pH for enzymes.