Definition: Hormones
Definition:
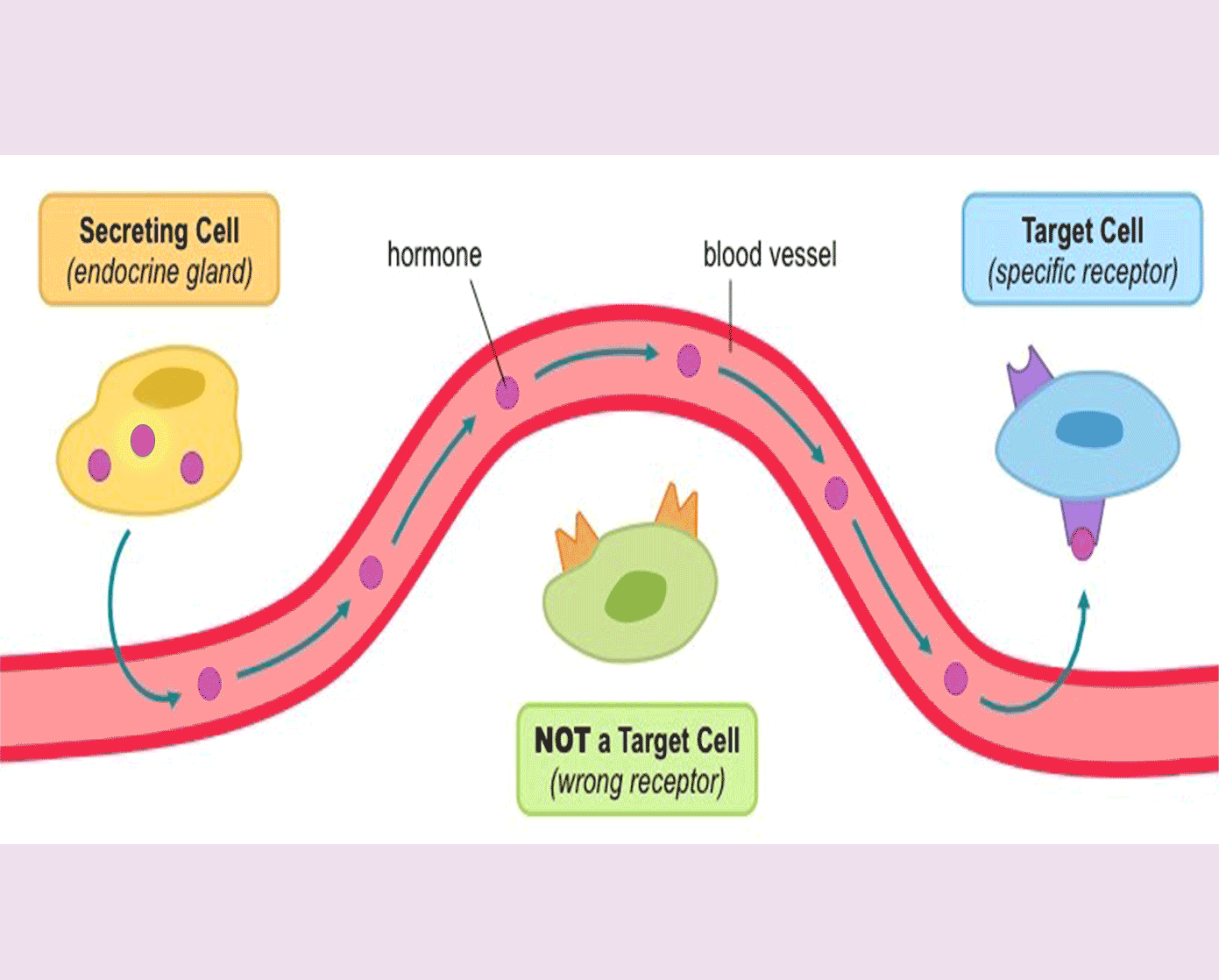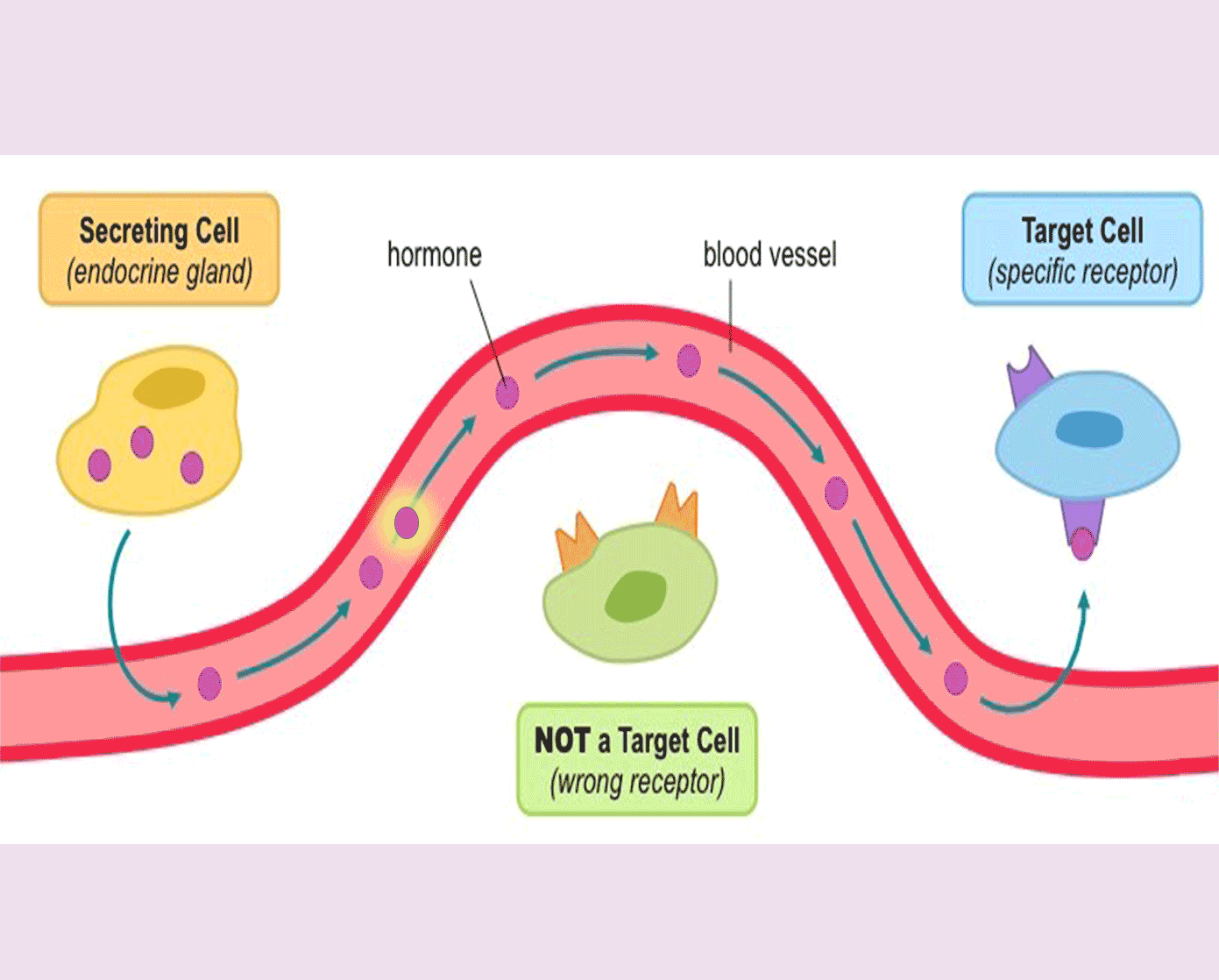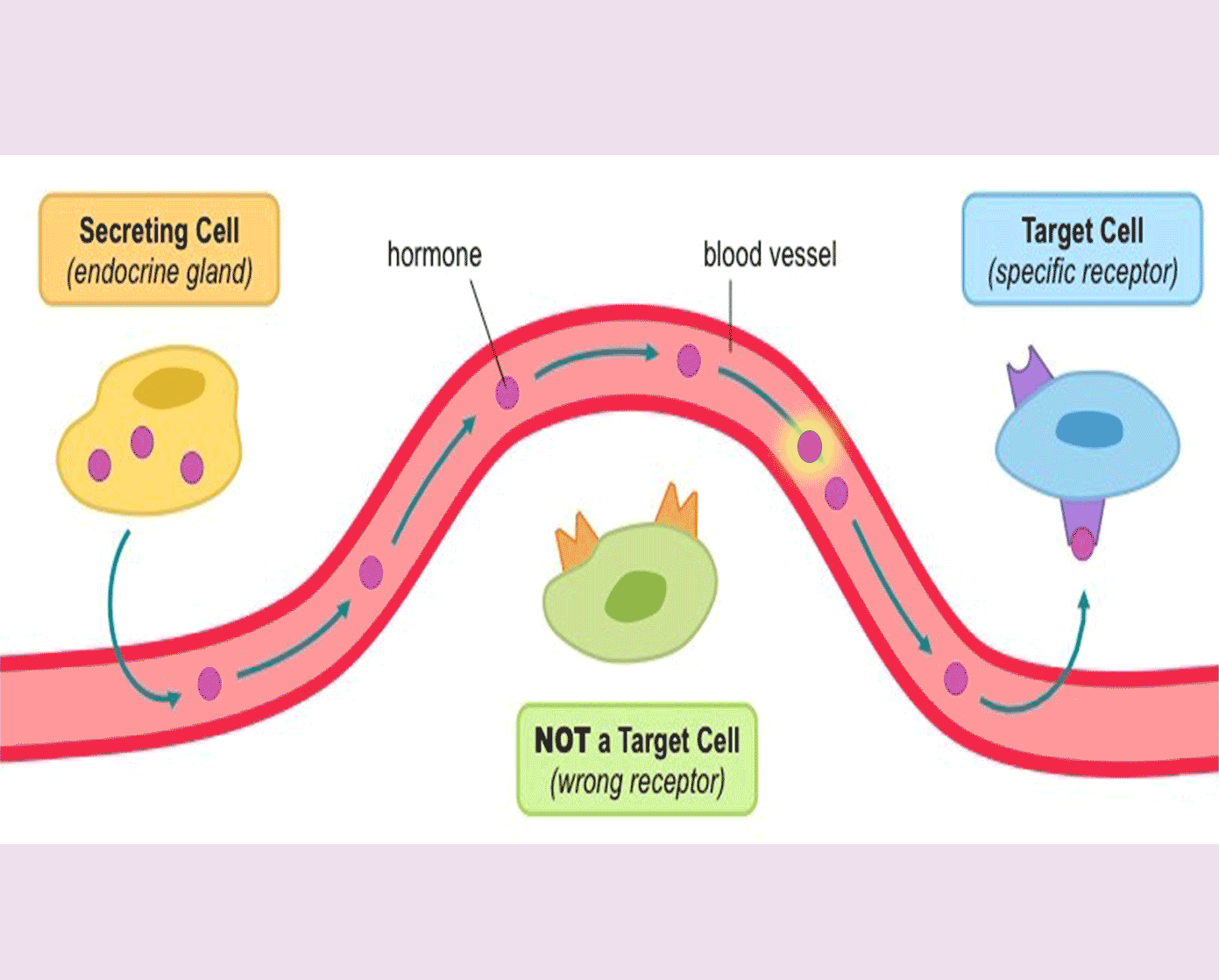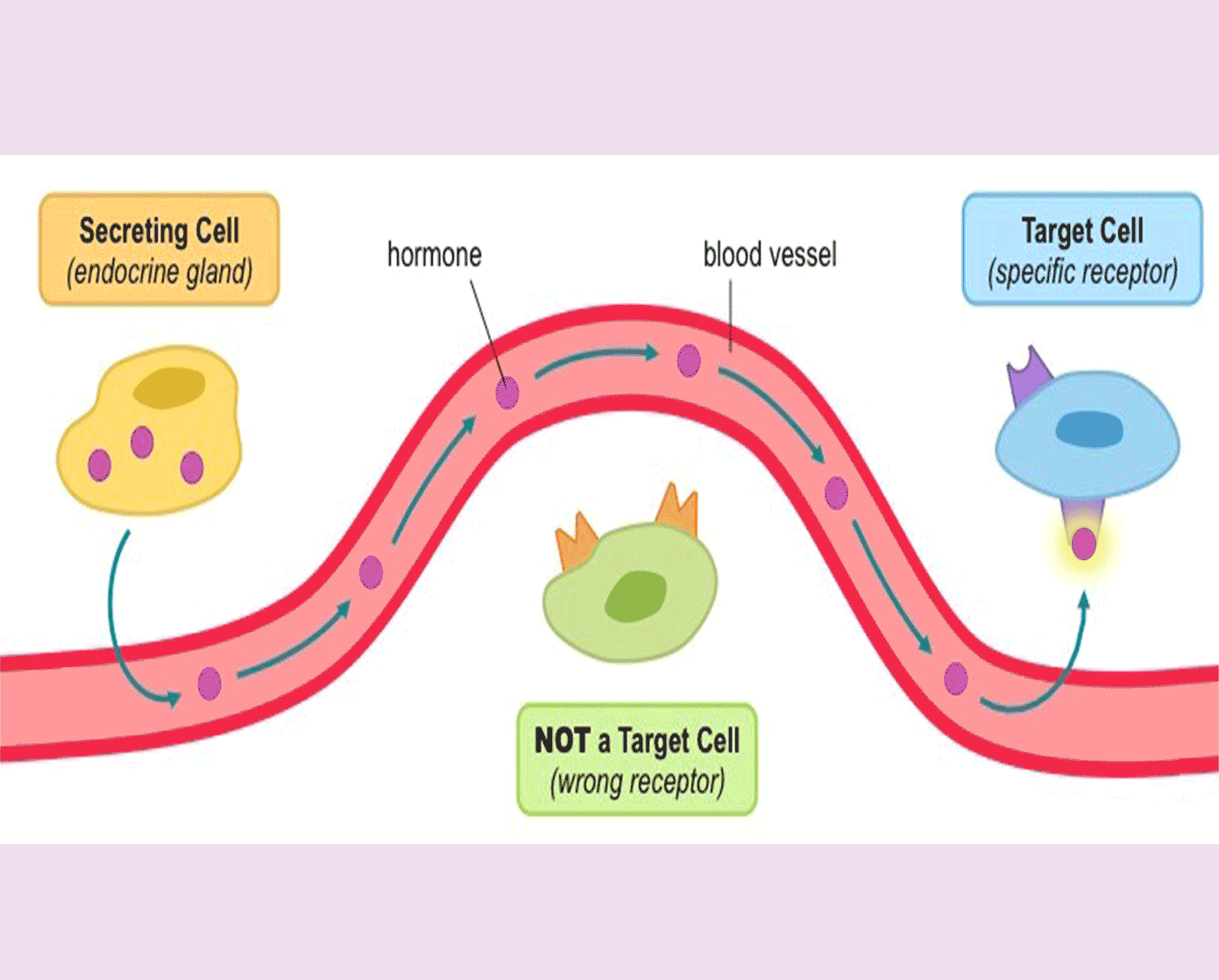
A hormone is a chemical substance, produced by a gland, carried by the blood, which alters the activity of one or more specific target organs.
Hormones
[Supplement] Effects of Adrenalin
Adrenaline is produced in a "fight or flight" situation: when you are scared or excited, your body produces adrenaline. Adrenaline is secreted by the adrenal glands (there is one above each kidney) and is released into the blood so that it can travel to the appropriate target organs.
Increased Pulse Rate
Pulse Rate increases to circulate blood more rapidly and deliver glucose and oxygen to muscle cells for increased activity.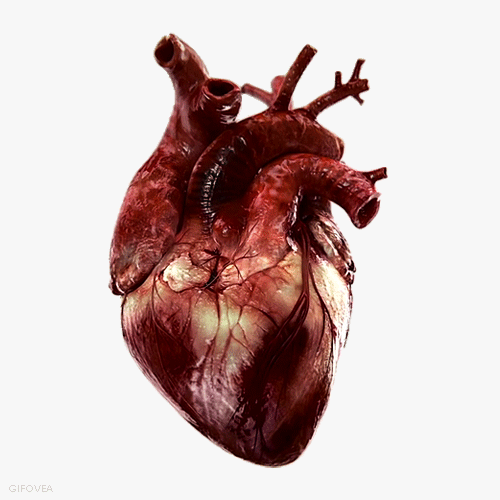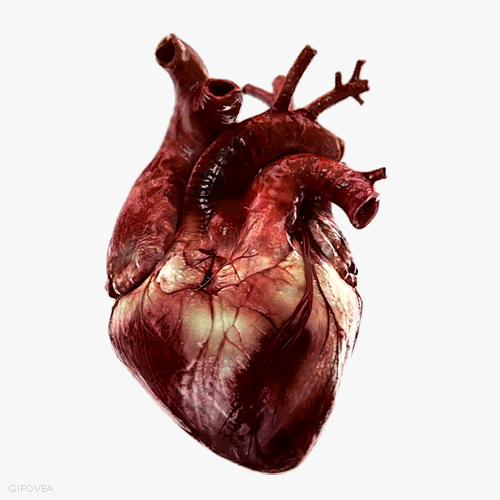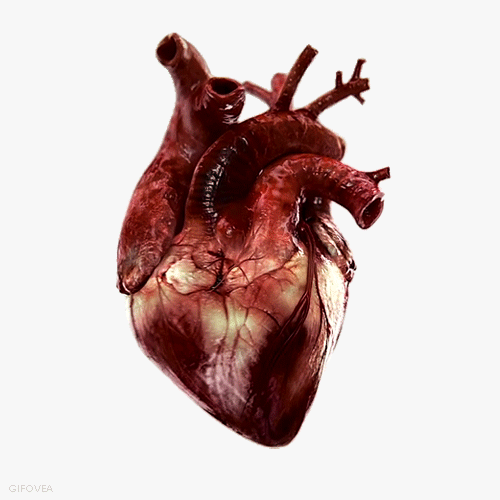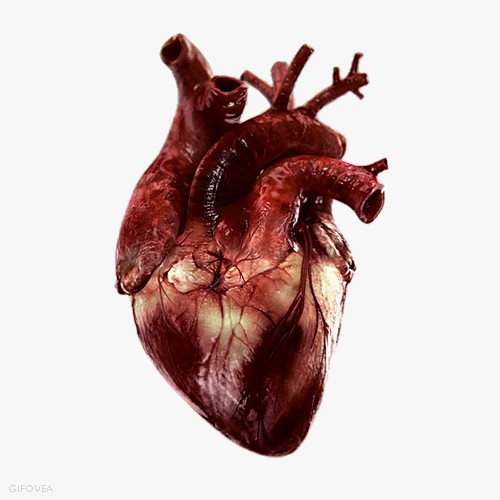
Breathing
Depth and rate of breathing increases to take in more oxygen to the body and remove more carbon dioxide rapidly from body.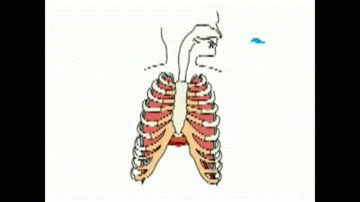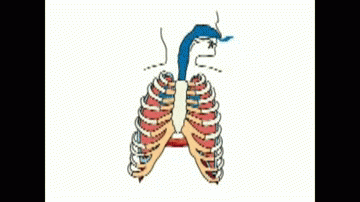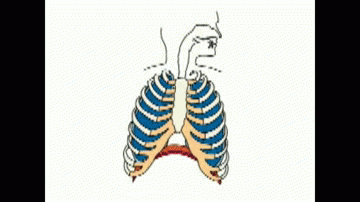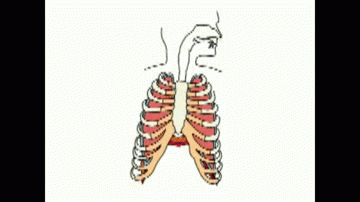
Dilated Pupils
Pupils dilate for better vision.
Situations of adrenalin secretion
As previously mentioned, adrenaline is secreted in "fight or flight" situations. Examples include writing an exam, being left alone in a horror house or riding a roller coaster.
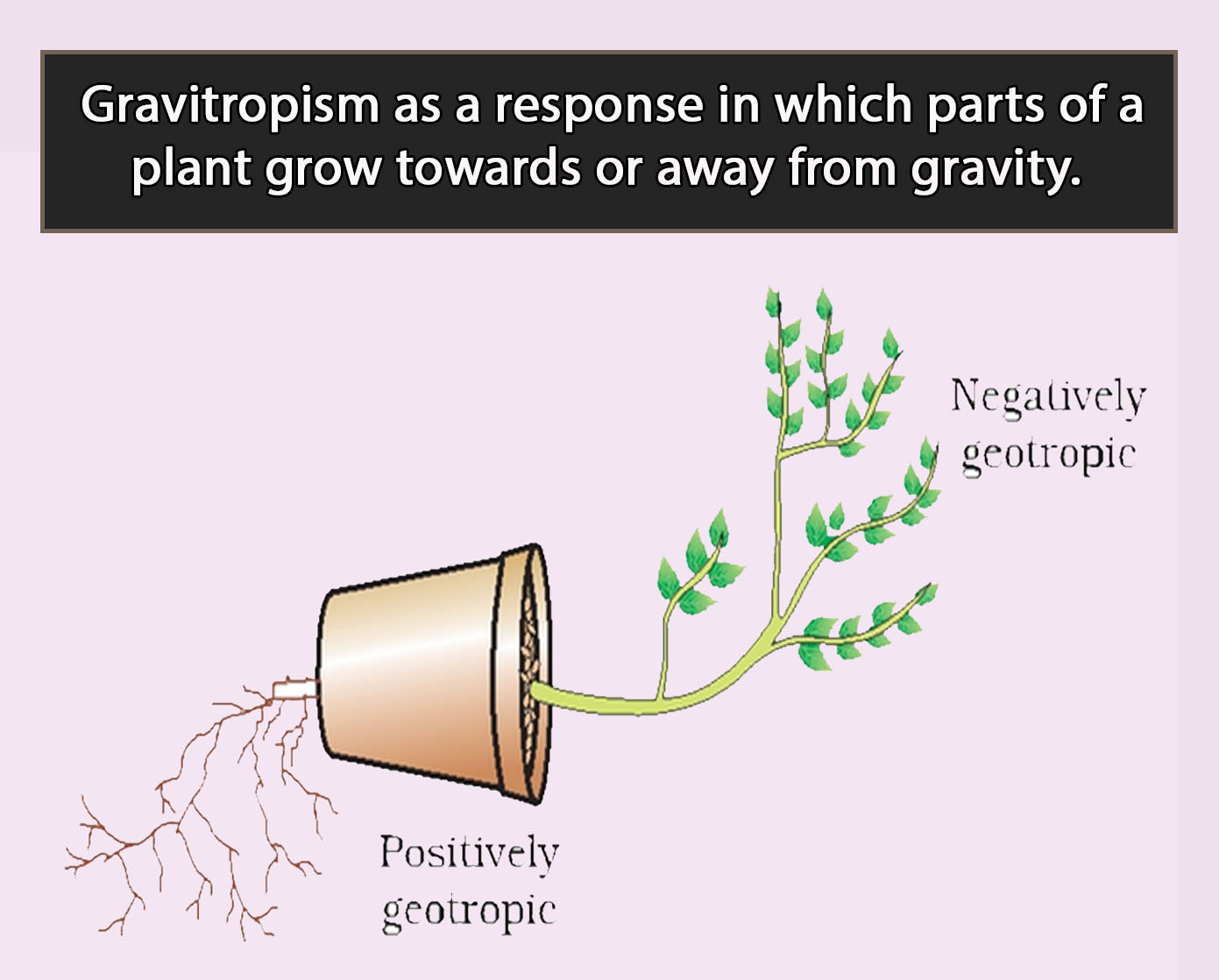
Definition: Gravitropism
Definition: Phototropism
[Supplementary] Investigating geotropism
The hormones that regulate plant growth are called auxins. Note that auxins in the shoot stimulate cell growth (by stimulating the absorption of water, forcing cells to expand) and that auxins in the root slow down cell growth.
Auxins are plant growth substances, produced by the shoot and root tips of growing plants.
Auxins in the shoot: stimulate cell growth, by the absorption of water.
Auxins in the root: slow down the cell growth.
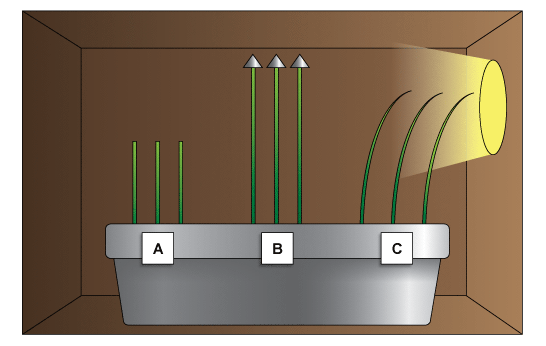
Auxin experiment
Auxin is a plant hormone responsible for controlling the direction of growth of root tips and stem tips in response to different stimuli including light and gravity. Auxin is made at the tips of stems and roots. It is moved in solution to older parts of the stem and root where it changes the elasticity of the cells. More elastic cells absorb more water and grow longer, causing bending in the stem or root. It is thought that light and gravity can interfere with the transport of auxin causing it to be unevenly distributed.
3 groups of seeds are grown in a cardboard box.
A: when the tips are removed, no auxin is made so the stems do not grow
B: when the tips are covered, auxin moves to all parts of the stem causing all parts to grow
C: when the tips are lit from one side only auxin accumulates on the shaded side causing it to grow more than the illuminated side
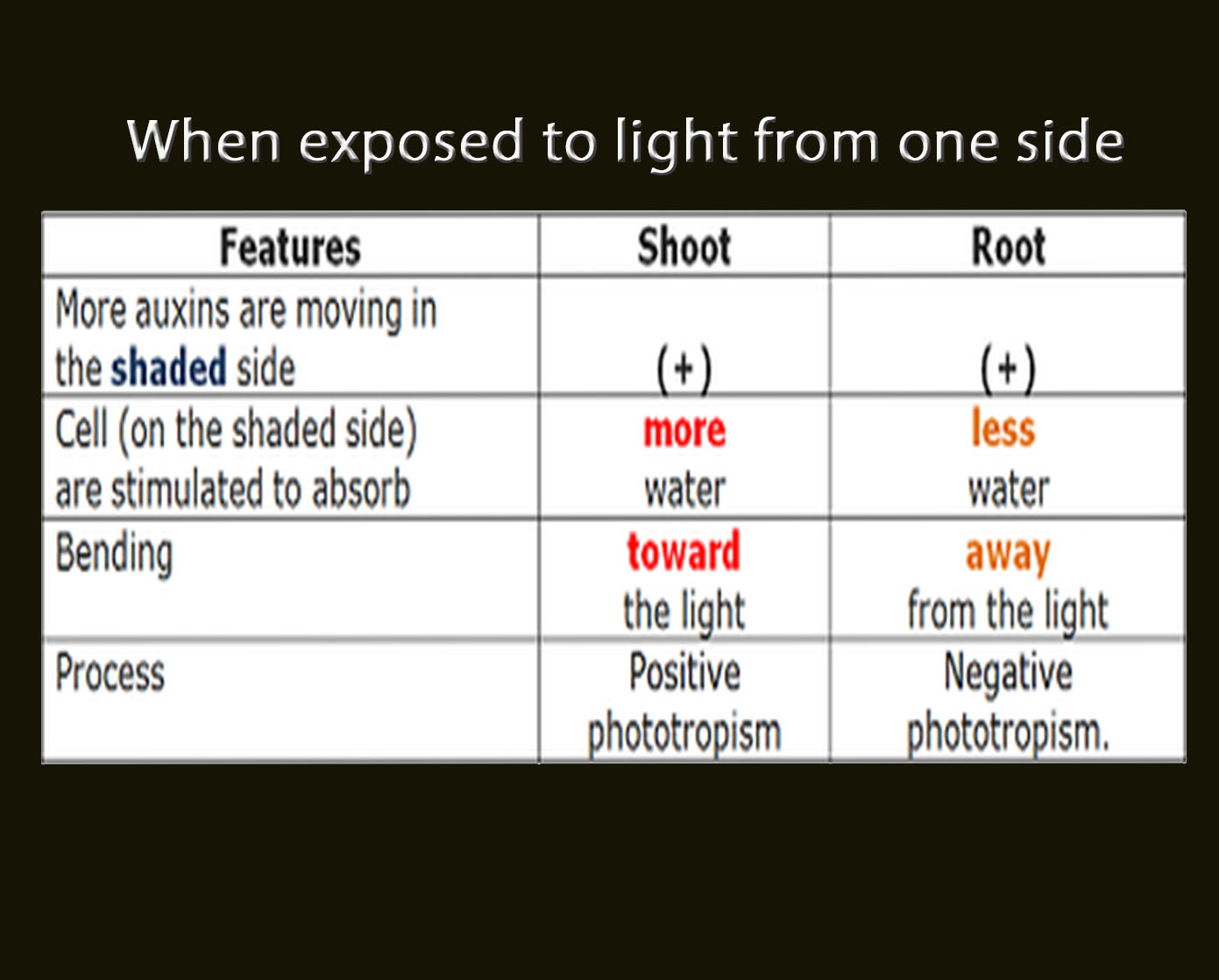
Auxins in phototropism (shoot)
If a shoot is exposed to light from one side, more auxins are moving in the shaded side (from the tip of the shoot). On this side, cells are stimulated to absorb more water and the plant grows more. Shoot bends toward the light. This is called positive phototropism.
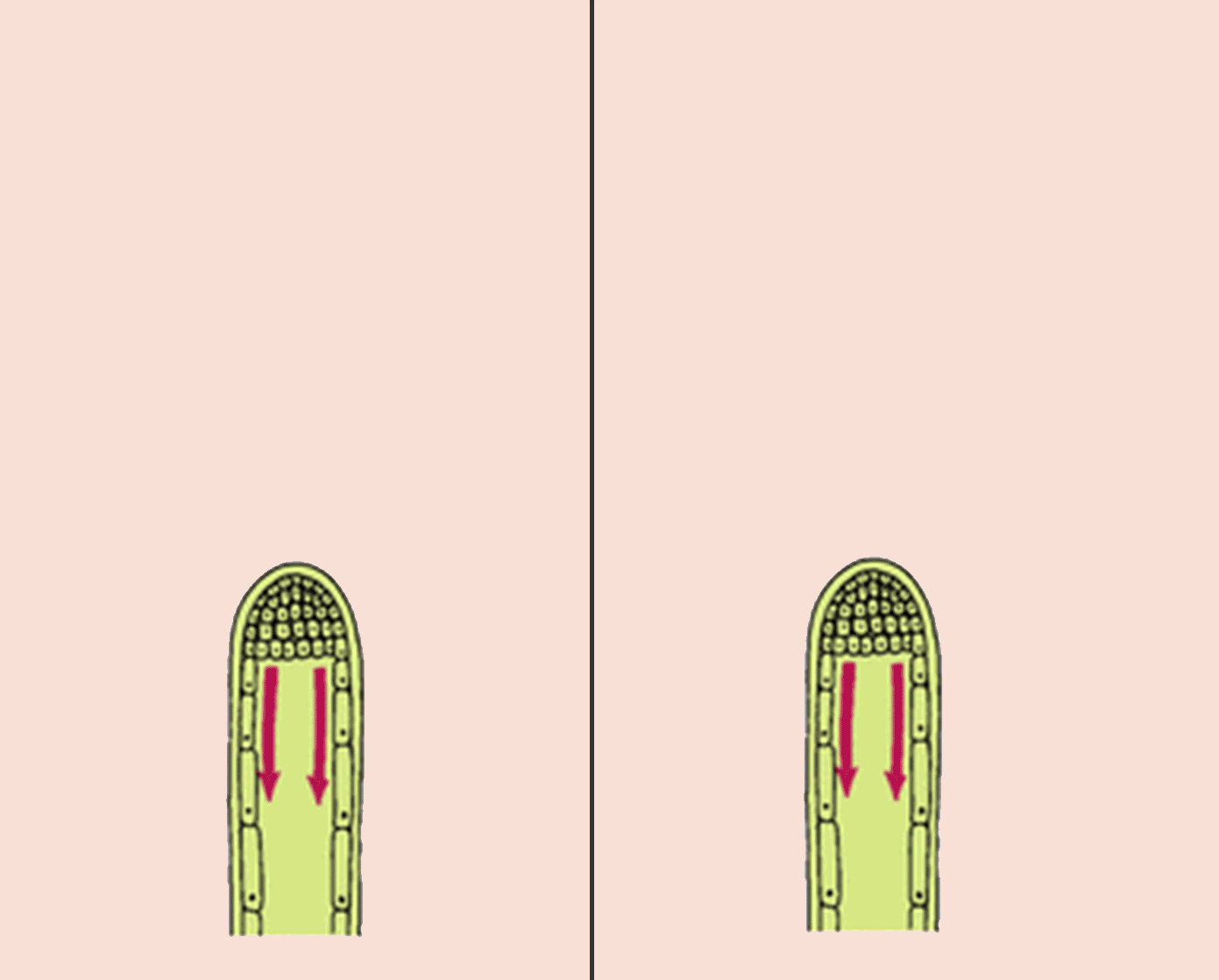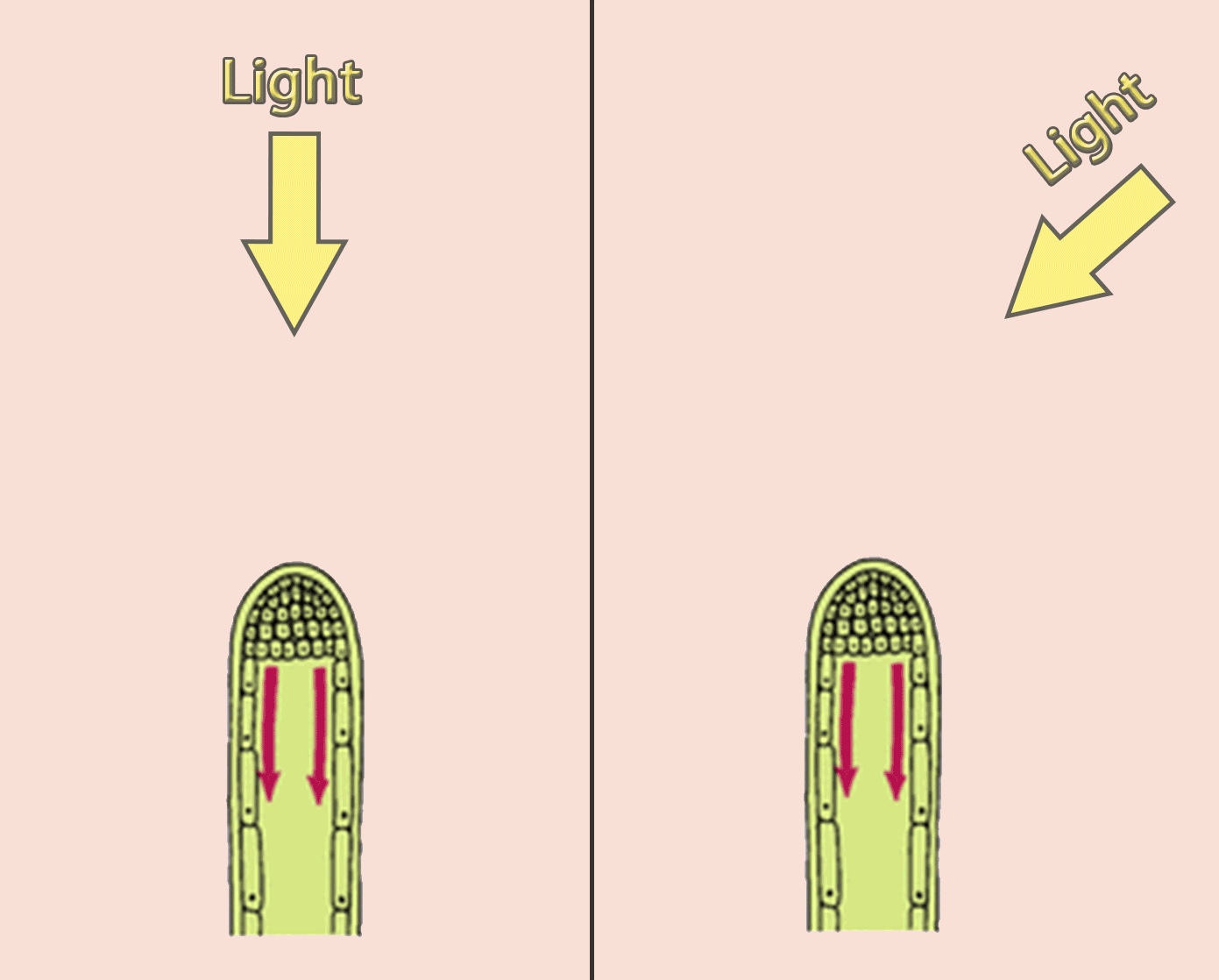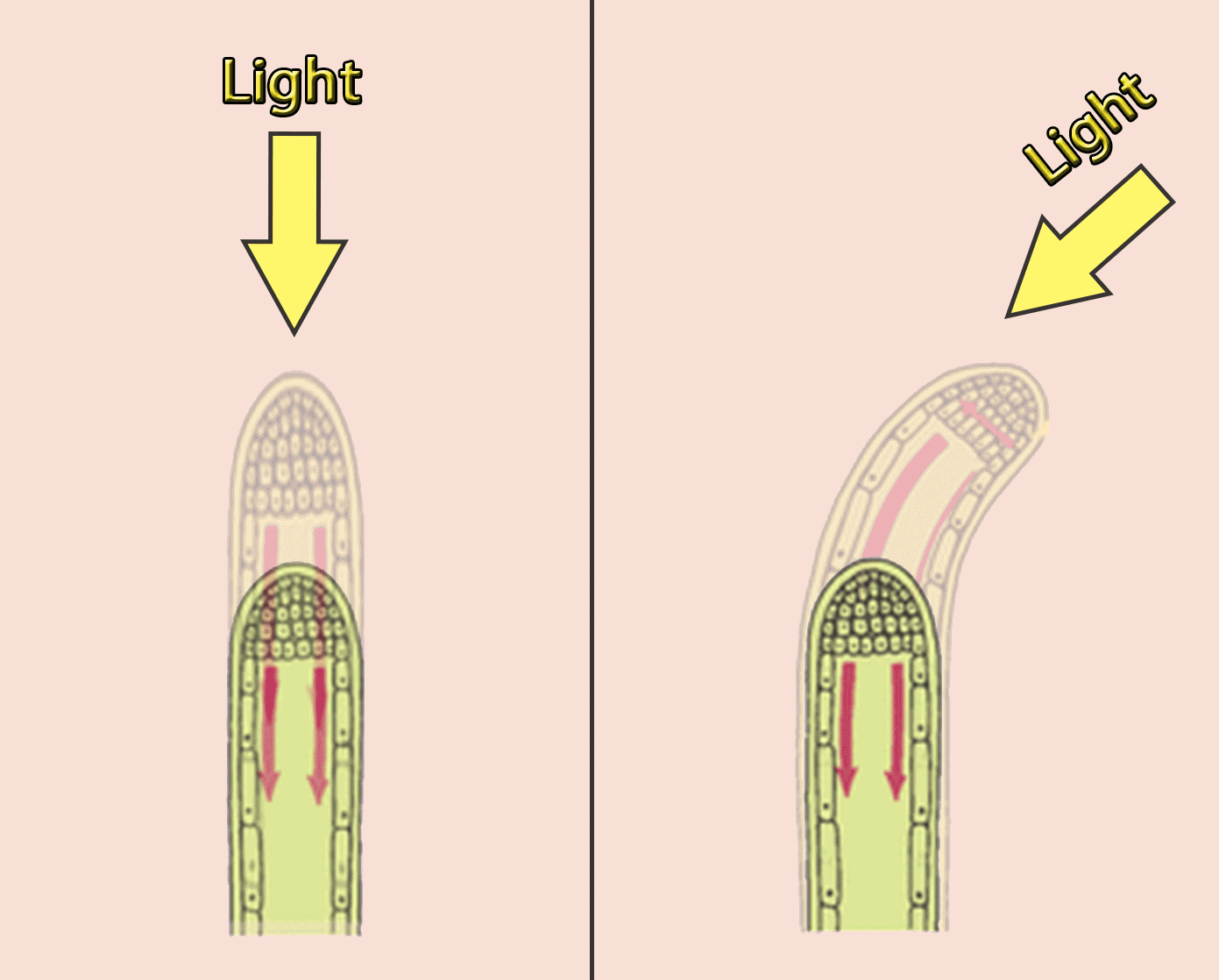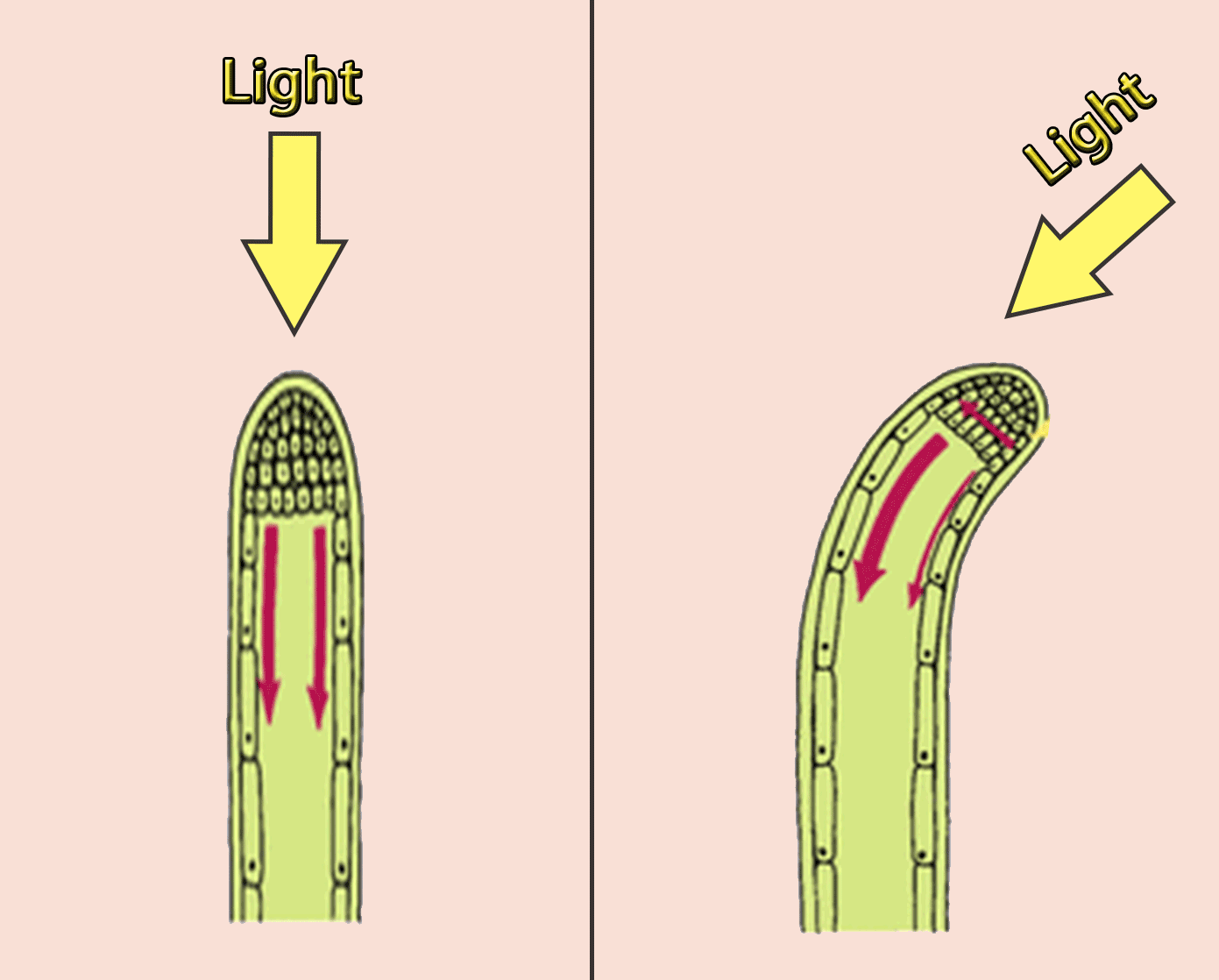
Auxins in phototropism (root)
If a root is exposed to light in the absence of gravity, more auxins are moving in the shaded side (from the tip of the root). On this side, cells are stimulated to absorb less water, plant grows less
Root bends away from the light. This is called negative phototropism.
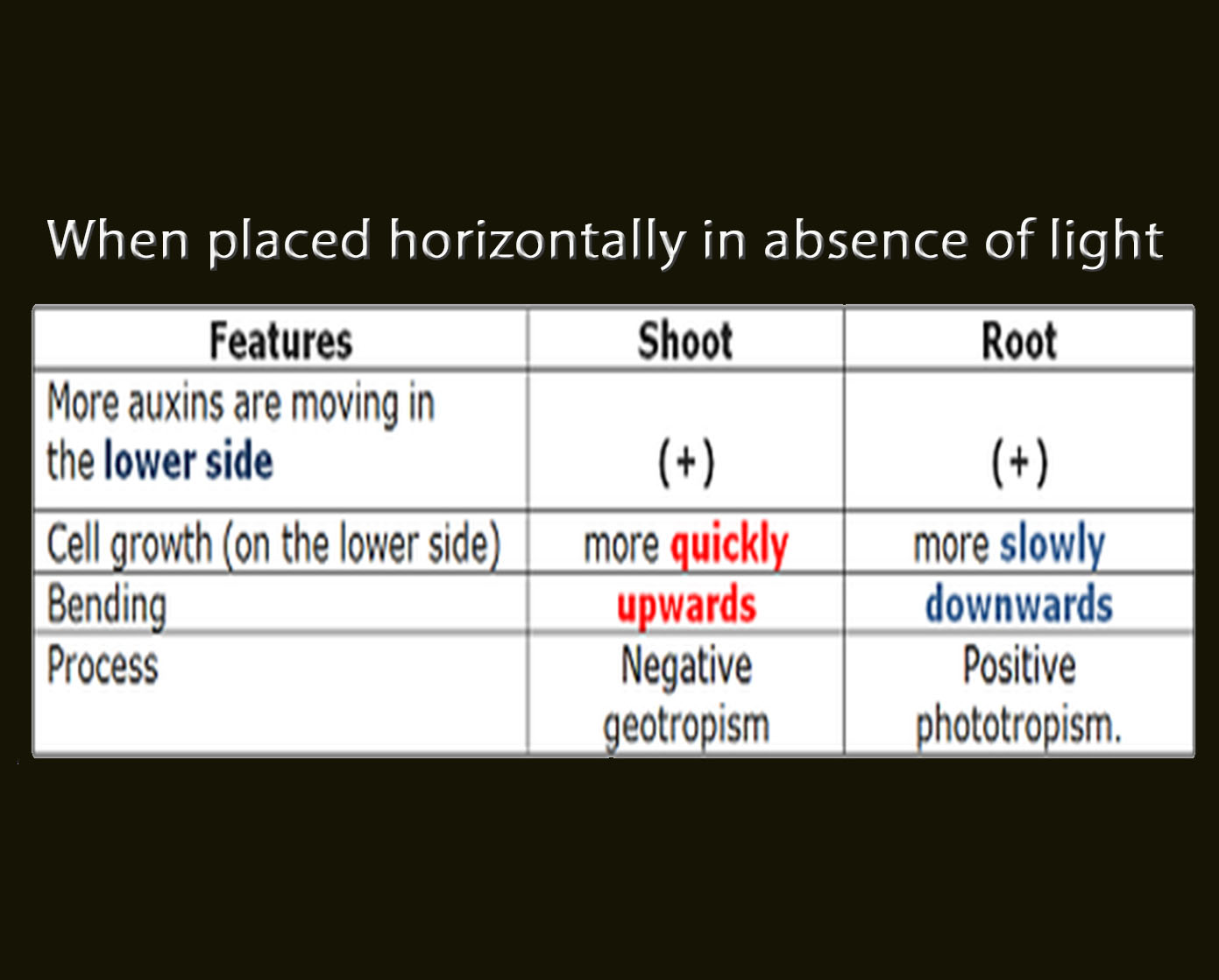
Auxins in geotropism
If a shoot is placed horizontally in the absence of light, auxins accumulate on the lower side of the shoot, due to gravity. Cells on the lower side grow more quickly and the shoot bends upwards. This is called negative geotropism.
If a root is placed horizontally in the absence of light, auxins accumulate on the lower side of the shoot, due to gravity. Cells on the lower side grow more slowly and the shoot bends downwards. This is called positive geotropism.
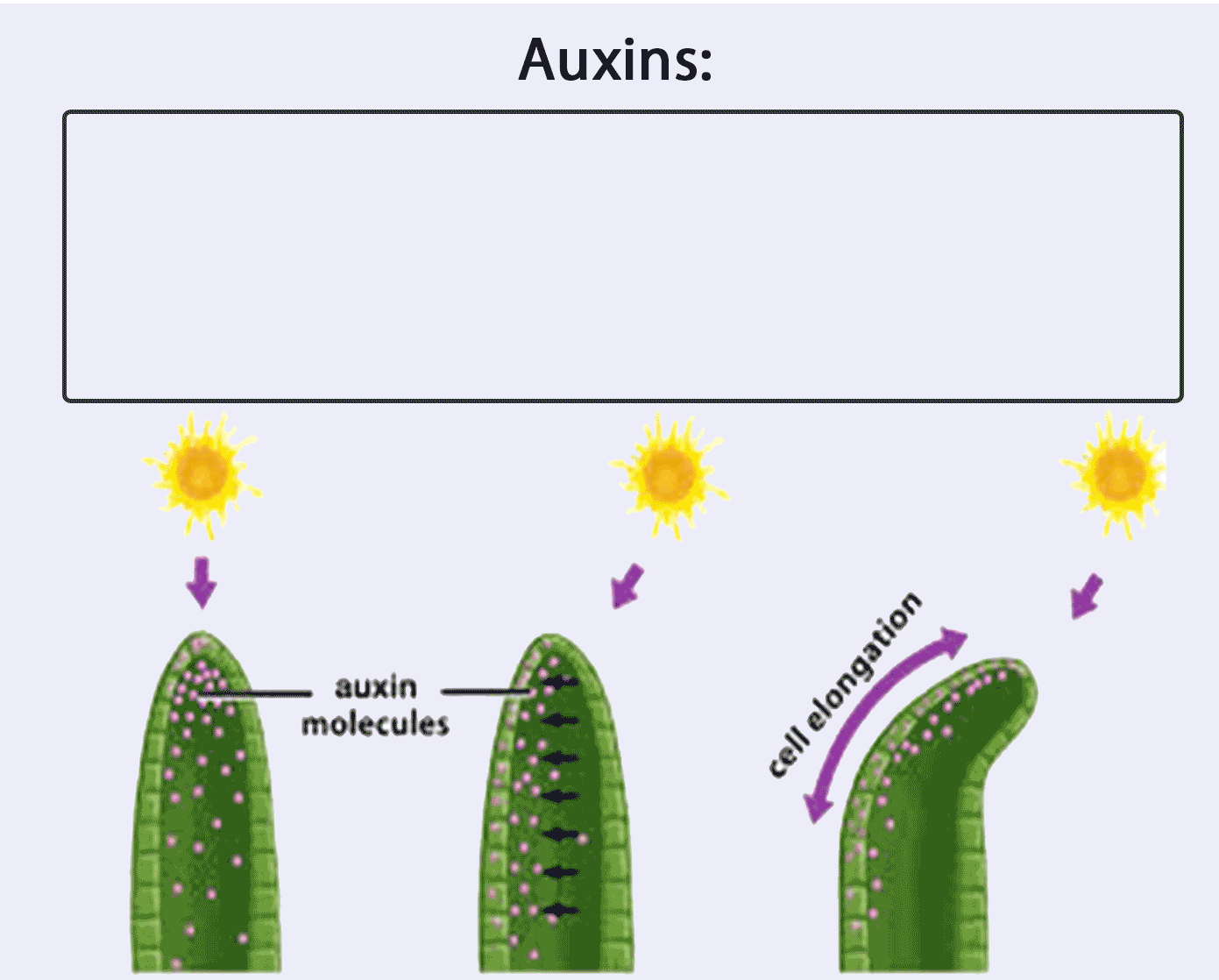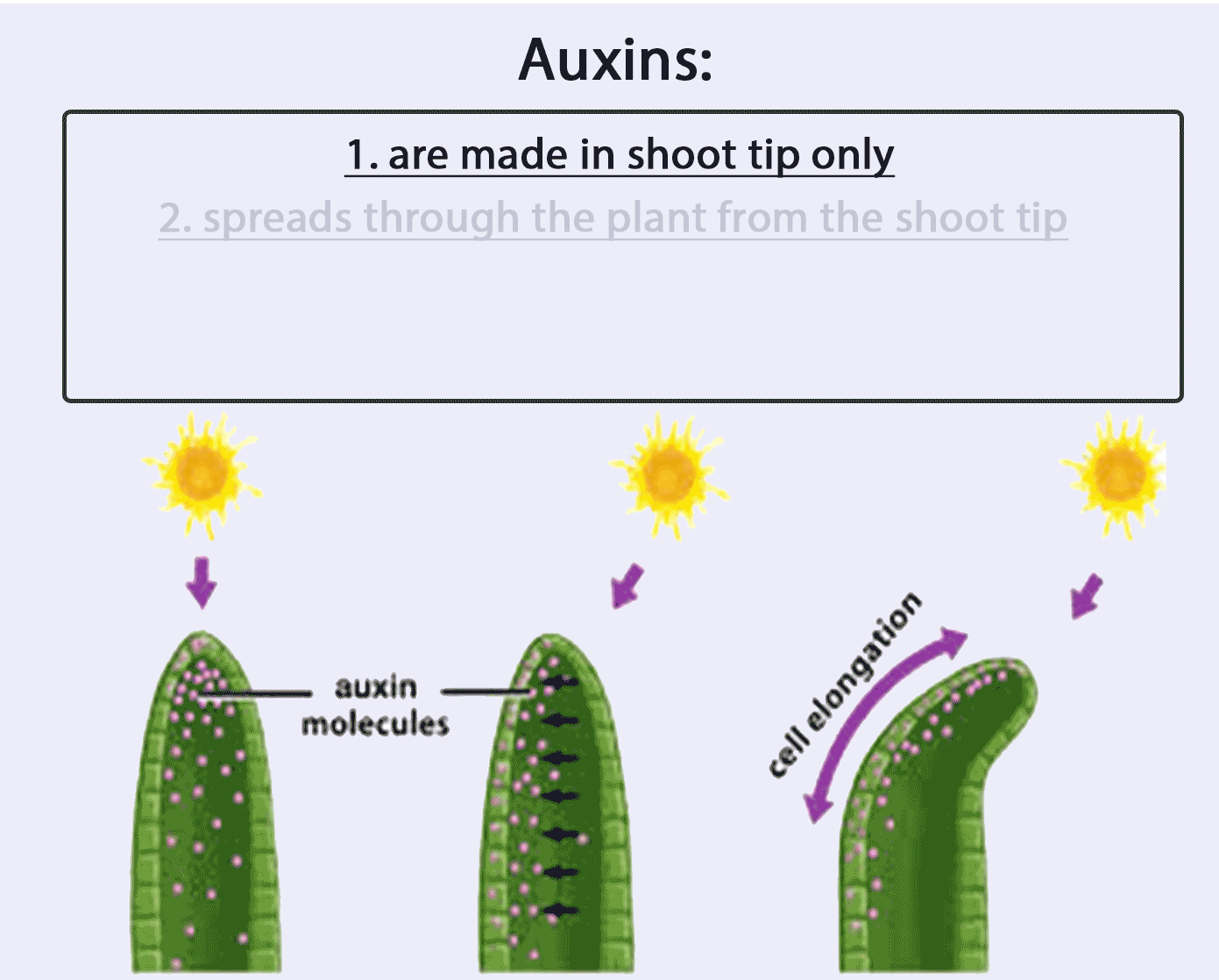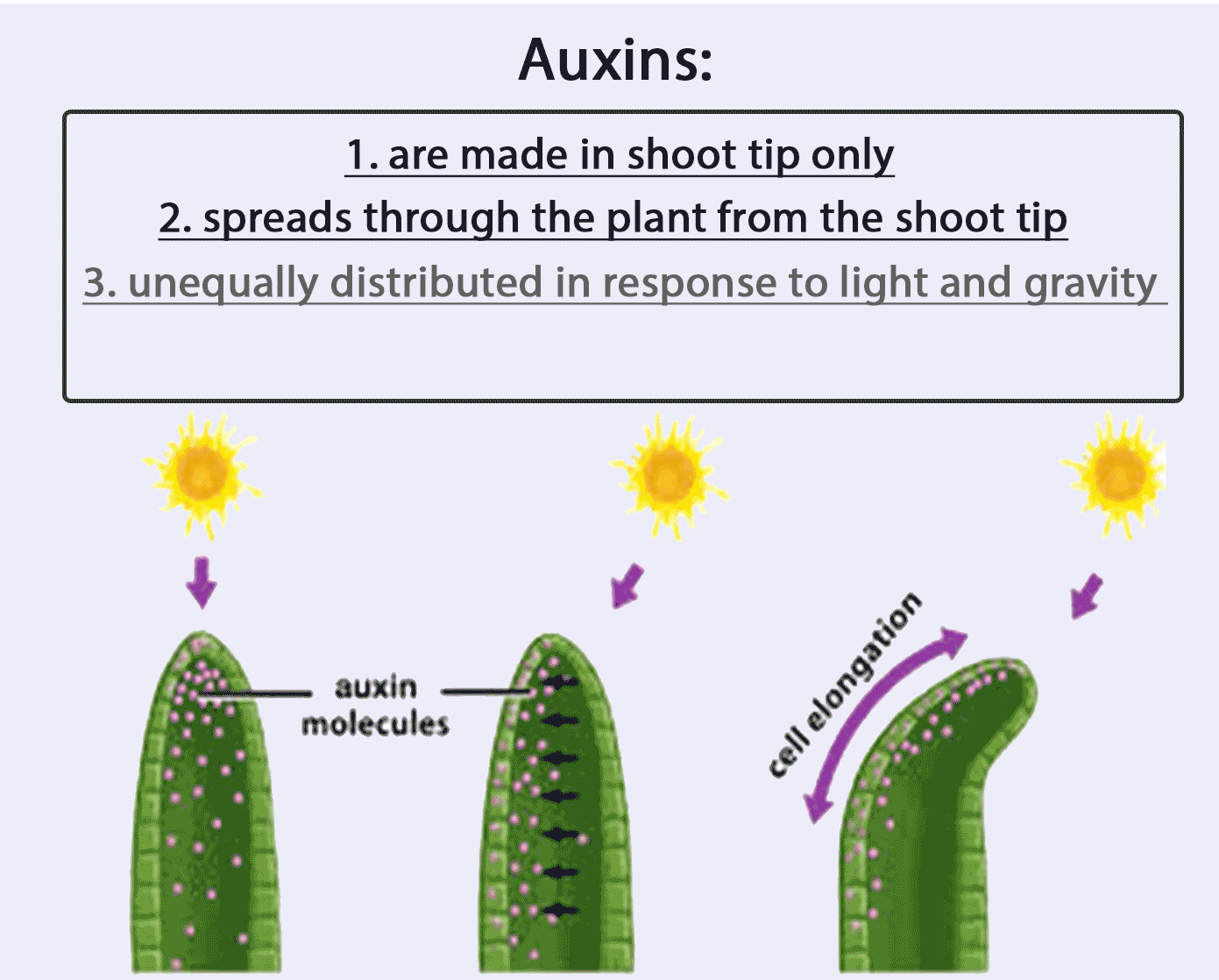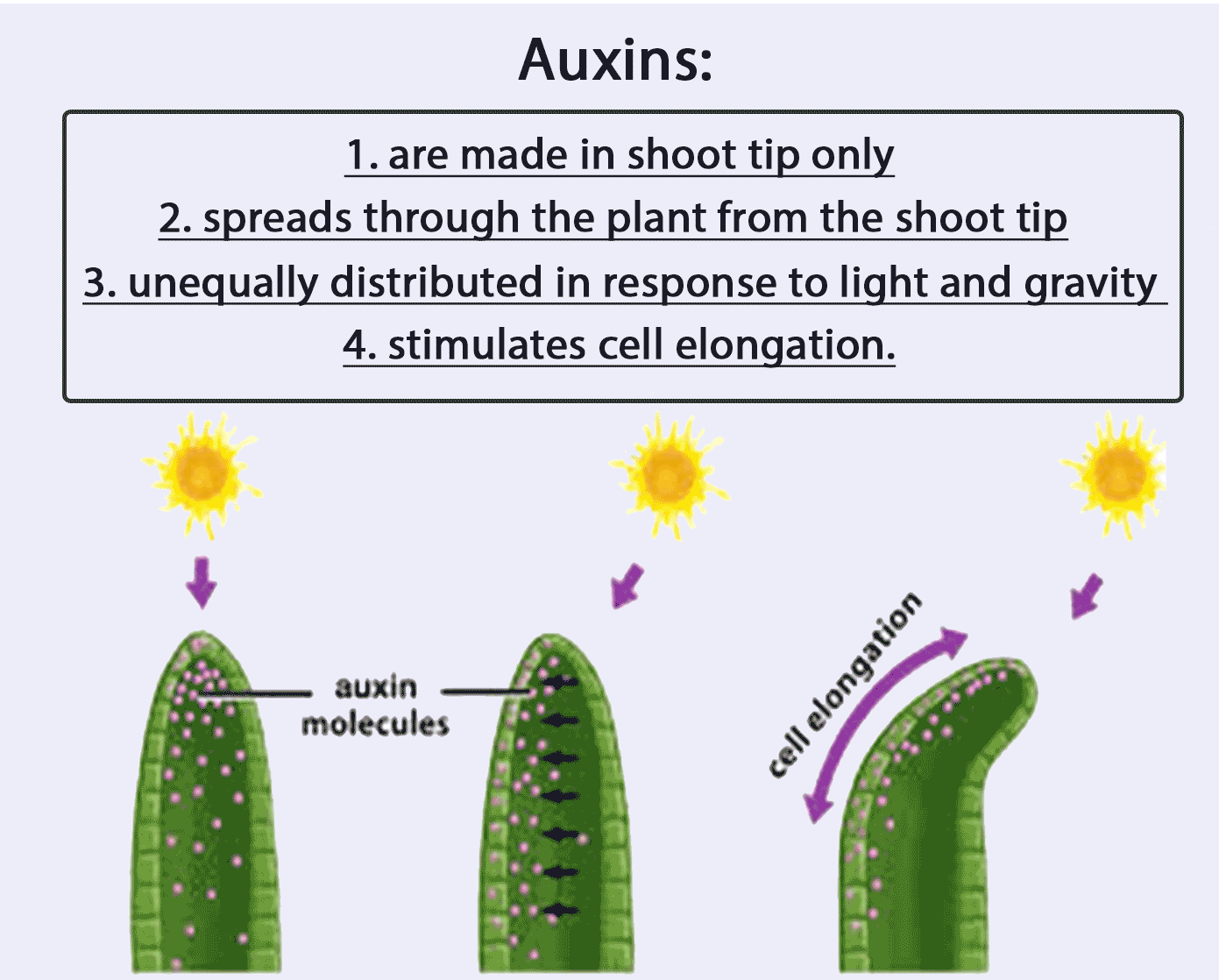
[Supplementary] Functions and characteristics of auxin
Auxins:
1. are made in shoot tip (only)
2. spreads through the plant from the shoot tip
3. unequally distributed in response to light and gravity
4. stimulates cell elongation.